* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1920s Economy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
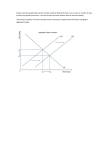
Late 1920s Economy 14.3 “Wonderful Prosperity” • Stock market value keeps increasing – 1925 = $27 billion – 1929 = $87 billion • Average wages had risen 40% since 1914. – Unemployment < 4% • Popular literature – Jesus, the businessman (The Man Nobody Knows) – “Everybody Ought to Be Rich” (article) Other Positives • Welfare Capitalism – Meeting the needs of workers to prevent labor strikes • • • • • Higher wages Paid vacations Health plans Recreation programs English classes for immigrants Bad Signs • Personal debt – America’s personal debt rose ~70% during the 1920s. – Buying fancy goods, but no money in the pocket • Stock Market Speculation – “Get rich quick” schemes – Investments: high-risk, high-reward • Buying on Margin – Purchasing a stock for only a fraction (10%) of the value – Borrow the rest of the money w/ high-interest loan – When (if) stock value increases, sell & pay off loan. Bad Signs • Overproduction of goods – Overstocked warehouses • Farmers / rural banks fail – President Coolidge vetoed any gov’t aid to farmers. – Banks failed when farmers could not pay back loans. • Uneven distribution of wealth – – – – Mainly, the rich got richer. 71% lived below the “minimum standard of living.” 80% of all families had no savings. 60% of the time, it works every time. How bad could it be? Pretty bad.