* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download angle
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
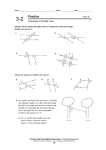
8-2 Classifying Angles Warm Up Problem of the Day Lesson Presentation Lesson Quizzes 8-2 Classifying Angles Math Journal (5 Min) • K-W-L - Each student will be given the title of the lesson that will be taught that day. They must then, at the beginning of class, write the “K” what they know and “W” what they want to know about the lesson before they have been taught the lesson, and at the end of class, write the “L” what they now know (Learned) about the lesson after they have been taught the lesson. Then, each student will discuss his/her answers within their group. Finally, to leave class, each student will have to give/write 1 sentence that they learned that pertained to the lesson. 8-2 Classifying Angles Homework Review (5 Min) 8-2 Classifying Angles Warm Up Draw each figure. 1. line segment 2. line 3. ray 4. plane 8-2 Classifying Angles Problem of the Day Find the measure of the smaller angle between the hour and minute hands on a clock at eight o’clock? 120° 8-2 Classifying Angles Textbook Examples (I Do) (5 Min) 8-2 Classifying Angles Learn to identify angles and angle pairs. 8-2 Classifying Angles Vocabulary angle vertex right angle acute angle obtuse angle straight angle complementary angles supplementary angles 8-2 Classifying Angles A Vertex An angle is formed by two rays with a common endpoint. The two rays are the sides of the angle. The common endpoint is the vertex. B 1 Angles are measured in degrees (°). C 8-2 Classifying Angles An angle’s measure determines the type of angle it is. A right angle is an angle that that measures exactly 90°. The symbol indicates a right angle. An acute angle is an angle that measures less than 90°. An obtuse angle is an angle that measures more than 90° but less than 180°. A straight angle is an angle that measures exactly 180°. 8-2 Classifying Angles Additional Example 1: Classifying Angles Tell whether each angle is acute, right, obtuse or straight. A. obtuse angle B. acute angle 8-2 Classifying Angles Reading Math A• B• 1 • C You can name this angle ABC, CBA, B, or 1. 8-2 Classifying Angles Check It Out: Example 1 Tell whether each angle is acute, right, obtuse, or straight. A. straight angle B. acute angle 8-2 Classifying Angles If the sum of the measures of two angles is 90°, then the angles are complementary angles. If the sum of the measures of two angles is 180°, then the angles are supplementary angles. 8-2 Classifying Angles Additional Example 2A: Identifying Complementary and Supplementary Angles Use the diagram to tell whether the angles are complementary, supplementary, or neither. OMP and PMQ To find mPMQ start with the measure that QM crosses, 105°, and subtract the measure that MP crosses, 75°. mPMQ = 105° - 75° = 30°. mOMP = P 60°. Q Since 60° + 30° = 90°, PMQ and OMP are complementary. O N M R 8-2 Classifying Angles Reading Math If the angle you are measuring appears obtuse, then its measure is greater than 90°. If the angle is acute, its measure is less than 90°. 8-2 Classifying Angles Additional Example 2B: Identifying Complementary and Supplementary Angles Use the diagram to tell whether the angles are complementary, supplementary, or neither. NMO and OMR mNMO = 15° and mOMR = 165° P Since 15° + 165° = 180°, NMO and OMR are supplementary. Reading Math Read mNMO as “the measure of angle NMO.” Q O N M R 8-2 Classifying Angles Additional Example 2C: Identifying Complementary and Supplementary Angles Use the diagram to tell whether the angles are complementary, supplementary, or neither. PMQ and QMR To find mPMQ start with the measure that QM crosses, 105°, and subtract the measure that MP crosses, 75°. mPMQ = 105° - 75° = 30°. mQMR = 75°. P Q Since 30° + 75° = 105°, PMQ and QMR are neither complementary nor supplementary. O N M R 8-2 Classifying Angles Check It Out: Example 2A Use the diagram to tell whether the angles are complementary, supplementary, or neither. BAC and CAF mBAC = 35° and mCAF = 145° Since 35° + 145° = 180°, BAC and CAF are supplementary. D E C F B A 8-2 Classifying Angles Check It Out: Example 2B Use the diagram to tell whether the angles are complementary, supplementary, or neither. CAD and EAF To find mCAD start with the measure that DA crosses, 90°, and subtract the measure that CA crosses, 35°. mCAD = 90° - 35° = 55°. mEAF = D 35°. Since 55° + 35° = 90°, CAD and EAF are complementary. E C F B A 8-2 Classifying Angles Check It Out: Example 2C Use the diagram to tell whether the angles are complementary, supplementary, or neither. BAC and EAF mBAC = 35° and mEAF = 35° Since 35° + 35° = 70°, BAC and EAF are neither supplementary nor complementary. D E C F B A 8-2 Classifying Angles Additional Example 3: Finding Angle Measures Angles A and B are complementary. If mA is 56°, what is the mB? Since A and B are complementary, mA + mB = 90°. mA + mB = 90° 56° + mB = 90° – 56° – 56° mB = 34° Substitute 56° for mA. Subtract 56° from both sides. The measure of B = 34°. 8-2 Classifying Angles Check It Out: Example 3 Angles P and Q are supplementary. If mP is 32°, what is the mQ? Since P and Q are supplementary, mP + mQ = 180°. mP + mQ = 180° 32° + mQ = 180° – 32° – 32° mQ = 148° Substitute 32° for mP. Subtract 32° from both sides.. The measure of Q = 148°. 8-2 Classifying Angles Class work Problems (We Do) (10 Min) • Pg. 318-319 (1-9) 8-2 Classifying Angles 8-2 Classifying Angles 8-2 Classifying Angles Small Group CW(Yall Do) (10 Min) • Pg. 318-319 (10-26 EOE) 8-2 Classifying Angles 8-2 Classifying Angles 8-2 Classifying Angles Homework (You Do) (10 Min) • Pg. 318-319 (11, 15, 17, 19, 23 odd) 8-2 Classifying Angles Math Journal (5 Min) • K-W-L - Each student will be given the title of the lesson that will be taught that day. They must then, at the beginning of class, write the “K” what they know and “W” what they want to know about the lesson before they have been taught the lesson, and at the end of class, write the “L” what they now know (Learned) about the lesson after they have been taught the lesson. Then, each student will discuss his/her answers within their group. Finally, to leave class, each student will have to give/write 1 sentence that they learned that pertained to the lesson. 8-2 Classifying Angles Lesson Quizzes Standard Lesson Quiz Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 8-2 Classifying Angles Lesson Quiz: Part I Tell whether each angle is acute, right, obtuse, or straight. 1. straight 2. obtuse 8-2 Classifying Angles Lesson Quiz: Part II Use the diagram to tell whether the angles are complementary, supplementary, or neither. 3. AZB and BZC neither 4. BZC and CZD complementary 5. Angles M and N are supplementary. If mM is 117°, what is mN? 63° 8-2 Classifying Angles Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 1. Identify the type of the given angle. A. acute B. obtuse C. right D. straight 8-2 Classifying Angles Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 2. Identify the type of the given angle. A. acute B. obtuse C. right D. straight 8-2 Classifying Angles Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 3. Use the diagram to identify the type of the given pair of angles. mAOB and mBOD A. complementary B. supplementary C. right D. none 8-2 Classifying Angles Lesson Quiz for Student Response Systems 4. Angles A and B are complementary. If mA is 36°, what is mB? A. 54° B. 90° C. 126° D. 144°