* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical Long Run Aggregate Supply
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Fei–Ranis model of economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Full employment wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Transformation in economics wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Long Depression wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
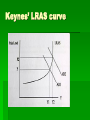
Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply The relationship between the price level in the economy and the level of total output. So now the question is: How much can the economy produce, not buy. Short term and long term Short term – at least one factor of production is fixed Long term – all factors of production are variable. Supply curve in an individual industry Do you get the same shape for aggregate supply? In the short run, yes What causes shifts in the short run aggregate supply curve 1. Changes in wage rates 2. Changes in the cost of raw materials. Commodities. 3. Taxation These come up a lot on 4 point questionss. If it is not one of these factors, it is long run supply. Supply Side Shock A large change in wage rates, raw material prices or taxation. This can have an effect on short run aggregate supply by pushing the supply curve upwards and to the left. Long run aggregate supply curve Firms face limitations in acquiring the land, labour, capital and enterprise they need. There are only so many computer programmers available to work for your IT company. There is a limit to the amount of mahonagy you can get your hands on to continue making expensive furniture So, Long Run Aggregate Supply Curve is Vertical or Fixed It is similar to the PPF. What does the LRAS show? Production Possibility Frontier of an economy. It can show an output gap (be careful looking at the output gap diagram) Shows an economy at full capacity Output Gap An economic measure of the difference between the actual output of an economy and the output it could achieve when it is most efficient, or at full capacity. There are two types of output gaps: positive and negative. A positive output gap occurs when actual output is more than the full-capacity output. Negative output gap occurs when actual output is less than full-capacity output. Negative Output Gap A negative output gap can be followed by a relatively elastic aggregate supply. This is because the economy is operating under a spare capacity. Shifts in LRAS Improvements in education Technological advancement (assembly line automation has resulted in far greater production than before Wise investment in capital equipment. LRAS will shift for basically the same reasons a PPF will shift. LRAS Shifts continued The invention of the air conditioner has shifted the LRAS of southern American states outwards, some would say at the expense of the northern industrial belt. Good industrial relations Pro-business government policy Saudi Arabia’s LRAS could shift right if half their workforce were allowed to work outside the home. Classical LRAS What effect does loose fiscal and monetary policy have on the economy according to the Classical Economists. Classical Thinking Loose fiscal and monetary policy only have the effect of increasing prices. Real output in the long run stays the same. Classical Long Run Aggregate Supply No matter how low the price level – the productive possibility of the economy remains the same. Classical Long Run Aggregate Supply Is that realistic? Unemployment in the US Unemployment in the US Simple economics If there is an excess supply of labour, it is very simple, cut the wages – and the demand for labour will go up again. Labour is basically the same as oranges, foot massages or plane tickets. However..... However, not everyone thinks that the LRAS curve is vertical. Guess who this is? Labour markets don’t clear, or find a new equilibrium, as easily as Classical Economists would have us believe. The economy is not flexible enough to provide full continuous employment. When downward pressure is put on wages, the Price Elasticity of Demand of labour is inelastic. Or putting it more easily. Wages are sticky downwards. Markets could set at a long run disequilibrium. Why are wages sticky downwards? There may be a national minimum wage which sets price floors. There may be limited mobility of labour. Why are wages sticky downwards? 1. Trade Unions may fight to keep higher price levels. 2. Managers may not treat labour like steel or oranges, and will not necessarily pay less and hire more workers in times of high unemployment. This might demotivate the staff. Keynes’ LRAS curve In between Y1 and Y2, labour is becoming scarce enough for an increase in the demand for labour to push up wages. This then leads to a higher price level. The nearer output gets to Y2, the full employment level of the output, the greater the effect of an increase in demand for labour on wages and therefore price level. Classical Economists Classical economists have argued that the economy always converges rapidly on an equilibrium at the natural rate of output, implying that policies affecting aggregate demand have an impact on prices only, leaving real output unnaffected. Aggregate supply remains vertical. Keynsian View The Keynsian view is that the economy may settle at an equilibrium that is below full employment, and there is some range where aggregate supply shifts upwards. Analyse the impact of a rise in the price of oil on the national economic output and price level. Use a diagram in your answer. Analyse the impact of increased spending on university education by the government on the national economic output and price level. Use a diagram in your answer.