* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Urinary System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
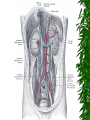
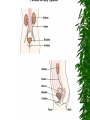
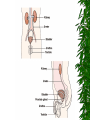
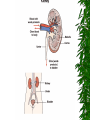
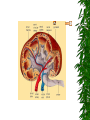
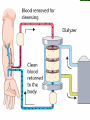
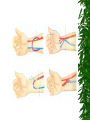
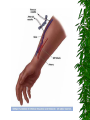
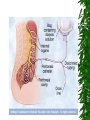
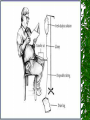
The Urinary System Anatomy and Physiology 2015 Structure Kidneys Ureters Urinary urethra bladder Function Maintains homeostasis Controls blood and water volume Maintains blood pressure Regulates electrolyte levels Eliminates protein wastes, excess salts and toxic materials from blood Balances acid/base (PH) Secretes renin and erythropoietin Kidney Structure 2 reddish brown, beanshaped organs Located in small of the back at lower edge of ribs on either side of spine “Retroperitoneal” How the kidneys Regulate BP ADH RENIN ALDOSTERONE 3 Parts Cortex Medulla Pelvis BecomeHealthyNo w.com Home Nephron Functional units of the kidney Cells that form urine Over 1 million nephrons in each kidney Glomerular Filtration Tubular Reabsorption Tubular Secretion WORD WALL 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Oliguria Anuria Dysuria Polyuria hematuria Urine Body excretes 1000-2000 ml of urine/day Is normally sterile Color varies with hydration Characteristics of Normal Urine CLARITY ODOR SPECIFIC GRAVITY THINK…. A STRONG, OFFENSIVE ODOR FROM FRESHLY VOIDED URINE IS SUGGESTIVE OF…….. Urinary Tract Infection Composition of Normal Urine Water Protein wastes products (urea, uric acid & creatinine) Excessive minerals from diet (Na+,K+, Ca,sulfates & phosphates Toxins Hormones Bile compounds Pigments from food/drugs WORD WALL Frequency Urgency Nocturia Enuresis retention Effects of Aging on the Urinary System Ability to filter blood, reabsorb electrolytes & secrete wastes decreases Less ability to return to normal after changes in blood volume Decrease in number & size of nephrons Decrease in GFR Smaller capacity of bladder Weaker bladder muscles Incontinence Not a normal consequence of age Common due to many reasons See Chpter 23 for more information on incontinence Nursing Assessment of The Urinary System HEALTH HISTORY Chief complaint History of Present Illness Past Medical History Family History Review of Systems Diagnostic & Laboratory Tests Urinary System URINE TESTS UA ( urinalysis ) C & S ( Culture & Sensitivity ) Creatinine Clearance (24 hr) BLOOD TESTS BUN ( blood urea nitrogen ) Serum Creatinine Serum Electrolytes Radiographic Studies KUB ( flat plate ) IVP Arteriogram Renal Scan US Invasive Procedures 1. 2. Renal Biopsy Cystoscopy What are Urodynamic Studies ?? What are common Therapeutic measures Related to “Catheterization” Catheter Types Foley Ureteral Suprapubic Nephrostomy Common Tubes and Catheters Ureteral Catheter Nephrostomy Urinary Stent Tube Pre-Op Care Urologic Surgery Evaluate fluid status Bowel cleansing Enterostomal Therapist/Nurse Counseling/Teaching Post-Op Care Urologic Surgery Report to MD U/O < 30 ml/hr Pain Management Mon. lung sounds Assess for Paralytic ileus Urinary Tract Inflammation and Infections Cystitis Inflammation of the urinary bladder Bacteria enters from the urethra, lymph nodes, infected kidneys Women more suseptible Causes E-coli Candida Albicans Coitus Diabetes mellitus See Box 40-2 Risk Factors for UTI’s Signs & Symptoms Dysuria, hematuria Frequency, urgency Low grade fever Pelvic or abd. discomfort Bladder spasms Med. Dx & Tx C&S and UA obtained Increase fluids 3-4 L / day Antibiotics (Cipro,Bactrim,Septra Analgesics(Pyridium) See Pt. Teaching pg. 898 Gerontologic Considerations Watch for signs of mental confusion Fever may be masked Sepsis develops quickly Pyelonephritis Bacterial infection of renal pelvis and kidney Most common form of kidney disease Often the result of reflux Signs & Symptoms Flank pain Chills, fever,N & V Dysuria, fatique Bladder irritation Med & Nursing Considerations Bedrest Increase fluids (8 8oz. Glasses water/day) IV Monitor I + O Protein & Na+ restrictions Mon. for circulatory overload Pharmacological TX Antibiotics (Bactrim) or Cipro Antipyretics Analgesics Antispasmotics Antihypertensives Glomerulonephritis Autoimmune disease Glomerulus becomes inflammed Symptoms dev. 1-3 wks after respiratory infection cau by group A- hemolytic strep Signs & Symptoms Tea colored urine Decrease in u/o Periobital edema HTN Hypervolemia Medical Dx Clinical Presentation UA Proteinuria BUN, Cr Strep. Antibody Tests Renal Biopsy or Ultrasound Medical Treatment Diuretics Antihypertensives Antibiotics Nursing Considerations Bedrest several weeks Strict I & O, daily weights Restrict Fluids if ordered Low Na, low protein diet Prognosis is good UA w/ RBC’s, Albumin, casts protein Treatment Low Na, protein diet Bedrest VS, BP… Strict I & O Restrict fluids Condition may lead to pulmonary edema, increased BP,anemia,cerebral hemorrage, CHF and ultimately uremia or ESRD In the absence of dialysis or kidney transplant, prognosis is poor. Defend your reasoning.. . Why should a patient with acute glomerulonephritis be sure to follow up with his or her physician? 2. Why would a streptococcal antibody test be ordered for a patient suspected of having acute glomerulonephritis? 3. Why might hypervolemia and hypertension develop in a patient with acute glomerulonephritis? Polycystic Kidney Disease Congenital, familial, also may be acquired Fluid-filled cysts Abdominal, low back or flank pain and headache Diagnosis X-ray or sonogram BUN & Creatinine Goal of management is….. Renal Failure A.K.A. Uremia May be Acute or Chronic Renal Failure Kidneys no longer meet everyday demands Kidneys unable to filter waste products from blood BUN & Creatinine levels elevate Causes of Renal Failure Glomerulonephritis IDDM Any condition which decreases blood supply to kidneys Injury Recurrent UTI Drug overdose Poisoning Nephrotoxic Drugs Acute Renal Failure CAUSED BY: 1. Prerenal Failure 2. Intrarenal Failure 3. Postrenal Failure Acute Renal Failure 4 PHASES 1.Onset 2.Oliguria 3.Diuresis 4.Recovery Medical & Drug Management Antihypertensives Diuretics Cardiotonics Dialysis if needed Diet & Fluids Diet based on consideration of serum electrolytes and BUN. Adequate carbs to prevent breakdown of fat & protein. Fluids calculated by adding 400-600ml to previous days output. Nursing Considerations Freq. BUN, Creatinine, Na & K levels Usually Low Na, K and protein diet Mon. I & O Chronic Renal Failure “ESRD” Irreversible Chronic abnormalities in internal environment of kidney Dialysis or kidney transplant necessary for survival Signs & Symptoms • • • • • • Azotemia Hyperkalemia Hypocalcemia Metabolic acidosis Hypernatremia and hypervolemia Insulin Resistance Medical Treatment IV Glucose and Insulin Calcium, Vitamin D and phosphates Fluid restriction & diuretics Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors Iron, folic acid and synthetic erythropoietin High carb/low protein diet Critically Think & Defend your reasoning.. What are the possible long-term effects of chronic infections of the urologic system? Urinary Tract Obstructions RENAL CALCULI Urolithiasis Calculus or stone formed in the urinary tract Etiology is unknown Can occur in renal pelvis, ureters, bladder or urethra Contributing Factors Infection & or Dehydration Urinary stasis Immobility Recurrent UTI’s Diet low in calcium Signs & Symptoms Size & location of stone affects degree of pain Spasm = “colic” Hematuria N & V Medical Treatment Opioids NSAIDS Antispasmodics IV Fluids Antibiotics Surgical Management Lithotripsy (ESWL) Urethroscopy Nephrolithotomy See Post-Op Care Goals pg. 906 Nursing Considerations Strain all urine & pain relief Send gravel or stones to lab Monitor of s/s infection Give antispasmodics Encourage fluids ; IV Manage Pain Hydronephrosis Distention of kidney Can cause permanent damage Maintain accurate I & O Strain all urine Send all stones for analysis Dialysis • • • • Mechanical Imitates the function of the nephron May be chronic or acute Removes body wastes through semipermeable membrane Dialysis Peritoneal Hemodialysis Hemodialysis Blood circulates through a machine outside the body Semipermeable membrane is within machine “Artificial kidney” Performed 3x/wk for approx. 4 hrs AV Shunts, fistula or cannula All allow access to the arterial system All must be assessed for patency by: “Feel the thrill” & “listen for the bruit” /cahe/respcared/cyberc as/dialysis/franvasc.ht ml Peritoneal Dialysis Uses the peritoneal lining of the abd. Cavity as semipermeable membrane Diffusion & osmosis occur through membrane Performed 4x/day 7 days/wk 3 Phases of Peritoneal Dialysis Inflow Dwell Drain All 3 phases comprise one exchange CAPD • • • • • Used in the home Freedom from machines Steady bld chemistry levels Process is shorter Less expensive CCPD Also called: Automated peritoneal dialysis Requires a cycler Free from exchanges during day Must take cycler if traveling Nursing Considerations Weigh before & after VS Observe for edema, resp. distress Check bleeding at access site Acc. I & O, ? Fluid restriction High calorie Low protein, Na & K diet Strict asepsis Skin care ( s/s infection) Kidney Transplant Kidney Donation Live donor or cadaver Tissue and blood-typed Amendment to Social Security Act Why is counseling advised for both donor and recipient? Before surgery… BP medications Immunosuppressant drugs Possible transfusion Dialyzed before transplantation Explore patient understanding Record VS Address questions Surgery & Complications See fig. 40-16 pg. 924 ATN, rejection, renal artery stenosis, hematomas, abscesses and leakage of ureteral or vascular anastomoses Organ Rejection Hyperacute Acute Chronic s/s fever, ^ BP, pain at site of new kidney Immunosuppressant drugs Why are they called: Immunosuppressants???? What is the patient predisposed to??? Routine Nursing Care Monitor urine output Monitor fluid intake VS Note weight changes TC & DB Control pain Bladder CA Most common site of urinary system CA Men bet. 50-70 yrs Most bladder tumors are malignant Risk Factors Cigarette smoking Lung cancer Caffeine intake Dyes found in industrial compounds Medical Treatment Cytoscopic resection Fulguration Laser photocoagulation Segmental resection Radical cystectomy Types of urinary Diversion Ileal conduit (most common) Colon conduit, ureterosigmoidostomy Cutaneous ureterostomy Internal ileal reservoir, aka: “Kock pouch” or “continent ileostomy” Nursing Interventions • • • • • • VS I&O Patency of tubes BS, stoma appearance Special skin care Signs of infection 3 Critical Thinking Case Studies Defend your reasoning CASE STUDY #1 An 85-year-old male patient with a history of multiple strokes and requiring the use of an indwelling urinary catheter is discharged from the hospital to a long-term care facility after being treated for urosepsis. What are some interventions the nurse can implement to prevent recurrence of the problem? CASE STUDY #2 An older man complains to the nurse that he has difficulty starting to urinate and then once he starts, he says that he has difficulty maintaining a steady stream of urine. He tells the nurse that for 2 days now he has had severe pain in the lower abdomen, left mid-back region, and left flank. What might be the cause of this patient’s symptoms? CASE STUDY #3 A married, 25-year-old woman is diagnosed with urethritis. She is experiencing acute pain during urination. She uses a spermicidal jelly for birth control. Discuss the most common causes of urethritis and the most common causative organisms involved. Discuss and develop a teaching plan for the following patient.