* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
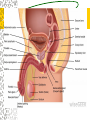
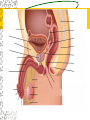
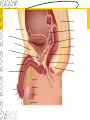
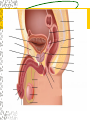
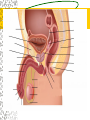
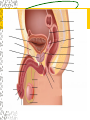
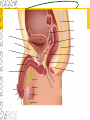
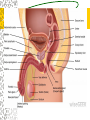
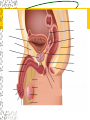
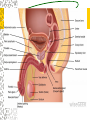
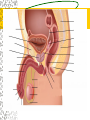
Male Reproductive System Do Now. Get the packet located in the front of the room. Try to answer “IS IT ON A GIRL OR BOY” located on the last sheet of the packet (very back page) Get ready to learn… Functions of the Male Reproductive System Produce Testosterone Produce Sperm Transfer Sperm to the Female Vagina during intercourse. External Organs Penis – – the organ of transfer of sperm to female. • Contains Blood vessels that fill when an individual is aroused. The penis contains no bone but is made up of spongy tissue. • Organs tip is covered with skin – foreskin that can be removed through circumcision. • Used for fertilization or intercourse and urination. Scrotum – – pouch-like sac holding both testicles in a separate compartment that hang underneath the penis. Keeps the testicles a little below 98.6 degrees for ideal conditions for sperm production. Circumcision: surgical removal of the foreskin of the penis. Function: it eliminates bacterial growth (smegma) Urethral Meatus: Opening at the tip of the Penis. Do Now What are some general ways in which a MALE can keep their reproductive organs safe and healthy? What are the 2 external Male Sex Organs? Sperm Is the Male Sex Cell that carries the genes of the father. Factors that Influence Sperm Production High Temperatures Certain jobs Tight underwear Radiation Steroids Lap top Disease Trauma Swimming for your life A sperm is a tiny package with a big responsibility – to fertilize the egg and create a human life. So that tiny package is loaded with “gear” for its important journey. A few facts: Daily sperm production by a healthy man: 10 million to 50 million Contents of average ejaculation: 50 million sperm; 25 million moving; 20 million deformed Maturation: 72 days Average swimming speed of a sperm: 8 inches per hour Survival time in a woman: 2 to 7 days 10 Foods that Help Increase Sperm Quality and Quantity https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NEwtj68RBX U Do Now Using the proper vocabulary describe how the body regulates the temperature of the testicles? Why is it important for testicular temperature to be regulated? What are 3 things that can prevent proper sperm production? Internal Male Organs Testicles (2) – – Produce sperm cells and the male hormone Testosterone. – Contain hundreds of yards of seminiferous tubules. – *500 sperm lined up end to end = 1 inch – Egg shaped organs that hang outside the body in Scrotum. Epididymis (2) – – The tubes in the testes join this larger coiled tube. – Maturation and storage of sperm – where the sperm grow their tails. – Located on top of each testicle. Internal Male Organs Vas Deferens (2) – – Tube that extends from the lower end of each epididymis and connects with the urethra. – As sperm move through here they are joined with fluid from the seminal vesicles, prostate and the cowper’s glands. Internal Male Organs Seminal Vesicles – – Secretes fluid to be mixed with the sperm to make them more mobile. Semen A white, milky fluid that mixes with sperm that eventually passes to the outside of the body. Contains sugars, lubricants and buffers (base) Internal Male Organs Prostate – – Walnut shaped gland that helps make semen in males. – The prostate surrounds the tube that carries urine away from the bladder and out of the body. – A young man's prostate is about the size of a walnut. It slowly grows larger with age. Internal Male Organs Ejaculatory duct – a short straight tube that passes into the prostate gland and opens into the urethra. – It prevents the sperm and urine from mixing. Internal Male Organs Cowper’s Gland – behind the base of the penis which secretes fluid to make semen and neutralize acid during sexual excitement. Pre Ejaculatory Fluid Pre-ejaculation is the liquid that seeps out of the penis before ejaculation occurs. This fluid is released from the cowper’s gland, located at the top of the urethra. The purpose of this fluid is to reduce the acidity in the urethra and provide lubricant for the sperm that is released once ejaculation occurs. Men have no control over it and cannot feel it coming out. Internal Male Organs Urethra – – Tube that carries semen and urine to the outside of the body. – (Cannot carry both at the same time) – Located in the center of the penis. Common Terms Erection - the process of the penis swelling with blood during arousal. It becomes stiff and hard. Spontaneous Erection – an erection that occurs without planning due to changing levels of testosterone. Ejaculation - the release of semen & sperm from the penis. Castration - Removal of the testes. Nocturnal Emission - aka. Wet dream – is an involuntary ejaculation that occurs during sleep. Impotence - the failure to get or maintain an erection. Sterility - Inability to reproduce because the sperm cells are unable to fertilize the ova. Vasectomy - Surgical procedure for sterilization of the male. Timelines Male Time Line: Infancy Erections begin Ages 11-14 Secondary sex characteristics appear Ages 13-16 Sperm produced in adult amounts (puberty) Late teens Peak sexual urges for boys Throughout life If good health is present, there is the sex urge and ability to father children. Activity Break up into 3 groups of 10 Get paper and markers and write down the vocab words for male reproductive system. When I say go, as separate groups, you need to organize yourself in the proper sequence that sperm travels from creation to ejaculation. Be prepared to describe the path, and what happens at each place the sperm travels through. Activity - WS Using your notes and the completed diagram. Draw the path sperm travels on your diagram from beginning to end. Using the proper vocabulary, describe the path the sperm travels from being created until it is released from the body. Words for Activity – in a random order Write on Construction Paper as a group one word per each sheet of paper. Urethra Cowper’s Gland Ejaculatory Duct Testicles Sperm Seminal Vesicles Penis Prostate Epididymis Vas Deferens Do Now Why is it important as a Male to know how to perform a Testicular Self Exam? What are secondary sex characteristics? What are some secondary sex characteristics in Males? Cancer Group Activity 3 groups Take Info packet on colon, prostate, or testicular cancer. Take blank packet form. Students read and discus and fill in blank worksheet as a group Class discussions on all the different cancers. Other groups must come up with at least 2 questions to ask the group presenting. Male Reproductive Cancers Testicular Cancer Young men (15-35). Undescended or partially descended testicle = higher risk. Symptoms: enlargement of testicle, dull ache in lower abdomen or groin or no pain at all. Treatment: surgery and/or radiation or chemo – replacement hormone therapy. Prostate Cancer Older men (65+) Risk increases with age. Higher risk in black men, and men with family history. Symptoms: Gland enlarges = urinary problems. Treatment: Surgery, hormone treatments, radiation,or anticancer drugs. Do Now Take Male reproductive system study guide. Last group get ready to discuss. Hand in any work that you owe me. – Sperm travel worksheet, cancer ws, etc… Male Early Detection Testicular – Monthly self-examination Roll each testicle between thumb & fingers. If any lumps are found, see doctor promptly. Doctor may perform Ultra Sound, MRI, or X-rays for accurate diagnosis. Prostate – Digital Rectal Exam Annually (40+) Prostate-specific antigen blood testing annually (50+) Ultra-sound for those at high risk If cancer is suspected, extensive tests such as blood and urine analysis, x-rays and biopsy, will be performed. Disorders Undescended Testicle - condition at birth where the testes do not descend into the scrotum. Inguinal Hernia - Inguinal ring does not narrow & a loop of the intestine may lose it’s blood supply. Prostatitis – inflammation of the prostate, usually caused by bacteria Jock Itch – Rash caused by improper ventilation and tight underwear. It’s a fungus Enlarged Prostate - a common problem in older men which may cause dribbling after urination or a need to go often, especially at night. Testicular Torsion - Testicular torsion is the twisting of the spermatic cord, which cuts off the blood supply to the testicle and surrounding structures within the scrotum. Hypospadias – A condition in which the external urinary meatus (opening) opens anywhere below the tip of the penis rather than at the tip.