* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Rocky Mountain Region
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
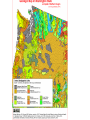
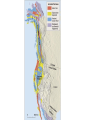
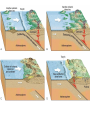
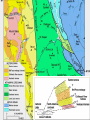
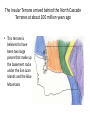
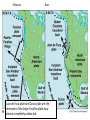
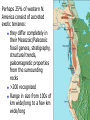
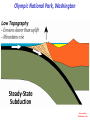
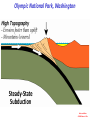
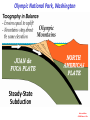
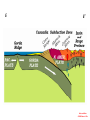
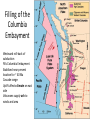
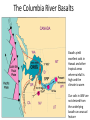
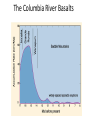
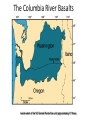
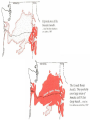
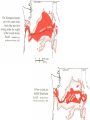
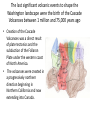
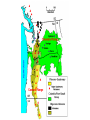
Cascadia Subduction Zone The Rocky Mountain Region – Steep hills that are foothills of the Rocky Mountains in the northern corner of the state Overview of the Geologic History of Washington State 1.5 Billion years-750 MY • Belt Supergroup– failed rift – Thick (70,000 ‘) sed seq – Lifeless plain clay-siltsand • Windermere 750 MY – Continental break-up west sid e of Belt Group dirfts west, Windermere sed rx deposited on the wedge The oldest rocks in Washington State are part of the 1 billion year old Belt Supergroup The North American Continental Coastline was located approximately 30 miles west of the the present day border of Idaho and Washington Pangea Breakup- 175 Ma • Continental rifting • Atlantic basin sends NAm to the west • Subduction zone set up on west coast The continued addition of material to the North American Continent was through the process of Plate Tectonics • Plate tectonics conveyed small volcanic islands and fragments of other continents called terranes onto the North American Continent and accreted them in the area of the existing coastline. Orogenies and Mobile Belts • Terranes originally were: – Island arcs (e.g., Japan) – Seamounts (e.g., Hawaii) – Fragments of continents etc. • Accreted to western margin of North America as the continent moved west and over-rode Pacific Ocean, starting with the Mesozoic Sevier orogeny. The first terrane to arrive was the Okanogan Micro-continent at 190 to 160 million years ago; formed from the collision of former islands Cache Creek, Quesnellia, and Stikinia. • This micro-continent crushed the coastal plain that had been building for 600 million years (800 to 200 myBP) between the North American Continent and the Okanogan creating an area of displaced marine sedimentary materials called the Kootenay Arc The next major addition occurred ~90 to 100 million years ago with the arrival of the North Cascade Terranes • The North Cascade Terranes are believed to be made up of a group of 6 different islands. • Each individual terrane can be distinguished by its unique rock type. • These terranes were covered later by volcanic materials and complicated their interpretation. The Insular Terrane arrived behind the North Cascade Terranes at about 100 million years ago • This terrane is believed to have been two large pieces that make up the basement rocks under the San Juan Islands and the Blue Mountains The last event to add to the Washington coastline was approximately 25 million years ago is called the Crescent Terrane located in the areas of the Puget Lowlands, Olympic Peninsula and the Willapa Hills • The Crescent Terrane is believed to be a portion of ocean crust that was stranded between an extinct trench and the present day trench. Some how more buoyant rocks were carried underneath the continental crust, then escaped pushing the overlying rocks as much as 2 miles above the ocean crust Miocene Now Juan de Fuca plate and Cocos plate are the remnants of the larger Farallon plate now almost completely subducted. Perhaps 25% of western N. America consist of accreted exotic terranes: they differ completely in their Mesozoic/Paleozoic fossil genera, stratigraphy, structural trends, paleomagnetic properties from the surrounding rocks >200 recognized Range in size from 100s of km wide/long to a few km wide/long Baja BC” hypothesis: Much of the western margin of British Columbia (including Vancouver Island) was moved approximately 3000 km northward, from a position close to the California – Mexico border, some time between 50 and 90 million years ago. Inferred movement of “Baja BC”: 2000-3000 km of displacement in 1540 million years ?! Subduction Produces Two Parallel Mountain Ranges in the Pacific Northwest Parks and Plates, ©2005 Robert J. Lillie Olympic National Park, Washington Steady-State Subduction Parks and Plates ©2005 Robert J. Lillie Olympic National Park, Washington Steady-State Subduction Parks and Plates ©2005 Robert J. Lillie Olympic National Park, Washington Steady-State Subduction Parks and Plates ©2005 Robert J. Lillie E E’ Parks and Plates ©2005 Robert J. Lillie Filling of the Columbia Embayment Westward roll-back of subduction Fills Columbia Embayment Stabilized near present location for ~ 40 Ma Cascade range: Uplift affects climate on east side Volcanoes supply ash to winds and area The Columbia River Basalts Basalts yield excellent soils in Hawaii and other tropical areas where rainfall is high and the climate is warm Our soils in WW are not derived from the underlying basalts-an unusual feature The Columbia River Basalts Table 15-1. Major Flood Basalt Provinces Name Volume 5 3 Age Locality CRB (1.7x10 km ) Miocene NW US Keeweenawan (4x105 km3) Precambrian Superior area Deccan (106 km3) Cret.-Eocene India Parana (area > 106 km2 ) early Cret. Karroo (2x106 km3?) Brazil early Jurassic S. Africa The Columbia River Basalts The Columbia River Basalts Aerial extent of the N2 Grande Ronde flow unit (approximately 21 flows). The Columbia River Basalts Location of the exposed feeder dikes red) and vents (blue V's) of the southeastern portion of the Columbia River Basalts. CRBs probably result from SRPYellowstone hot-spot- difficult to explain northward deflection WW The last significant volcanic events to shape the Washington landscape were the birth of the Cascade Volcanoes between 1 million and 75,000 years ago • Creation of the Cascade Volcanoes was a direct result of plate tectonics and the subduction of the Fallaron Plate under the western coast of North America. • The volcanoes were created in a progressively northern direction beginning in Northern California and now extending into Canada. SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES PACIFIC NORTHWEST 2/28/2001 M6.8 Nisqually earthquake SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKE PACIFIC NORTHWEST 2001 Nisqually earthquake M6.8 Normal fault Earthquake hypocenter 52.40 km depth under Tacoma Because it was so deep caused remarkably little damage at the surface. Seismicity in the Pacific Northwest Washington Geology 4. Cascades continental volcanic arc begins (30 million years ago to present) 5. Columbia River basalts erupt (17-6 million years ago, mostly around 15 Ma) 6. Cordilleran glaciation (2 million years – 11,000 years ago and again?) 7. Lake Missoula floods (13,000 years ago to present) Pleistocene ice sheets and glaciers that occurred from 2 million to 500 years ago • The area we are in was carved by the glaciers and the sharp features on the high peaks are called aretes, horns, cirques and hanging valleys. • Many of the lakes were created by the glaciers and glacial outwash called till and loess blanket the region. The Great Floods ~ 12,000 years ago