* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Optics
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Bicycle lighting wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
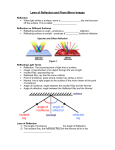
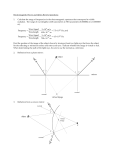
Light In this Unit you will learn: • • • • • • • Light is form of energy Properties of light Laws of reflection reflection Understand how to locate an image by no parallax Lateral inversion How images are formed in plane mirrors Uses of plane mirrors Keywords reflection No parallax normal Light ray Diffuse reflection Ange of incidence Virtual image Lateral inversion Regular reflection Angle of reflection Convergin g ray periscope nonluminous Incident ray Energy luminous Reflected ray Diverging ray Light is form of energy • • • Light can do work eg. Crookes radiometer Light can be converted to other forms of energy e.g. Solar cell, light to electricity. (show demo model of this) Other forms of energy can be converted to light e.g. Fire. Part 2 – Properties of Light Light travels in straight lines: Laser Light travels VERY FAST – around 300,000 kilometres per second. At this speed it can go around the world 8 times in one second. Light travels much faster than sound. For example: 1) Thunder and lightning start at the same time, but we will see the lightning first. 2) When a starting pistol is fired we see the smoke first and then hear the bang. We see things because they reflect light into our eyes: Homework Luminous and non-luminous objects A luminous object is one that produces light. A non-luminous object is one that reflects light. Name 3 luminous sources of light and 3 reflectors Luminous objects Reflectors Shadows Shadows are places where light is “blocked”: Rays of light Properties of Light summary • • • • • Light is a form of energy Light travels in straight lines Light travels much faster than sound We see things because they reflect light into our eyes Shadows are formed when light is blocked by an object Reflection The bouncing of light of an object is called reflection A straight líne showing the direction in which the light is travelling is called a light ray Beams of light can be coverging, diverging or parallel. Clear vs. Diffuse Reflection Smooth, shiny surfaces have a clear reflection: Rough, dull surfaces have a diffuse reflection. Diffuse reflection is when light is scattered in different directions Reflection Reflection from a plane mirror: Normal Reflected ray Incident ray Angle of incidence Angle of reflection Mirror The Laws of Reflection Incident ray, reflected ray and normal lie on the same plane Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection In other words, light gets reflected (bounced) from a surface at ____ _____ angle it hits it. The same !!! Normal How an Image is formed in a plane mirror The image is located ón the perpendicular form the object to the mirror. The image is the sames distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror. Experiments 1) To demonstrate the laws of reflection using a plane mirror. 2)To locate an image in a plane mirror the method of no parallax Lateral Inversion Lateral inversion is where the left of an object appears to the right image and vice versa. Real and Virtual images A virtual image is an image formed by th apparent intersection of light rays. Use of plane mirrors Two examples: 1) A periscope 2) looking at yourself Using no parallax to find an image The apparent relative motion of the two pencils due to the motion of the observer is called parallax In diagram (b) there is not apparent relative motion of the pencils due to the motion of the observer, this is called no parallax