* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pseudocoelom
Play (activity) wikipedia , lookup
Animal locomotion wikipedia , lookup
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology (through 1859) wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
Insect physiology wikipedia , lookup
Animal coloration wikipedia , lookup
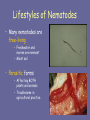
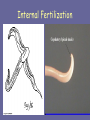
Phylum Nematoda The Roundworms What are Nematodes? • 80,000 species of roundworms are known • There may be about 800,000 species that have yet to be identified! • They are among the most numerous of all animals » > 1 million roundworms present in one shovel load of soil . . . Lifestyles of Nematodes • Many nematodes are free-living • Freshwater and marine environment • Moist soil • Parasitic forms • Affecting BOTH plants and animals • Troublesome in agricultural practice “What do they look like?!?” ~ General Characteristics ~ • Bilateral Symmetry • Anterior / posterior • Dorsal / ventral • Cylindrical bodies • Tapered at both ends • Covered by tough cuticle Nematoda • Range in size • < 1 mm extending up to > 1 meter But what about the inside? Internal Structure of Nematodes • Pseudocoelom … at last!!!! . . .but its fake!!! » NOT completely lined with mesoderm • They have a “tube-within-a-tube” structure What about digestion? • Simplest animals having a complete digestive system: – Two separate openings – One-way flow – Digestive gland to aid in digestion Definitely motile . . . • Roundworms have a simple nervous system and welldeveloped muscles – Muscle fibers located in body wall – Move in whip-like fashion The Success of Roundworms • Specialized Reproductive System – Separate sexes – Internal fertilization within female – Fertilized eggs have thick outer shell (free-living forms) – some release juvenile larva(parasitic forms) Internal Fertilization Parasitic Roundworms • Many harmful effects – Agricultural »Deformatio n of roots – Health related »Infection of other animals Agricultural Parasites • Roundworm damages plant cells – Nematode can pierce through tissues • Results in damage to roots – Inhibits efficient root function – Limits growth Carrot root nematodes Health Concerns • 250 million people in the tropics are infected by roundworms of the group Filaria – Results in conditions such as elephantiasis Sanitation: an end to roundworms • Many of the diseases caused by roundworms can be prevented through adequate sanitation practices – Good personal hygiene – Water treatment facilities – Washing and proper cooking practices Phylum Nematoda : looking back • Major advancements include: – The presence of a coelom – But, remember . . . » Pseudocoelom!! – Complete digestive tract – Separate mouth and anus – Accessory digestive gland – Reliance on sexual reproduction – With internal fertilization – Production of capsule around egg – Release of larval stage