* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is management?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
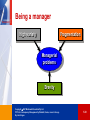
Chapter 1 What is management? Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-1 Learning objectives After studying the chapter, you should be able to: • Describe what management is, why management is important, what managers do and how managers utilise organisational resources efficiently and effectively to achieve organisational goals • Distinguish among planning, organising, leading and controlling (the four managerial functions), and explain how managers’ ability to handle each one can affect organisational performance Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-2 Learning objectives (cont.) • Differentiate among three levels of management, and understand the responsibilities of managers at different levels in the organisational hierarchy • Identify the roles managers perform, the skills they need to execute these roles effectively and the way new information technology is affecting these roles and skills • Discuss the principal challenges managers face in today’s increasingly competitive global environment Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-3 Janine Allis – Boost Juice How does Janine Allis pursue high-performance management at Boost Juice? Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-4 What is management? • The planning, organising, leading and controlling of human and other resources to achieve organisational goals effectively and efficiently Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-5 Managers • Managers are the people responsible for supervising the use of an organisation’s resources to meet its goals • Resources include people, skills, knowledge, machinery, computers and IT, and financial capital Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-6 Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-7 Organisational performance • A measure of how efficiently and effectively managers are using organisational resources to satisfy customers and achieve goals • Efficiency – A measure of how well or productively resources are used to achieve a goal • Effectiveness – A measure of the appropriateness of the goals an organisation is pursuing and the degree to which they are achieved Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-8 Why study management? • Understanding what managers do and how they do it is of central importance to understanding how a society works and how it creates wealth • Helps people deal with their bosses and coworkers • Opens a path to a well-paying job and a satisfying career Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-9 Managerial functions • Managers at all levels in all organisations perform each of the functions of planning, organising, leading and controlling • Henri Fayol outlined the four managerial functions in his book General Industrial Management (New York: IEEE Press, 1984) Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-10 Four functions of management Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-11 Planning • Process of identifying and selecting appropriate goals and courses of action Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-12 Steps in the planning process • Deciding which goals to pursue • Deciding what courses of action to adopt • Deciding how to allocate resources Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-13 Organising • Process of establishing a structure of working relationships in a way that allows organisational members to work together to achieve organisational goals Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-14 Organisational structure • A formal system of task and reporting relationships that coordinates and motivates organisational members Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-15 Leading • Articulating a clear vision to follow, and energising and enabling organisational members so they understand the part they play in attaining organisational goals • Leadership involves using power, influence, vision, persuasion and communication skills • Outcome of leadership is highly motivated and committed organisational members Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-16 Controlling • Evaluating how well an organisation is achieving its goals and taking action to maintain or improve performance – The outcome of the control process is the ability to measure performance accurately and regulate efficiency and effectiveness Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-17 Types of managers • First-line managers – Responsible for day-to-day operations. Supervise people performing activities required to make the good or service • Middle managers – Supervise first-line managers. Responsible for finding the best way to use departmental resources to achieve goals • Top managers – Responsible for the performance of all departments and have cross-departmental responsibility. Establish organisational goals and monitor middle managers Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-18 Levels of management Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-19 Relative amount of time that managers spend on the four managerial functions Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-20 Management functional areas • Department – A group of people who work together and possess similar skills or use the same knowledge, tools, or techniques – Can include Finance, Marketing, Human Resources, Production, Warehousing, Maintenance, Sales etc., each of which have managers Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-21 Restructuring • Often involves the use of information technology (IT) to downsize an organisation by eliminating the jobs of large numbers of top, middle, or first-line managers and non-managerial employees • Restructuring can have negative effects if changes are not managed properly, e.g. morale loss, excess workload for remaining employees Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-22 Outsourcing • Contracting with another company, at times in a low labour/infrastructure cost country abroad, to perform an activity the company previously performed itself • Promotes efficiency by reducing costs and allowing an organisation to make better use of its remaining resources Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-23 Empowerment • Expanding employees’ knowledge, tasks and responsibilities by involving them to various degrees in decision making; seeking their input as to how things may be done; delegating tasks and giving employees responsibility Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-24 Self-managed teams • Groups of employees with the responsibility for supervising their own actions such that the team can monitor its members and the quality of the work performed Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-25 Managerial roles and skills • Managerial role: the set of specific tasks that a person is expected to perform because of the position he or she holds in the organisation • Mintzberg identified three categories of roles – Decisional – Informational – Interpersonal Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-26 Decisional roles • Roles associated with methods managers use in planning strategy and utilising resources – Entrepreneur: deciding which new projects or programs to initiate and to invest resources in – Disturbance handler: managing an unexpected event or crisis – Resource allocator: assigning resources between functions and divisions, setting the budgets/salaries of lower managers – Negotiator: reaching agreements between other managers, unions, customers or shareholders Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-27 Informational roles • Roles associated with the tasks needed to obtain and transmit information in the process of managing the organisation – Monitor: analysing information from both the internal and external environment – Disseminator: transmitting information to influence the attitudes and behaviour of employees, colleagues and other stakeholders outside the organisation – Spokesperson: representing the organisation and using information to positively influence the way people in and out of the organisation respond to it Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-28 Interpersonal roles • Roles that managers assume to provide direction and supervision to both employees and the organisation as a whole. – Figurehead: symbolising the organisation’s mission, values and what it is seeking to achieve – Leader: training, counselling, mentoring, setting goals and expectations, initiating change, role modelling, decision making – Liaison: linking and coordinating the activities of people and groups both inside and outside the organisation Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-29 Being a manager High variety Fragmentation Managerial problems Brevity Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-30 Managerial skills • Conceptual skills: the ability to analyse and diagnose a situation and distinguish between cause and effect • Human skills: the ability to understand, alter, lead and control the behaviour of other individuals and groups • Technical skills: the job-specific knowledge and techniques required to perform a functional organisational role, e.g. accounting, marketing, information technology (IT), human resources, welding Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-31 Skill types needed Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-32 Competencies • Specific set of skills, abilities and experiences that gives one manager the ability to perform at a higher level than another manager in a particular organisational setting • The manager knows what has to be done and can do it to the required standard within an appropriate timeframe Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-33 Challenges for management in a global environment • Emergence and growth of global organisations • Building and maintaining competitive advantage • Building and maintaining ethical and socially responsible standards • Managing a diverse workforce • Staying abreast of and deploying IT and new business models growing out of it and developments in e-commerce Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-34 Building and maintaining competitive advantage • • • • • Increasing efficiency Increasing effectiveness Increasing quality Increasing speed, flexibility and innovation Increasing responsiveness to customers Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-35 Building blocks of competitive advantage Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-36 Work–life balance challenge • Increase in working hours • Increase in emotional commitment • Impact on personal life • Workaholism • Disturbing trajectory of work behaviours • Steps to redress working life trends Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-37 Summary 1: Role of managers • Managers are responsible for supervising the organisation’s resources for achieving organisational goals • Organisations are collections of people working together to achieve mutual goals • Planning, organising, leading and controlling helps an organisation reach its goals efficiently and effectively • Organisations create goods and services that customers want Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-38 Summary 2: Management functions • • • • Planning Organising Leading Controlling Carried out efficiently and effectively Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-39 Summary 3: Levels of managers • Typically, three levels – first line – middle – senior • Roles differ in emphasis in the range of activities carried out • Managerial hierarchies have been altered by restructuring, employee empowerment, self-managing teams and IT in yet further attempts to achieve efficiencies and increased effectiveness Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-40 Summary 4: Manager roles • According to Mintzberg, ten roles – Figurehead – Spokesperson – Leader – Entrepreneur – Liaison – Disturbance handler – Monitor – Resource allocator – Disseminator – Negotiator Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-41 Summary 5: Management challenges • Building competitive advantage through efficiency, quality, speed, flexibility, innovation, responsiveness • Ethical behaviour • Managing diversity • Utilising new technologies and systems • Work–life balance Copyright 2007 McGraw-Hill Australia Pty Ltd PPTs t/a Contemporary Management by Waddell, Devine, Jones & George By John Dugas 1-42