* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hormonal
Prenatal development wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
Fertility and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Female infertility wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Infertility wikipedia , lookup
Female promiscuity wikipedia , lookup
Sub-replacement fertility wikipedia , lookup
Body odour and sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive health wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sexual abstinence wikipedia , lookup
Fertility factor (demography) wikipedia , lookup
Father absence wikipedia , lookup
Sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Unintended pregnancy wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
History of birth control wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial insemination wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Anovulation wikipedia , lookup
Catholic theology of sexuality wikipedia , lookup
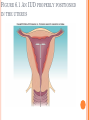
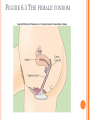
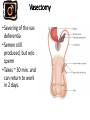
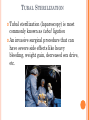
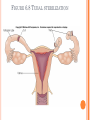
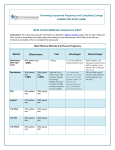
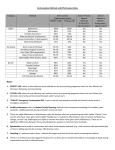
CONTRACEPTION Chapter 6 CONTRACEPTION Definition: Contraception: preventing conception by blocking the female’s egg from uniting with the male’s sperm 2 PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACEPTION Effectiveness Contraceptive failure rate- % of women experiencing an unintended pregnancy in the 1st yr. of contraceptive use Continuation rate- % of people who continue to use the method after a specified period of time PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACEPTION Based on the physiology of reproduction Types of contraception: Hormonal Barrier Natural methods Surgical Factors affecting choice Advantages and disadvantages 4 HORMONAL METHODS ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES: THE PILL Hormonal contraceptive Mimics the corpus luteum Secretes estrogen & progestin (Combination pill) to suppress ovulation Most common type of birth control Advantages: Easy to use, effective (99.9%), fertility returns after use Disadvantages : no protection against STD’s, exp. symptoms of pregnancy, prescription required, stroke, blood clots in older women who smoke 6 CONTRACEPTIVE SKIN PATCH Hormonal contraceptive Releases estrogen and progestin into bloodstream Prevents pregnancy the same way as OCs Worn for 1 week, replaced on the same day for 3 consecutive weeks. 4th wk. no patch Advantages: same as OC’s, week long protection Disadvantages: same as OCs 7 VAGINAL CONTRACEPTIVE RING Hormonal contraceptive Flexible vaginal ring molded w/ progestin and estrogen Slowly releases hormones into bloodstream Worn for 3 wks., removed at start of 4th wk. (ring free) new ring inserted same day, following wk. Advantages : 1 month of protection, no daily/weekly action required Disadvantages : similar to OCs and patch 8 CONTRACEPTIVE IMPLANTS Hormonal contraceptive Placed under skin of upper arm/leg Delivers progestin over a period of 4 years Advantages: Highly effective, no further action required after insertion, contains no estrogen, so no estrogen related side effects Disadvantages: no protection against STDs, menstrual irregularities, uncomfortable appearance 9 INJECTABLE CONTRACEPTIVES Depo-Provera Injectable progestin every 12 weeks Provides protection like implants Advantages: Highly effective, requires little action on part of user ; No estrogenrelated side effects, minor injection Disadvantages: visit to health care facility every 3 months, weight gain, infertility after stopping use 10 EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION “Morning-after Pill”, Plan B Should not be used as a contraceptive but can be used if birth control has failed, if forced to have sex, etc. Most common is the two dose regimen May inhibit/delay ovulation or altering the transport of sperm/egg; does not affect a fertilized, implanted egg Needs to be taken within 72 hours. Best used within 24 hours 11 THE INTRAUTERINE DEVICE (IUD) Small plastic device placed in the uterus ParaGard (copper; protects up to10 yrs.) Mirena (protects up to 5 yrs.) Releases small amounts of progestin May work by thickening cervical mucus, or thins lining of uterus Advantages: highly reliable, once inserted a simple check of string is all that’s needed; reduced risk of endometrial cancer; fertility restored after use Disadvantages: heavy menstrual flow, uterine cramping, backache, spontaneous expulsion, may puncture uterine wall 12 FIGURE 6.1 AN IUD PROPERLY POSITIONED IN THE UTERUS 13 BARRIER METHODS BARRIER METHODS MALE CONDOMS Thin latex, or polyurethane Most widely used barrier method Advantages: Protects against pregnancy and STD’s, easy to purchase, no prescription Disadvantages: Most common complaints are reduced sensitivity and interfering with sexual intercourse 16 FEMALE CONDOMS Polyurethane sheath with two flexible rings Advantages: offers potentially more protection against genital warts and herpes b/c it covers base of penis Disadvantage: more expensive, more difficult to use 17 FIGURE 6.3 THE FEMALE CONDOM 18 NATURAL METHODS ABSTINENCE Abstinence Without sexual intercourse for a chosen period of time Benefits More self respect and respect for others Security that you are not being pursued for sexual reasons. Less worry about STDs and Pregnancy. 20 THE FERTILITY AWARENESS METHOD Only one egg released each month Lives for ~ 24 hrs. unless fertilized Sperm can live in the body for 6-7 days Only 8 days/month when conception can happen FAM Calendar method Temperature method A woman releases an egg 14-16 days before her next period A woman’s BT drops slightly before ovulation and rises slightly after Withdrawal Coitus interruptus 21 SURGICAL METHODS Vasectomy •Severing of the vas deferentia •Semen still produced, but w/o sperm •Takes ~ 30 min. and can return to work in 2 days. 23 TUBAL STERILIZATION Tubal sterilization (laparoscopy) is most commonly known as tubal ligation An invasive surgical procedure that can have severe side effects like heavy bleeding, weight gain, decreased sex drive, etc. 24 FIGURE 6.8 TUBAL STERILIZATION 25 WHICH CONTRACEPTIVE METHOD IS RIGHT FOR YOU? Key considerations include: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Health risks Implications of an unplanned pregnancy STD risk Convenience and comfort level Type of relationship Ease and cost of obtaining and maintaining each method Religious or philosophical beliefs 26