* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Pythagorean Theorem
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
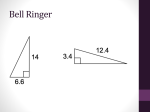
The Pythagorean Theorem Geometry Mrs. Pam Miller January 2010 The Pythagorean Theorem • Greek Mathematician, Pythagoras, proved this theorem. • Applies to right triangles. • Many different proofs exist, including one by President Garfield. The Theorem For any right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs. hypotenuse leg leg2 + leg2 = hyp2 leg The Abbreviated Version We often see the Pythagorean Theorem stated as: a 2 + b2 = c2 c a b Some Examples Find the value of x. ( Remember that the length of a segment must be a positive number.) leg2 + leg2 = hyp2 a) x 3 32 + 72 = x2 9 + 49 = x2 7 58 = x2 √58 = √x2 √58 = x Examples (cont’d.) 8 b) 10 leg2 + leg2 = hyp2 x 82 + x2 = 102 64 + x2 = 100 64 - 64 + x2 = 100 - 64 X2 = 36 √x2 = √36 X=6 Practice with Radicals Work with the Pythagorean Theorem often requires us to work with radicals. Simplify each expression: A) (√3) 2 √3 × √3 √9 3 B) ( 3 √ 11 ) 2 3 √ 11 × 3 √ 11 9 × √ 121 9 99 × 11 Your Turn Simplify each expression: A. (√ 5) 2 B. (2 √ 7) 2 E. F. 2 3 5 2 2 2 C. (7 √ 2 ) 2 G. D. (2n) 2 2 3 6 2 The Answers Simplify each expression: A. (√ 5) 2 =5 B. (2 √ 7) 2 = 28 C. (7 √ 2 ) 2 = 98 E. F. G. D. (2n) 2 = 4n2 2 3 5 2 2 = 9/5 2 = 1/2 2 2 = 24/9 6 3 Pythagorean Triples 3, 4, 5 5, 12, 13 6, 8, 10 10, 24, 26 8, 15, 17 7, 24, 25 9, 12, 15 12, 16, 20 15, 20, 25 In every triple, the largest # is the length of the hypotenuse and the 2 smaller numbers are the lengths of the legs of the right triangle. The Converse If the square of 1 side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle. More simply… if c2 = a2 + b2, then the triangle is a right triangle. c a b Pythagorean Inequalities If c2 > a2 + b2, then the triangle is obtuse. If c2 < a2 + b2, then the triangle is acute. c a b Practice The sides for 3 triangles are given. Decide if each triangle is acute, right or obtuse. A) 14, 7, 9 B) 2.5, 6, 6.5 C) 2, 3, 3.5 142 ___ 72 + 92 6.52 ___ 2.52 + 62 3.52 ___ 22 + 32 196 ___ 49 + 81 42.25 ___ 6.25 + 36 12.25 ___ 4 + 9 196 > 130 42.25 = 42.25 12.25 < 13 It’s obtuse! It’s right! It’s acute! Check It Out A triangle has sides with the following lengths: 9, 40, & 41. Is this a right triangle? Does 412 = 92 + 402 ? Does 1681 = 81 + 1600? YES !! So, the triangle is a right triangle. More Practice A right triangle has one leg with a length of 48 and a hypotenuse with a length of 80. What is the length of the other leg? Here’s how: 482 + x2 = 802 x2 = 4096 2304 + x2 = 6400 √ x2 = √ 4096 x2 = 6400 - 2304 x = 64 64 Practice (cont’d) A triangle has side lengths of 7, 10, & 12. Is the triangle a right triangle? Use the Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem! Here’s How: Does c2 = a2 + b2 ? Does 122 = 72 + 102 ? Does 144 = 49 + 100? NO ! Practice (cont’d) A triangle has side lengths of 8, 15, and 18. Is the triangle right, acute, or obtuse? Remember: If c2 < a2 + b2, you have an acute triangle. If c2 = a2 + b2, you have a right triangle. If c2 > a2 + b2, you have an obtuse triangle. Here’s How: 182 ____ 82 + 152 324 > 289 324 ____ 64 + 225 It’s obtuse! Other Applications Find the area of the figure. Leave your answer in radical form. 8 8 Area of a triangle = 1/2 bh 8 Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find “h”: h 8 4 42 + h2 = 82 h2 = 48 16 + h2 = 64 √ h2 = h2 = 64 - 16 h=4√ 3 √ 48 More…. Find the Area of the Triangle Area = 1/2 bh 8 4√ 3 4 Area = 1/2 (8) (4 √ 3) Area = 16 √ 3 8 8 8 Last Problem! Find the area of the square. Leave your answer in radical form. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the length of the sides (s). s2 + s2 = 62 √ s2 = √ 18 2s2 = 36 s=3√ 2 s2 = 18 So the area of the square is : 3√ 2×3√ 2 6 s s =9√ 4 = 9×2 = 18 What Have You Learned? • • • • • Pythagorean Theorem Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem Pythagorean Triples Pythagorean Inequalities Applications