* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 8.5 PowerPoint File
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
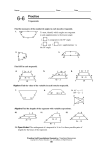
Use the figure to answer the questions. 1. What are the values of x and y? ANSWER 125, 125 2. If AX and BY intersect at point P, what kind of triangle is XPY? ANSWER isosceles EXAMPLE 1 Use a coordinate plane Show that ORST is a trapezoid. SOLUTION Compare the slopes of opposite sides. 4–3 Slope of RS = 2 – 0 = 2–0 Slope of OT = 4 – 0 = 1 2 1 2 = 2 4 The slopes of RS and OT are the same, so RS OT . EXAMPLE 1 Slope of ST = Use a coordinate plane 2 – 4 –2 –1 4–2= 2 = 3 , Slope of OR = 30 –– 00 = 0 which is undefined The slopes of ST and OR are not the same, so ST is not parallel to OR . ANSWER Because quadrilateral ORST has exactly one pair of parallel sides, it is a trapezoid. GUIDED PRACTICE for Example 1 1. What If? In Example 1, suppose the coordinates of point S are (4, 5). What type of quadrilateral is ORST? Explain. ANSWER Parallelogram; opposite pairs of sides are parallel. 2. In Example 1, which of the interior angles of quadrilateral ORST are supplementary angles? Explain your reasoning. ANSWER O and R , T and S; Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem EXAMPLE 2 Use properties of isosceles trapezoids Arch The stone above the arch in the diagram is an isosceles trapezoid. Find m K, m M, and m J. SOLUTION STEP 1 Find m K. JKLM is an isosceles trapezoid, so K and L are congruent base angles, and m K = m L= 85o. EXAMPLE 2 Use properties of isosceles trapezoids STEP 2 Find m M. Because L and M are consecutive interior angles formed by LM intersecting two parallel lines, they are supplementary. So, m M = 180o – 85o = 95o. STEP 3 Find m J. Because J and M are a pair of base angles, they are congruent, and m J = m M = 95o. ANSWER So, m J = 95o, m K = 85o, and m M = 95o. EXAMPLE 3 Use the midsegment of a trapezoid In the diagram, MN is the midsegment of trapezoid PQRS. Find MN. SOLUTION Use Theorem 8.17 to find MN. MN = 1 (PQ + SR) 2 1 = 2 (12 + 28) = 20 ANSWER Apply Theorem 8.17. Substitute 12 for PQ and 28 for XU. Simplify. The length MN is 20 inches. GUIDED PRACTICE for Examples 2 and 3 In Exercises 3 and 4, use the diagram of trapezoid EFGH. 3. If EG = FH, is trapezoid EFGH isosceles? Explain. ANSWER yes, Theorem 8.16 GUIDED PRACTICE 4. for Examples 2 and 3 If m HEF = 70o and m FGH = 110o, is trapezoid EFGH isosceles? Explain. SAMPLE ANSWER Yes; m EFG = 70° by Consecutive Interior Angles Theorem making EFGH an isosceles trapezoid by Theorem 8.15. GUIDED PRACTICE 5. for Examples 2 and 3 In trapezoid JKLM, J and M are right angles, and JK = 9 cm. The length of the midsegment NP of trapezoid JKLM is 12 cm. Sketch trapezoid JKLM and its midsegment. Find ML. Explain your reasoning. ANSWER J 9 cm N 12 cm M K P L 1 15 cm; Solve 2 ( 9 + x ) = 12 for x to find ML. EXAMPLE 4 Find m Apply Theorem 8.19 D in the kite shown at the right. SOLUTION By Theorem 8.19, DEFG has exactly one pair of congruent opposite angles. Because E G, D and F must be congruent. So, m D = m F.Write and solve an equation to find m D. EXAMPLE 4 Apply Theorem 8.19 m D+m F +124o + 80o = 360o Corollary to Theorem 8.1 m D+m D +124o + 80o = 360o Substitute m 2(m D) +204o = 360o m D = 78o D for m Combine like terms. Solve for m D. F. GUIDED PRACTICE 6. for Example 4 In a kite, the measures of the angles are 3xo, 75o, 90o, and 120o. Find the value of x. What are the measures of the angles that are congruent? ANSWER 25; 75o Homework: Page 546: 1 – 5 odd, 7 – 15, 17 – 23, 25 – 27, 34, 37