* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 3: Supply and Demand: Theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
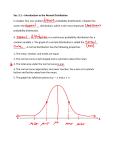
Ch. 3: Supply and Demand: Theory Demand • Demand is: the _________and ability of buyers to purchase different quantities of a good at different prices during a _______________. • The Law of Demand: as the price of a good rises, ______________ of that good falls; as the price of a good falls, quantity demanded of that good rises. Prices • Absolute Price: the price of a good _____________ (Ex: A new Car costs $30,000). • Relative Price: the price of a good _______________ (Ex: A new Car costs 30 computers) • Relative price is calculated by __________the absolute price of one product with the absolute price of another product (Ex: A Car costs $30,000; A Computer costs $1,000; The relative cost of a Car is 30 Computers) Why Quantity Demanded Goes Down As Price Goes Up • People ___________ lower-priced goods for higher-priced goods. • The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility: for a given time period, the marginal (additional) utility or ________ gained by consuming equal ______________units of a good will ___________ as the amount consumed increases. Four Ways to Represent The Law Of Demand • In Words: “As price rises, _________________” • In Symbols: PQd • In a ________ Schedule • In a ___________ Curve Demand Schedule Causes of Change in the Demand Curve • • • • • Income Preferences __________________ Number of Buyers ______________________ Income Changes in Demand Shifts in Demand Curves • The demand for a good increases if people are willing and able to buy more of the good at all prices. • A normal good is a good the ________ for which rises(falls) as ________ rises(falls). • An inferior good is a good the _______ for which rises(falls) as _______ falls(rises). Preferences, Substitutes and Related Goods • Preferences affect the amount of a good they are willing to buy at a particular price (Ex: favorite food, favorite author) • If the demand for Coke ________ as the price for _____________, and the _______ for Coke falls as the ______________, Coke and Pepsi are___________. • If __________ of product A falls as the __________ for product B rises, and the price of product A rises as the _______________, A and B are Related Goods (Ex: Ketchup and Hot Dog Buns). Shifting the Demand Curve • A change in Demand causes a __________________ curve. • A change in the _________ Demanded _______ a point ______ the current Demand curve. • If Demand increases, the curve shifts to the right. • If Demand decreases, the curve shifts to the left. Q&A • As Sandi’s income rises, her demand for popcorn rises. As Mark’s income falls, his demand for prepaid telephone cards rises. What kinds of goods are popcorn and telephone cards for the people who demand each? • Why are demand curves downward sloping? • Give an example that illustrates how to derive a market demand curve. • What factors can change demand? What factors can change quantity demanded? Supply • Supply is the _______ and _____ of sellers to _______ and ____________ different quantities of a good at different prices during a specific period of time • Law of Supply: As the price of a good ____, the quantity _______ of the good ____; and as the price of a good falls, the quantity supplied of the good falls. The Supply Curve Why Supply Curves Slope Upwards An Upward-sloping supply curve reflects the fact that under certain conditions, a higher price is an _______ to producers to produce more of a good. Market Supply Curve • The Market Supply Curve represents the _____ _____ combinations for all sellers of a particular good. • An Individual supply curve represents the pricequantity combinations for a single seller Supply Curve Shifters • If the price of a relevant ______ changes, the supply curve will ____ (EX: wood prices increase, cost of a new house increases as well) • ________ can increase the quantity supplied by producing more of a product with the same quantity of resources supplied. • If the _________ increase, the supply curve will shift. • If the price of a good is _________ to be higher in the future, the supply curve will shift Supply Curve Shifters • _______ increase unit costs • Government ___________ can change the supply curve by increasing or limiting production. Shifting the Supply Curve • A Change in the Supply Curve is a shift in the Supply Curve, not merely moving up and down the same curve. Q&A • Which way (if any) does the Supply Curve shift if there is a decrease in the number of sellers? If there is a per-unit tax is placed on the production of the good? If the price of a relevant resource falls? • Why do most Supply Curves slope upward? The Market Putting Supply and Demand Together Market Language • If the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded, the good has a ________ or excess supply. • If quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied, a ________ or excess demand exists. • The price at which a quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied is the ______________, or the market-clearing price. • A market that has too much of a good or too little of a good is considered to be in ________________. Moving to Equilibrium 1. Why does the price fall when there is a surplus? 2. Why does the price rise when there is a shortage? • _______________________________________. Price Controls • • 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Price Ceiling: a __________ mandated price above which __________ may not be made. Price Ceilings may cause: _________ Fewer Exchanges Non-price Rationing Devices Buying and Selling at a Prohibited Price (Black Market) Tie in Sales Price Floor • A price floor is a government _________ minimum price _____ which legal trades cannot be made. • Price floors can cause ________ and Fewer Exchanges. Q&A • Do buyers prefer lower prices to higher prices? • Who might argue for a Price Ceiling? A Price Floor? Why would they argue their viewpoint?