* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Gold *any riches (gold, silver, resources) Most important to
Colonial American bastardy laws wikipedia , lookup
Plymouth Colony wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown, Virginia wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American military history wikipedia , lookup
Province of Maryland wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Colony of Virginia wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
History of Jamestown, Virginia (1607–99) wikipedia , lookup
Massachusetts Bay Colony wikipedia , lookup
Colonial period of South Carolina wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church in the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
Jamestown supply missions wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
London Company wikipedia , lookup
Roanoke Colony wikipedia , lookup
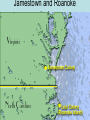
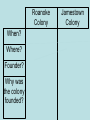
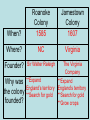
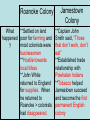
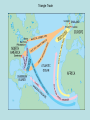
Colonization and Settlement of America Reasons for Exploration • Expanding populations—needed more space • Trade increased – merchants wanted access to Asia – spices, silk, porcelain • Three G’s—in this order • 1. Gold *any riches (gold, silver, resources) Most important to most explorers • 2. God *to convert natives • 3. Glory *to make a name for themselves • First European explorers to reach the Americas were Vikings – Leif Eriksson – Canada – around 1000 A.D. • Christopher Columbus – Caribbean - 1492 A.D. • Spain is first European country to permanently colonize the New World • Amerigo Vespucci—first European to map North and South America (1501) • Giovanni da Verrazzano – first European to reach North Carolina (1524) • Natives were treated poorly – Plantation System – used for agricultural (sugar cane) and mining work (gold and silver) • Columbian Exchange – movement of stuff (animals, plants, diseases, religions, knowledge, technology, culture, resources etc.) between Old World and New World • Old World – Europe/Africa/Asia • New World – North and South America Columbian Exchange Video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dxl9RP LwvC8 Columbian exchange Smallpox Victim Native populations were devastated by disease Sir Walter Raleigh & the Roanoke Colony • English aristocrat and explorer – Funded his own voyages – Supported by Queen Elizabeth I • 1584 - Landed at Roanoke Island – Made connections with local Native Americans – Decided to bring settlers back Roanoke Colony, cont. • 1585 – 108 soldiers come to Roanoke to establish first colony • 1586 – Colonists and Native Americans at “war,” and colony is abandoned • 1587 – Second settlement attempted –117 colonists come to Roanoke –Governor John White Roanoke, cont. • 1587 – John White returns to England to get supplies • 1590 – White returns to Roanoke, but finds the colony has disappeared The mystery of the lost colony Video • http://www.schooltube. com/video/89c920dac 3962b0ae572/ • What do you think happened to them? Jamestown and Roanoke colonies Jamestown • 1st permanent English settlement – Virginia in 1607 – established for profit – Virginia Company • John Smith (military leader), John Rolfe (tobacco – made the colony successful), Pocahontas (married Rolfe, not Smith) • Colony almost did not survive – bad location • 1609-1610 – Starving Time – only 60 of 215 survive – colony survived because new colonists came each year. • 1619 (a big year): House of Burgess (1st representative assembly), English women arrive, Africans brought as Indentured Servants Jamestown Timeline http://www.virtualjamestown.org/timeline2.html 1608 Settlers at Jamestown die in great numbers (38 of 104 remain) 1609 • 500 more settlers come to Virginia • Relations with Native Americans grow tense 1610 SeptemberMay: The “Starving Time” reduces population to 60 (from 500600) John Rolfe marries Pocahontas John Smith Pocahontas • http://www.history.com/shows/america-thestory-of-us/videos/life-in-jamestown#life-injamestown http://www.history.com/shows/america-thestory-of-us/articles/episode-1-rebels Roanoke Colony When? Where? Founder? Why was the colony founded? Jamestown Colony When? Roanoke Colony 1585 Jamestown Colony 1607 Where? NC Virginia Founder? Sir Walter Raleigh Why was the colony founded? The Virginia Company **Expand **Expand England’s territory England’s territory **Search for gold **Search for gold **Grow crops Roanoke Colony What happened ? Jamestown Colony Roanoke Colony **Settled on land What happened poor for farming and most colonists were ? businessmen **Hostile towards local tribes **John White returned to England for supplies. When he returned to Roanoke > colonists had disappeared. Jamestown Colony **Captain John Smith said, “Those that don’t work, don’t eat” **Established trade relationship with Powhatan Indians **Tobacco helped Jamestown succeed and become the first permanent English colony Colonies developed different identities according to climate and charter English Colonies • Split into three regions • New England (MA, NH,RI,CN) – settled by many people seeking religious freedom –Economy was based on fishing, lumbering, and shipbuilding • Middle Colonies (NY, NJ,PA,DE) ––More of a mix coming for religious freedom and economic opportunities – more diverse backgrounds – farming and trade 13 Colonies • Southern Colonies –(MD, VA, NC, SC, GA) mostly came for economic opportunities • Economy was based on agriculture – Tobacco, Cotton, Rice, Indigo • Georgia – place for debtors and poor to live The New England Colonies • • • • Massachusetts Rhode Island Connecticut New Hampshire The Middle Colonies • • • • New York Delaware New Jersey Pennsylvania The Southern Colonies • • • • • Virginia Maryland North Carolina South Carolina Georgia 13 COLONIES MAP ACTIVITY Colonies New England Colonies Middle Colonies Southern Colonies Motivations Economy What caused each region to develop differently than the others? What prediction can you make for the future development of each region? (Use Concepts) Giovanni da Verrazzano • Italian explorer, commissioned by France • Discovers North Carolina in 1524 –First European since around 1000 AD to explore the Atlantic coast of North America between the Carolinas and Newfoundland Carolina • Settled by members of the other colonies. Original settlers English. Granted a private company in 1663 and divided into two colonies in 1711. • Great place to grow indigo, rice, and tobacco. • Name came from the Latin word carolus, meaning “Charles.” • Officially became a state on November 21, 1789. Immigrant Groups of the 13 colonies • New England • Pilgrims - Settled in Massachusetts in 1620 – Plymouth • Puritans - Settled in Massachusetts in 1630 – Boston • Wanted religious freedom • Middle Colonies • Catholics • Quakers –William Penn • More tolerant and diverse • Lords Proprietors – 8 noble supporters of Charles II, awarded Carolina in return for their support – 1663 • 1706 – Bath – first NC town • 1710 – New Bern founded – became 1st capital of NC • Three regions • 1. Coastal Plain in east – first region settled by Europeans • 2. Piedmont in central • 3. Mountains in west • • • • • • • • • New Immigration NC becomes royal colony in 1728. New settlers 1. Scots-Irish – settled in east 2. Highland Scots – settled in east 3. Germans and Moravians –settled in Piedmont – backcountry Great Wagon Road – main route to travel through backcountry Moravians – name their land Wachovia 1766 – establish the towns of Bethabara and Salem 4. Africans – brought as slaves – fewer than many other southern colonies Great Wagon Road • Were the reasons why people immigrated to the 13 colonies similar to the reasons why people immigrate to America today? Economy/Social Structure • Economy – North Carolina was mostly agricultural. • Cash Crops – Tobacco, Rice, and Indigo • Naval Stores – tar, pitch, turpentine • Trade was difficult due to NC’s lack of roads and difficult waterways. Mercantilism – the colonies existed for the economic benefit of England • Social Classes • 1. Gentry – rich planters, doctors, lawyers • 2. Artisans – craftsmen – blacksmith, cobblers • 3. Small Farmers – Yeomen – biggest group • 4. Indentured Servants – poor people who bought their passage to America with their service. • 5. Slaves/Indians • Triangle Trade – three-part voyage • A. Europe to Africa – manufactured trade goods • B. Africa to America (Middle Passage)- slaves • C. America to Europe – raw materials (lumber, cotton, tobacco) • Growing conflict between Eastern and Western NC over taxes and political power. Triangle Trade Early Government in the Colonies • Magna Carta – Even the King had to obey the law • English Bill of Rights – limited King’s power; gave representative government (Parliament) more power • Representative Government – the people elect representatives to speak for them in government • Mayflower Compact – first attempt at selfgovernment in the English colonies • Town meetings – first form of American government in which all free men could participate • House of Burgess – first representative government in America • Proprietary colony – privately-owned colony • Royal colony – government-run colony • Which common theme did each of these government examples have that led to the colonists’ desire for independence?