* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Church History
Son of man (Christianity) wikipedia , lookup
Salvation in Christianity wikipedia , lookup
Extra Ecclesiam nulla salus wikipedia , lookup
Universal reconciliation wikipedia , lookup
Divinization (Christian) wikipedia , lookup
Christology wikipedia , lookup
Binitarianism wikipedia , lookup
Nontrinitarianism wikipedia , lookup
Wesleyanism wikipedia , lookup
Japanese Independent Churches wikipedia , lookup
Monothelitism wikipedia , lookup
Christian pacifism wikipedia , lookup
Church Fathers wikipedia , lookup
Trinitarian universalism wikipedia , lookup
Christianity and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Heresy in Christianity wikipedia , lookup
Millennialism wikipedia , lookup
Conversion to Christianity wikipedia , lookup
Re-Imagining wikipedia , lookup
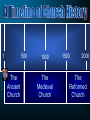
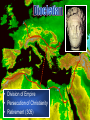
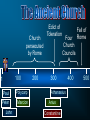
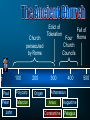
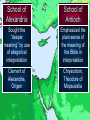
The Victorious Church © John Stevenson, 2016 Class Objectives • • • To recall, summarize and evaluate the fortunes of Christianity from the late patristic period (5th century) through the high middle ages of medieval Christianity (13th century). To describe how the doctrine of the Incarnation came to be defined by the early Church. To summarize and evaluate the rise and spread of the Monastic movement. Class Objectives • • • To recognize the factors that gave rise to the growth of the Roman Catholic Church and the office of the Papacy. To recognize and name the ecclesiastical differences between the Church in the East from that in the West which resulted in a profound schism. To define and describe what Scholasticism is and analyze what it reveals about medieval Christianity. “Thou hast conquered, Oh Galilean!” ― Julian the Apostate 1 500 The Ancient Church 1000 The Medieval Church 1500 2000 The Reformed Church Tertullian 155-222 We are but of yesterday, and we have filled every place among you - cities, islands, fortresses, towns, market-places, the very camp, tribes, companies, palace, senate, forum… (Apologeticus 37) Church persecuted by Rome 100 1 Paul Polycarp Peter Marcion John 200 Edict of Toleration 300 Diocletian Tertullian Constantine 400 500 • Division of Empire • Persecution of Christianity • Retirement (305) Edict of Toleration Christians may again exist and rebuild the houses in which they used to meet, on condition that they do nothing contrary to public order. (Quoted from Eusebius, History of the Church 8:17:5). Constantine • Battle for the Milvian Bridge (312) Constantine • Battle for the Milvian Bridge (312) • “In this sign conquer” • Edict of Milan: Restated & expanded the Edict of Toleration (313) • Reunification of Roman Empire • Favored status (324) Christianity as Favored Religion • Bishops given the right to judge civil cases • Sunday made into a public holiday • New Edict of Toleration: Christians not allowed to persecute pagans What should be the attitude of Christians to the gaining of political power? Before Constantine After Constantine Purity within the church Long periods of catechism training before receiving baptism Less purity within the church Christians known for their strict lifestyle Loosening of the standards Martyr mentality among the pious Monastic mentality began to emerge among the pious Requirements to become a Christian were minimized ! ! Donatus Magnus (Died 355) What about those who have been baptized or married by fallen bishops? Work as a group to formulate a detailed description of what you believe about Jesus • • • • As to His deity As to His sonship from God As He relates to the Holy Spirit As to His humanity • Tertullian of Carthage (160-220 A.D.). – Coined the term “Trinity” – Spoke of how the son proceeded from God “Thus, the Father makes him equal to himself; and the Son, by proceeding from him, was made first-begotten, since he was begotten before all things; and the only-begotten, because he alone was begotten of God, in a manner peculiar to himself” (Against Praxeas). • Tertullian of Carthage (160-220 A.D.). – Coined the term “Trinity” – Spoke of how the son proceeded from God – Argued against modalism • Origen of Alexandria (165-254 A.D.). – Although the Son is begotten of the Father, it is an eternal begetting Arius • Priest in Alexandria, Egypt • Taught that Christ was a created being • Christ was the first created being who then created all the rest of creation • Claimed Tertullian for support, but denied that Jesus was God Arius “God was not always a father; indeed, there was a time when God was alone, and he was not yet a father. Afterwards, he became a father. The son was not always… before he was begotten, he was not; rather, he has a beginning.” – The Banquet Arius • Deposed by Alexander, bishop of Alexandria • Became friends with Eusebius of Nicomedia – Shared Christological views – Bishop of Nicomedia – Distant relative of Constantine 296 - 373 • Egyptian Christian family • Childhood: Playing at baptism • Ordained as a deacon in 319 • Assistant to Bishop Alexander at Council of Nicea Constantinople Nicaea Council of Nicaea • Met at Nicaea in 325 • 300 Bishops in attendance (5 from west) • Alexander & Athanasius versus Arius The Nicene Creed We believe in one God the Father All-sovereign, Maker of all things. And in one Lord Jesus Christ, the Son of God, begotten of the Father, only-begotten, that is, of the substance of the Father God of God, Light of Light, true God of true God, begotten not made, of one substance with the Father… • • • • Nicaean Creed Celebration of Easter Lapsed bishops Celibacy of the clergy (argued but not mandated) • Prohibition of kneeling on Sundays Church Councils of the 4th and 5th Centuries Council of Nicaea 325 Jesus is of the same substance as the Father Holy Spirit is co-eternal with Council of 381 the Father and Son, but the Constantinople three are distinct Homoousia Homoinousia Same Substance Similar substance 381 • Three Cappadocian Fathers – Basil the Great: Bishop of Caesarea – Gregory of Nyssa (Basil’s younger brother): Scholar – Gregory of Nazianzus (Eventual patriarch of Constantinople): Orator • One substance (ousia) in three persons (hypostaseis) • Arianism condemned Church Councils of the 4th and 5th Centuries Council of Nicaea 325 Jesus is of the same substance as the Father Holy Spirit is co-eternal with Council of 381 the Father and Son, but the Constantinople three are distinct Council of Ephesus 431 Jesus is one person, fully divine and fully human Bishop of Constantinople Bishop of Alexandria Mary as Christotokos Mary as Theototokos (“Christ-bearer”) (“God-bearer”) 431 431 • Called by Emperor Theodosius II • Began before the eastern bishops had arrived • Nestorius was deposed and declared a “new Judas” • Eastern bishops convened their own council under John of Antioch 431 • Eastern bishops deposed Cyril • Council deposed John of Antioch • Emperor upheld the decision of both councils Church Councils of the 4th and 5th Centuries Council of Nicaea 325 Jesus is of the same substance as the Father Holy Spirit is co-eternal with Council of 381 the Father and Son, but the Constantinople three are distinct Council of Ephesus Council of Chalcedon 431 Jesus is one person, fully divine and fully human 451 The human and divine natures of Jesus are unmixed Christ only seemed to be Docetic human Christ only seemed to be Ebionite divine Christ was created by God and Arian then created all else Christ had no human spirit; Apollinarian Logos came and replaced it Jesus became the Christ as Monoarchian His baptism One God reveals Himself in Sabellianism three ways Logos indwelt the person of Nestorian Jesus making Christ a Godbearer Human nature of Christ Eutyches absorbed by the Logos Monophysite Christ had only one nature Christ had no human will; only Monothelite one divine will Adapted from Robert Walton Church persecuted by Rome 100 1 Paul Polycarp Peter Marcion John 200 Edict of Toleration Four Church Councils 300 Athanasius Arius Constantine 400 Fall of Rome 500 Emperor from 361-363 • Nephew to Constantine the Great • Renounced Christianity and sought to restore paganism • Tried to rebuild Jewish temple in Jerusalem • Sought to invade Persia Emperor from 379-395 • Ended state support for paganism • Put an end to the Olympic Games • Excommunicated by Ambrose after riot in Thessalonica Emperor from 379-395 Eugenius 394 What was the rationale for the formation of the monastic movement? St. Anthony 251-356 • Christian in Egypt • Heard a sermon on Christ’s words to the rich young ruler: “Go and sell all your possessions and follow me.” • Gave away his possessions and moved into the desert, living the life of a hermit Simeon Stylites 390-459 Removed himself to the top of a pillar in Syria What are some of the Biblical pros and cons of a solitary monastic lifestyle? Pachomius 292-348 • Born in Thebes • Forcibly inducted into military • Converted to Christianity • Followed example of Anthony • Organized nine groups of both male and female monasteries Monasticism in Monasticism in the West the East Communal living, but usually within some proximity to civilization Desert living; sometimes in community and sometimes alone Emphasis on reaching out to culture Emphasis on escaping culture Benedict of Nursia 480-542 • Ran away to live in a cave at the age of 14. • Established a monastery at Monte Cassino • Rule of St. Benedict Rule of St. Benedict Idleness is the enemy of the soul. And therefore, at fixed times, the brothers ought to be occupied in manual labor; and again, at fixed times, in sacred reading (Documents of the Christian Church, P.133). Rule of St. Benedict The brothers shall wait on each other in turn so that no one shall be excused from the kitchen-work, unless he be prevented by sickness, or by preoccupation with some matter of great necessity… (Documents of the Christian Church, P.132). Rule of St. Benedict Let not the younger brothers have beds by themselves, but dispersed among the seniors. And when they rise for the service of God let them gently encourage one another, because the sleepy ones are apt to make excuses (Documents of the Christian Church, P.129). What are some of the Biblical pros and cons of a communal monastic lifestyle? What sort of lifestyle changes were necessary for one to become a monk? How did the monastic movement contribute to the Church and society? Church persecuted by Rome 100 1 Paul Polycarp Peter Marcion John 200 Origen Edict of Toleration Four Church Councils 300 400 Athanasius Arius Augustine Constantine Pelagius Fall of Rome 500 Church persecuted by Rome 100 1 Paul Polycarp Peter Marcion John 200 Origen Edict of Toleration Fall of Rome Theodosius 300 400 Athanasius Arius Augustine Constantine Pelagius 500 How much diversity in matters of Christian doctrine should the church tolerate? Acts 20:28 Be on guard for yourselves and for all the flock, among which the Holy Spirit has made you overseers, to shepherd the church of God which He purchased with His own blood. Acts 20:29-31 I know that after my departure savage wolves will come in among you, not sparing the flock; 30 and from among your own selves men will arise, speaking perverse things, to draw away the disciples after them. 31 Therefore be on the alert… Rome Constantinople Antioch Jerusalem Alexandria Ambrose of Milan 339 - 397 • Governor of Milan • Civil strife over Arian controversy upon death of Bishop of Milan • Ambrose called for peace and was nominated as bishop though unbaptized • Gave away his property and studied for ministry Ambrose of Milan 339 - 397 • Withstood the Arians • Justina, the regent for her son, demanded that the church adopt Arianism. Ambrose refused. • Brought congregational singing into the church • Excommunicated Theodosius in 390 Jerome 347-420 • Traveled to Syria and learned Hebrew, later traveled through Palestine and Egypt • Settled in Palestine where he devoted himself to writing • Translated the Bible into Latin (Vulgate) John Chrysostom 347-407 • His nickname was Chrysostom (“golden-tongue”) • Trained in law before studying for ministry • He was a preacher at Antioch • Appointed to be bishop of Constantinople • Known for preaching exegetically from the Bible School of Alexandria Sought the “deeper meaning” by use of allegorical interpretation ClementAlexandria of Alexandria, Origen School of Antioch Antioch Emphasized the plain sense of the meaning of the Bible in interpretation Chrysostom, Theodore of Mopsuestia John Chrysostom 347-407 • The Empress Eudoxia had him exiled because she was displeased with his preaching on Elijah and Jezebel. • He was banished to Pontus. Augustine 354-430 • Mother was Monica, a Christian • Teacher of rhetoric in Milan • Admired Ambrose for his speaking ability • “Take up and read” Augustine 354-430 Let us behave properly as in the day, not in carousing and drunkenness, not in sexual promiscuity and sensuality, not in strife and jealousy… Augustine 354-430 But put on the Lord Jesus Christ, and make no provision for the flesh in regard to its lusts. (Romans 13:13-14) Augustine 354-430 • Bishop of Hippo, North Africa • Confessions: Tells story of his coming to Christianity • Rome sacked by Visigoths (410) • City of God The City of God • The Kingdom of God is not to be found in today’s political arena • The Christian’s true citizenship is in the city of God Accordingly, two cities have been formed by two loves: the earthly by the love of self, even to the contempt of God; the heavenly by the love of God, even to the contempt of self. The former, in a word, glories in itself, the latter in the Lord. (City of God 16:28) The earthly city, which does not live by faith, seeks an earthly peace, and the end it proposes, in the well-ordered concord of civic obedience and rule, is the combination of men's wills to attain the things which are helpful to this life. The heavenly city, or rather the part of it which sojourns on earth and lives by faith, makes use of this peace only because it must, until this mortal condition which necessitates it shall pass away. (City of God 19:17) Augustine versus Pelagius Man is born in sin and spiritually dead Man is essentially good Man’s will was affected by the fall so that, apart from the Spirit, he does not choose God Man’s will is neutral; he has the free will to either follow God or reject God Salvation is a gift of God to undeserving men Salvation comes as men imitate Christ Predestination Free Will