* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
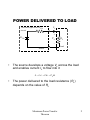
MAXIMUM POWER TRANSFER THEOREM • • • • • In many electrical and electronic applications, we are interested in the amount of power received by a particular load (speaker, electric motor, antenna) Electric systems are a source of power and a load connected to that source Sources – Amplifiers, generators, power supplies All linearly constructed sources can be reduced to their Thevenin equivalent In DC circuits, the load can be represented by a resistance RL Maximum Power Transfer Theorem 1 POWER DELIVERED TO LOAD T hevenin equivalent circuit RTH IL + ETH VL RL Load Source • The source develops a voltage VL across the load and enables current IL to flow into it PL VL I L I L2 RL VL2 RL • The power delivered to the load resistance (RL) depends on the value of RL Maximum Power Transfer Theorem 2 MAXIMUM POWER, CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CONDITIONS • • • • • • • • Maximum current IL occurs when RL = 0 (shorted terminals) The maximum voltage VL occurs when RL = (open circuited terminals) Yet load power PL = 0 for both cases PL is maximum when RL equals the Thevenin equivalent resistance of the source, I.e. when RL = RTH The maximum power transfer theorem is thus: Maximum power is developed in a load when the load resistance equals the Thevenin resistance of the source to which it is connected Maximum power is delivered when VL = ETH/2 Thus 2 VL2 ETH PL (max) RL 4 RTH Maximum Power Transfer Theorem 3