* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Taiga Biome
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
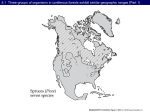
Taiga Biome Background The taiga is the biome of the needle leaf forest. The taiga is cold and lonely for the people who choose to live there. The low temperatures make it very hard to find food. Most animals in the taiga hibernate in the winter, while some fly south. Climate The winters in a taiga are very cold, and only consist of snowfall, while the summers are nice and warm with a lot rain and very humid. The average temperature is below freezing for 6 out of the 12 months of the year. winter temperatures range from –54 to –1 degrees Celsius. Summer temperatures range from –7 to 21 degrees Celsius. The summers good weather only lasts about 50 to 100 days until the frost and cold weather returns. Climate continued The total precipitation in a year is 30- 85 cm. Most precipitation falls in the summer. The seasons of spring and autumn are so short you hardly knew they happened. Species Most organisms can not live in a taiga due to its harsh conditions. There are some mosses and lichens, but most are coniferous like Douglas fir, hemlock, and white spruce. Most abundant is the Evergreen Growth Form Adaptations The reason that the plants of the taiga can live there is their growth from adaptations. Conical shape- allows snow to slide off trees and prevents the breaking of branches. Needle leaves- small needle like leaves that help keep the plant hydrated while also preventing snow build-up. Evergreen habit- instead of waiting in the spring for the plant to grow, these plants can go straight into preforming photosynthesis. Dark color- allows maximum sunlight to be absorbed into the plant. Species continued. Carnivores consist of lynx wolverines bobcats minks and ermines. Herbivores consist of snowshoe rabbits, red squirrels, and voles. Red deer, elk, and moose are found where deciduous trees are. Distribution Most boreal forests are found in the northern hemisphere. More facts Besides the tundra this is the coldest biome on the earth Covers most inland of Alaska, Canada, Sweden, Finland, Norway, Siberia, northern Minnesota, upstate new York, new Hampshire, and Maine. It’s a major source of lumber. Helps moderate weather extremes and its impacts. Websites! http://www.thewildclassroom.com/biome s/taiga.html http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/taiga. htm