* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Star Life Cycles Stellar Nebula
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
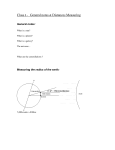
Star Life Cycles Stellar Nebula Stars begin life as cloud of gas + dust Cloud condenses and becomes more massive Nuclear fission begins (the power source of stars) Proto-star (Embryonic star) Stellar Nebula continues to collapse under its own weight and star grows more massive Main Sequence Star In this stage, the outward pressure of fusion (energy) and inward pressure of gravity are balanced Star spends more than 90% of its life Our sun is in this stage Variable Star Star undergoes variations in luminosity (brightness) because the forces are becoming unbalanced Supernova Star runs out of fuel, and force of gravity starts to condense remaining material Incredible inward force restarts nuclear fusion, causing an incredible explosion Supernova Remnant After explosion, an ever-expanding shock wave spreads out. Cloud of debris and other stellar material is seen expanding from explosion Black Hole… After explosion, star material can become so dense that all material, even light, can collapse into an infinitely small space …or, a Neutron Star If not as much mass remains, the leftover material can recondense and become a star again Much smaller and less bright than parent star The Cycle