* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9._the_confederation_and_the_constitution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
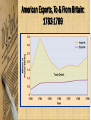
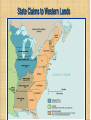
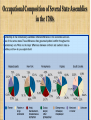
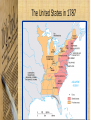
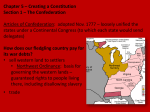
The Confederation and the Constitution 1776-1790 By: Mr. Michael R. Kahoe Del Valle High School Impact of American Revolution • Many people in Europe saw the American Revolution as a turning point in history – Americans had enforced the Social Contract – Ended foreign rule and oppression – Established the first democracy since ancient times • America served as a model for a better world The Pursuit of Equality • Equality was all the rage after the Declaration of Independence – Voting restrictions reduced – Indentured servitude ends – Primogeniture dropped The Pursuit of Equality • Separation of church & state – Anglican church fell in prominence – Congregational church still legally established in New England – Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom The Pursuit of Equality • Slavery was challenged – Vote to end slave trade – Abolitionist societies emerge in Philadelphia & some N.E. states abolish slavery outright – Blacks were still discriminated against • (property, jobs, education, marriage) • But, why was slavery allowed to continue? The Pursuit of Equality • Women were still unequal – Yet women, as the caregivers, were seen as purveyors of the “civic virtue” – Expected to teach children republican ideals – Led to expanded educational opportunities Constitution Making • In 1776, colonies drafted individual state constitutions – Defined powers of government – Authority from the people – Represented the fundamental law • Most included: – Bill of Rights – Require an annual election of legislatures • Had the most power – Created weak executive & judicial branches Economic Crosscurrents • States gained control of former crown & loyalist landholdings • Commerce with Britain drastically reduced – Americans forced to manufacture products on their own – New trade sought out (ex. China) American Exports, To & From Britain: 1783-1789 Economic Crosscurrents • U.S. economy was in the gutter – Profiteers had gotten rich – Rich had become poor – Runaway inflation – Many unpaid war debts – Distaste for taxes • British navigation laws now working against America A Shaky Start Toward Union • U.S. was a union only in name – Suspicion of authority of government • British manufacturers began selling goods at cut-rate prices – Hurt burgeoning American industries • People encouraged to buy products made in the USA A Shaky Start Toward Union • There was still hope for the Union – All 13 states had similar governments – Each had a shared history • Political inheritance from Britain • History of self-rule – Great political leaders • • • • • Washington Jefferson John Adams James Madison Alexander Hamilton Creating a Confederation • Second Continental Congress had no real authority during war – All 13 states were essentially sovereign • Articles of Confederation written in 1777 (ratified in 1781) – Chief argument was over western lands • Some had claims out West & some didn’t • Argued that states with land could pay war debts – Maryland held out until 1781 • NY & Virginia to surrender land claims • Congress promises to create new states from these areas State Claims to Western Lands Articles of Confederation • Provided for a “firm league of friendship” – Linked together to deal with common problems – Run by congress (no executive) • Congress: – Each state had 1 vote – Laws need 9 states – 13 votes to change the Articles Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation • • • • • • No central taxing authority Each state issued its own currency Could not command or control states No central army – only state militias No national control of commerce (trade, tariffs) No sense of national identity Strengths of the Articles of Confederation • Held states together until the new constitution • Could make treaties • Created a postal service Occupational Composition of Several State Assemblies in the 1780s Landmarks in Landlaws • Congress passed farsighted pieces of legislation regarding Old Northwest – Land Ordinance of 1785 – land in Old Northwest to be sold to pay off war debts • Surveyed, divvyed up & sold to townships (public schools) • Very orderly Land Ordinance of 1785 Landmarks in Land Laws – Northwest Ordinance of 1787 • Land would be a territory subordinate to U.S. government • With 60,000 inhabitants, statehood could be sought • Solved problem of having colonies The World’s Ugly Duckling • America had troubled foreign relations after the War • England: – Refused to send a minister to “backwoods” capital of Philadelphia – Refused to make a commercial treaty or repeal Navigation Laws • Lord Sheffield said England would eventually win back all American trade – Closed profitable West Indies • Colonists resort to smuggling The World’s Ugly Duckling • Spain: – Controlled the Mississippi River & New Orleans – Schemed with neighboring Indians • France: – Demanded repayment of money loaned – Restricted trade with West Indies • Pirates in Mediterranean were attacking American ships Disputed Territories Between Spain & the U.S. The United States in 1787 The Horrid Specter of Anarchy • Raising money difficult for congress – States refused to pay – Public debt increasing – Foreign credit drying up – “Rag Money” – depreciating paper money • Quarrels over state boundaries • States taxed each other’s goods Shays’ Rebellion • 1786 – Mass. Farmers upset over losing farms • Captain Daniel Shays – revolutionary vet leads rebellion – Felt he was fighting tyranny – Demanded: • State issued paper money • Lower taxes • Stop property seizures Shays’ Rebellion • Small army is raised to squash rebellion – 3 Shaysites killed & 1 wounded – Shays sentenced to death (later pardoned) – Rebellion crushed Shays’ Rebellion • Result of Shays’ Rebellion: – Debtor relief laws passed – Fear of too much liberty – Talk of stronger central government • A King maybe? • “Cement to the Union” • “A hoop to the barrel” “The tree of liberty must be refreshed from time to time with the blood of patriots and tyrants.” – Thomas Jefferson A Convention of “Demigods” • Squabbling over interstate commerce led to changes to the Articles • 1786 – Annapolis Convention – Only 5 delegates show • Alexander Hamilton (NY) calls for a future meeting in Philadelphia • 1787 – Constitutional Convention – 55 delegates meet • Washington was chair • Franklin elder statesman at 81 • James Madison – “Father of the Constitution” • Alexander Hamilton – Advocate for strong central government Patriots in Philadelphia • Goals of Convention: – Preserve the Union – Curb unrestrained democracy • Shays Rebellion – Wanted a strong central government Hammering Out a Bundle of Compromises • Delegates decide to scrap the Articles all together • Legislative Branch (makes laws) – Virginia’s “large state plan” • Representation in two houses based on state’s population – New Jersey’s “small state plan” • One house congress • Each state with one vote Hammering Out a Bundle of Compromises – “The Great Compromise” • Legislative Branch – House of Representatives – based on state population – All tax bills originate in the house – Senate – 2 senate seats per state • Executive Branch (carries out laws) – Makes appointments • Ex. Supreme Court justices – Commander in Chief – Veto power – Can’t declare war Hammering Out a Bundle of Compromises • Slaves – Are they counted as citizens? – 3/5 compromise – African slave trade shut down by 1807 • Georgia last to stop Safeguards for Conservatism • • • • • • Created sound money Protection of private property Checks & balances Limited government Republic – “we the people” Indirect Election: – President – electoral college – Senators – by state legislatures – Supreme Court – appointed – House – by voters Federalists vs. Antifederalists • Federalists supported the Constitution & strong government • Antifederalists – opposed a strong central government – – – – – – No bill of rights No annual election for House Federal Stronghold (D.C.) Standing Army No mention of God Ratified by only 2/3 vote • Constitution adopted by 9 states in 1788 – All but Virginia, NY, NC, & RI Patrick Henry The Four Laggard States • Virginia - ratified it 89 to 79 • New York – Federalist Papers, written by John Jay, James Madison, and Alexander Hamilton • North Carolina & Rhode Island later ratified A Conservative Triumph • The minority had triumphed – – • 1/4 of the adult white males in the country had voted for the delegates Conservationism was victorious Federalists believed every branch of government represented the people