* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War 1945-1989
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cuban Missile Crisis wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Mutual assured destruction wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
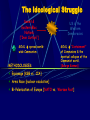
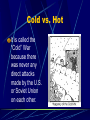
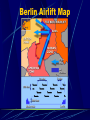
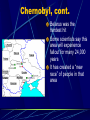
The Cold War 1945-1989 What is the Cold War It was an intense rivalry between the United States and Russia – between West and East and between capitalism and communism that dominated the years following WW II. The Ideological Struggle Soviet & Eastern Bloc Nations [“Iron Curtain”] GOAL spread worldwide Communism METHODOLOGIES: US & the Western Democracies GOAL “Containment” of Communism & the eventual collapse of the Communist world. [George Kennan] Espionage [KGB vs. CIA] Arms Race [nuclear escalation] Bi-Polarization of Europe [NATO vs. Warsaw Pact] Words of Wisdom Winston Churchill; “Germany is finished. The real problem is Russia. I can’t get Americans to see it.” -- 1945 Cold vs. Hot It is called the “Cold” War because there was never any direct attacks made by the U.S. or Soviet Union on each other. The United Nations The Big Three all agreed on establishing this international peace keeping organization. Goal: to promote justice and cooperation First official meeting held in London in 1946 Permanent headquarters established in New York in 1953. FDR dies; Truman Takes Command Roosevelt never saw his dream of the UN come to life FDR died on April 12, 1945 Truman, his Vice President for only a few months, became the leader of our country Conflicting Postwar Goals Americans: wanted democracy and economic opportunities for the countries of Europe and Asia Soviets: Wanted to rebuild their nation in order to protect their own interests. They wanted to establish satellite nations, countries controlled by the Soviets along the western boundaries of the Soviet Union. Following Communist doctrine, Stalin wanted to overthrow capitalism around the world and install Communist governments. Satellite Nations Like dominoes, one by one countries in Eastern Europe fell to Stalin and communism Poland, Romania, Bulgaria, East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Albania. The Iron Curtain A phrase coined by Winston Churchill in 1946 it refers to the division between Communist and non-Communist nations Became symbol of division between East and West The “Iron Curtain” From Stettin in the Balkans, to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lies the ancient capitals of Central and Eastern Europe. -- Sir Winston Churchill, 1946 Containment This became the dominant U.S. policy during the Cold War Developed by George Kennan, it stated that the U.S. could not do anything in Eastern Europe where Russia already took over, but that it should attempt to stop the formation of Communist governments any where else in the world. The Truman Doctrine “I believe that it must be the policy of the U.S. to support free peoples who are resisting (conquest) by armed minorities or by outside pressures.” – President Truman, 1947 We will support any nation threatened by Communism. Marshall Plan [1948] 1. “European Recovery Program.” 2. Secretary of State, George Marshall 3. The U. S. should provide aid to all European nations that need it. This move is not against any country or doctrine, but against hunger, poverty, desperation, and chaos. 4. $12.5 billion of US aid to Western Europe extended to Eastern Europe & USSR, [but this was rejected]. Germany: A Land Divided By 1949 there were two Germany’s in Europe: 1. West Germany: democratic 2. East Germany: communist The capital of Berlin was also divided – by a wall! Post-War Germany Berlin Airlift Many Eastern Europeans who did not like living under Soviet communist rule fled their homes and escaped to West Berlin. Stalin wanted to stop this escape route by forcing the Western Powers to abandon West Berlin. Stalin blockaded all Allied shipments to West Berlin through East Germany. This threatened severe shortages of food and other needed supplies in West Berlin. Truman did not a war with the Soviets, nor did he want to give up West Berlin. During the next 15 months both British and U.S. aircraft delivered food, fuel, etc. by plane to the city. The Soviets finally gave up in 1949 and ended the blockade. Berlin Airlift Map Berlin Blockade & Airlift (1948-49) NATO- North Atlantic Treaty Organization Because the Soviet Union used its veto power to block any action that stopped communism in the United Nations, the West needed another way to deal with Soviet aggression. In 1949 12 nations formed NATO. The guiding principle of NATO is; “an armed attack against one or more…shall be considered an attack against them all.” This is an example of collective securitymutual military assistance among nations. North Atlantic Treaty Organization (1949) United States Luxemburg Belgium Netherlands Britain Norway Canada Portugal Denmark 1952: Greece & Turkey France Iceland Italy 1955: West Germany 1983: Spain China Falls To Communism A civil war had existed between the Nationalists and Communists in China since the 1920s. In 1949, under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the Communists won and established the People’s Republic of China. The Nationalists fled to Taiwan and claimed to be the legitimate government of China, establishing the Republic of China. The U.S. and UN recognized this Republic as the true government of China. Many Americans wanted Truman and the government to focus not only on Europe but also on Asia in their policy of containment. Mao’s Revolution: 1949 Who lost China? Chairman Mao Zedong Chinese Revolution Poster: 1949 The Arms Race The greatest area where the Soviet Union and the U.S. competed for world domination was in the arms race - the struggle to gain weapons superiority. The Arms Race: A “Missile Gap?” } The Soviet Union exploded its first A-bomb in 1949. } Now there were two nuclear superpowers! Modern Day Arms Race: Pakistan and India Korean War After WW II Japan was forced to give up control of Korea. The Soviets accepted the surrender above the 38th parallel and the U.S. accepted it below that line. Division was never the goal but became a reality: a communist controlled north and a democratically controlled south. The Korean War: A “Police Action” (1950-1953) Kim Il-Sung Syngman Rhee “Domino Theory” Conflict in Korea Citizens on both sides of the parallel wanted to reunite their country. War breaks out when North Korean troops came across the 38th parallel to try to unite the country by force. The Forgotten War The UN (mostly American) sent troops to Korea The UN troops do well initially but are driven back close to the original 38th parallel. The war becomes a stalemate and in 1953 an armistice is signed agreeing to keep Korea divided. Map of Korea Warsaw Pact Eastern Europe’s response to NATO Formed in 1955, its function was collective self-defense against external aggression (attack on one is attack on all) All Eastern/Communist nations join initially, except Yugoslavia Ended in 1991 with fall of communism Warsaw Pact (1955) } U. S. S. R. } East Germany } Albania } Hungary } Bulgaria } Poland } Czechoslovakia } Rumania Yugoslavia the Rebel Leader Josip Tito (part Croat and part Slovene) was unique in the East since he broke away from Stalin and kept Yugoslavia independent of U.S.S.R. interference. Although communist, Yugoslavia ( provinces of Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Slovenia), received special privileges from the West Citizens were far more free than in the Sovietbloc countries Success of Yugoslavia was based in illusion (western loans) Yugoslavia, cont. When Tito finally died in 1980, a void was left He had spent his time emphasizing unity over ethnic differences Nationalist feelings arose when sense of unity died with Tito The evil Slobodan Milosevic took power – wanting to create Serbian dominance Cold War and Space In 1957 the Soviet Union proved that they were ahead of the U.S. in the technology war when they launched Sputnik into space. Sputnik was the first artificial satellite to orbit the earth. Problem: The rocket used to launch Sputnik could just as easily carry a nuclear bomb to America’s shores! In response the U.S. created NASA in 1958 and increased spending on science and math in America’s school. Sputnik Sputnik I (1957) The Russians have beaten America in space—they have the technological edge! Paris, 1961 Khrushchev & JFK meet to discuss Berlin and nuclear proliferation. Khrushchev thinks that JFK is young, inexperienced, and can be rolled. The Berlin Wall Goes Up (1961) Checkpoint Charlie Ich bin ein Berliner! (1963) President Kennedy tells Berliners that the West is with them! Cold War and Cuba In October of 1962 U.S. spy photography revealed that the Soviet Union was building missile bases on Cuba. What followed, the Cuban Missile Crisis, is the closest the world ever came to nuclear war. Khruschev Embraces Castro, 1961 Bay of Pigs Debacle (1961) Cuban Missile Crisis The Soviets placed these missiles in Cuba, 90 miles from the U.S., to counter the missiles the U.S. had in Turkey – very close to the U.S.S.R. These missiles in Turkey were old and probably wouldn’t work – but the U.S.S.R., under Nikita Khruschev, did not care about that detail. Kennedy Decides After much deliberation, president Kennedy decided to use a U.S. naval quarantine of Cuba to prevent any Soviet ships carrying weapons into Cuba Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) We went eyeball-to-eyeball with the Russians, and the other man blinked! Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) Disaster Avoided After some secret negotiations, in the final hour, the U.S. agreed to remove its missiles from Turkey while Russia would remove their missiles from Cuba. It appeared that if Russia either broke the quarantine or refused to remove their missiles, Kennedy would have used nuclear weapons on Cuba and maybe the Soviet Union directly!!! Chernobyl Nuclear chemistry not only used in weapons, but also as a power source April 26, 1986 – Ukraine – worst nuclear accident in history Disaster released 300 times more fallout than the bomb dropped on Hiroshima Contamination numbers uncertain, but parts of Russia, Ukraine and Belarus are still experiencing health problems Chernobyl, cont. Belarus was the hardest hit Some scientists say this area will experience fallout for many 24,000 years It has created a “new race” of people in that area Communism Falls Root: 1980 Poland/ Solidarity movement, a democratic-based political and economic party, challenges communist leadership 1985: Mikhail Gorbachev abandons old Soviet policy of using military force to keep communist rulers in power and rather encourages individual nations to adopt reforms, not threats, to keep people loyal to communism These reforms often allowed free elections – all across Europe the vote was anti-communist Poland – 1989- first country to install a noncommunist regime – Solidarity (Lech Walesa leader) Revolutions erupted in the East in 1989 – by 1991, communism collapsed and the Cold War ended Conclusion The Cold War was a tense time and a time of great uncertainty and fear No one knew if the Soviets or the U.S. would use one of their many weapons of mass destruction -- they came close but never did! The Cold War ended when the U.S.S.R. collapsed and communism failed to make the people happy or meet their basic needs.