* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download foundations of america
Province of Maryland wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American military history wikipedia , lookup
Colonial American bastardy laws wikipedia , lookup
Massachusetts Bay Colony wikipedia , lookup
Indentured servitude in the Americas wikipedia , lookup
Dominion of New England wikipedia , lookup
Province of New York wikipedia , lookup
Province of Massachusetts Bay wikipedia , lookup
Indentured servitude in Pennsylvania wikipedia , lookup
Shipbuilding in the American colonies wikipedia , lookup
Slavery in the colonial United States wikipedia , lookup
Stamp Act Congress wikipedia , lookup
English overseas possessions in the Wars of the Three Kingdoms wikipedia , lookup
Cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies wikipedia , lookup
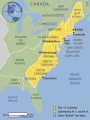
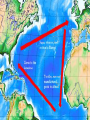
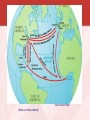
FOUNDATIONS OF AMERICA • Looking to escape the control of the Church of England, British and European immigrants came to the shores of North America in search of new lives and religious freedom. • The number one reason people came to the new world was religious freedom • The Puritans and Quakers are examples of religious dissenters that founded colonies in North America ECONOMIC GROWTH • The colonies operated under an economic system called MERCANTILISM: making $ for the mother country. • It was an early modern European economic philosophy that supported the idea of creating colonies for getting $ for their natural resources. Mercantilism • “making money for the mother country” • On your exams it will say “an economic philosophy that supported one country from another's resources.” • It is saying the same thing, England made money off of selling the colonies resources REGIONAL DIVISIONS IN THE COLONIES Colonies divided into: • Northern-Also called the New England Colonies • MA, NH, CT, R.I. • Middle-Also called the Bread Basket Colonies • NY, NJ, DE, PA • Southern Regions • NC, GA, VA, MD NEW ENGLAND (NORTHERN) COLONIES CHARACTERISTICS • Poor rocky soil • Religious freedom • Subsistence farming (a plot of land produces only enough food to feed the family working it) Think “Self Farming” • Accessible ports and Harbors • First colonies to develop Cities. • Why would these colonies develop cities first? New England Colonies - background : MIDDLE COLONIES Characteristics of Middle Colonies: Dense forests lumber trading of excess food. Subsistence Farming Harsh Winters Nickname: “Bread basket” SOUTHERN COLONIES: Characteristics of Southern Colonies: Rich fertile soil Plantation System evolution of Slavery Cash Crops Good Weather Questions to think about and answer… • 1.) Describe what you see? • 2.) What is being represented in this picture? What emotion does the picture portray? • 3.) What Geographical area is being represented? How do you know? Big Idea • If you had to choose one word that would explain the reason why the colonies developed differently what would it be? • *******GEOGRAPHY******* JAMESTOWN, VIRGINIA • Founded in 1607, the first successful permanent English colony in America. Founded by religious dissenters: people who did not agree with the Church of England. *What were the two Groups of religious dissenters called? *After settlers arrived the Indian population went from close to 10 million down to 1 million due to diseases brought from European settlers A Weroan or great Lorde of Virginia “The Princes of Virginia are attired in suche a manner as is expressed in this figure. . . .” Engraving by Theodore de Bry in Thomas Hariot, A Briefe and True Report of the New Found Land of Virginia (1590). • The Quakers settled in Pennsylvania in 1682 under their leader, William Penn. It was considered a safe place for the religious group to live and practice their faith. "It would be far better to be of no church than to be bitter of any." William Penn Separatists: - those that wanted to break away completely. (Another Religious Group) American Colony • Meet the Hutterites — a small religious colony in rural Montana who holds desperately to their sacred traditions while fighting the modern temptations of the outside world. King Colony is made up of 59 people, and they are almost all related. This family lives together, works together, and worships God together — 7 days a week, 365 days a year, for their entire lives. And, like any family, this one doesn't always agree. – National Geographic • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BT0ZlopRVhk • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=royX9X_fGQk&playnext=1&list=PL8ACDA953B5E452F 2&feature=results_video A Healthy Supper • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I9nvamq3IEg&playnext=1&list=PLD15100274D6B675 E&feature=results_video Growing up in the Colony Wesley Gives a Tour In the early years of the colonies, the labor supply came from Indentured Servants. They agreed to work for a landowner for a period of 4 to 7 years in return for passage to America, food and housing. By the late 1600’s the system of Slavery increased to meet the demand for labor in the American Colonies. INDENTURED SERVITUDE Running Away Servants may not, under any circumstances, run away from their masters. Punished by whipping, and at the Governor's discretion, may have had the term of indenture extended to compensate for lost time and any damages incurred by masters. Threats to Masters Servants may not threaten their masters or steal from their masters, or resist the authority of their masters. Punished by whipping. Abuse of Servants Masters may not abuse, make hard usage or show cruelty in correcting their servants. Punished by levying a fine and public reprimand. • The slave trade worked by the Triangular Trade Route between Europe, West Africa and North American colonies. • The route began at the tip of the triangle in Europe, the second and longest part of the triangle was known as the Middle Passage. Trade Route Map What are they trading? MIDDLE PASSAGE • The Middle Passage refers to the forced transportation of West Africans to North America as part of the Atlantic Slave Trade. *Between 1450 and 1850 more than 12 million Africans were exported from Africa on slave ships (est.) Quote from Olaudah Equiano about the Middle Passage • “I now saw myself deprived of all chance of returning to my native country or even the least glimpse of hope of gaining the shore, which I now considered as friendly; and I even wished for my former slavery in preference to my present situation, which was filled with horrors of every kind…There I received such a salutation in my nostrils as I had never experienced in my life: so that, with the loathsomeness of the stench and the crying together, I became so sick and low that I was not able to eat, nor has I the least desire to taste anything. I now wished for the last friend, Death, to relieve me.” “DREAD AND TREMBLING” CHPT. 8 Olaudah Equiano offers a first- hand account of his arrival in the West Indies in 1756. We were conducted immediately to the merchant's yard, where we were all pent up together, like so many sheep in a fold, without regard to sex or age. As every object was new to me, everything I saw filled me with surprise. What struck me first was that the houses were built with bricks and stories, and in every respect different from those I had seen in Africa, but I was still more astonished to see people on horseback. I did not know what this could mean, and indeed I thought these people were full of nothing but magical arts. While I was in this astonishment, one of my fellow prisoners spoke to a countryman of his about the horses who said they were the same kind they had in their country. I understood them, though they were from a distant part of Africa and I thought it odd I had not seen any horses there; but afterwards when I came to converse with different Africans, I found they had many horses amongst them, and much larger than those I then saw. Source: The Interesting Narrative of the Life of Olaudah Equiano or Gustavus Vassa the African (London, 1789). COLONIAL DIVISONS • ROYAL COLONIES: Controlled by the Crown (king/queen) NH, MA, NY, NJ, VA, NC, SC, GA • PROPRIETARY COLONIES: Colony for which the king gave land to one or a few people to oversee. MD, PA, DE • JOINT-STOCK COLONIES: Investors paid for shares of the eventual profit. (Most colonies began as Joint Stock) • SELF GOVERNING (Charter Colony): Colony that exercised political authority over itself. CT, RI Practice Question Which term BEST describes the practice of creating and maintaining wealth by carefully controlling trade? A. Economic Profit B. Smuggling C. Triangular Trade D. Mercantilism ASSIGNMENT • Writing Prompt: • Please write a paragraph about the development of the colonies and the significance of geography on the development. Also include how mercantilism and religious freedom impacted colonization. State the significance of Indentured servitude and labor to the colonies. Do you think the colonies would have survived without them? Why? • Please write legibly. There are several detailed questions in the prompt, all must be addressed. There is no limit to how long it has to be, however it has to make sense and answer all questions. No Bullet point answers!!!! Post Card Note Card • Since people corresponded through letter during this time period, pick a colonial region from the lesson that you want to explain back to relatives in Europe. What would you say to encourage someone to visit and STAY in Colonial America? • *you must Include an illustration and details about your region. • Las Vegas Postcard – Looks so exciting and fun, makes one want to visit! Newspaper Article – November 1764 • Please look on the Wiki site to read the article and answer the questions completely.