* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download light_presentationsimple
Gravitational lens wikipedia , lookup
Architectural lighting design wikipedia , lookup
Light pollution wikipedia , lookup
Daylighting wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
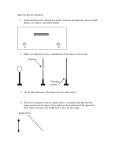
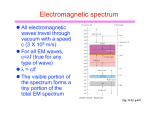
LIGHT!!!! Properties of Light •Light travels in straight lines: Laser •Light travels VERY FAST – around 300,000 kilometres per second. At this speed it can go around the world 8 times in one second. •We see things because they reflect light into our eyes: Homework Nature of Light • Particle? • Wave? • Both!!!!!! • Photon Wavelength Electromagnetic Spectrum Increasing Wavelength Visible Light The Visible Spectrum 400nm 500nm 600nm 700nm Wavelength means COLOR WAVE PROPERTIES 1. Reflection 2. Refraction 3. Diffraction 4. Interference Part 1 - Reflection • Reflection from a mirror: Normal Reflected ray Incident ray Angle of incidence Angle of reflection Mirror •The Law of Reflection Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection The same !!! 2. REFRACTION -Bending of light as it travels from one medium into another due to a change in velocity 3. DIFFRACTION – Bending of wave through openings 4. Wave Interference Basically - Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation (like radio waves, infrared, xrays) It travels like a wave (no medium required) It is the fastest thing we know It is made up of photons (which also transmit electromagnetic forces) The photon is considered massless (yet it has momentum) Photons are created when energy is released, energy is absorbed when photons are absorbed Calculations – Speed of light in a vacuum (C) •d (distance) = C x t (seconds) •d = 300,000 km/s x t •Or = 300,000,000 m/s x t •How far will light travel in 1 minute? •d = 300,000 km/s x 1 min x 60 s/min •d = 18,000,000 km Practice Questions 1. 2. 3. 4. How far will light travel in 1 year? If the earth is 150,000,000 km away how long will it take the light to reach us from the sun? If it take 2 hours for a radio signal to travel to a far away planet, how far is the planet? Andromeda is 2.6 million light years away, how far is that? More on Refraction •The bending of light is due to the change in speed of light as it travels into a new medium. •The index of refraction is known as the fraction of speed of light in a vacuum over the speed of light in another medium • n=C/V •Ex. What is the index of refraction of glass if the speed of light is 210,000 km/s? • n = 300,000 km/s = 1.4 • 210,000 km/s Practice Questions 1. What is the speed of light in diamond if n= 2.4? 2. If the speed of light is 225,000,000 m/s what is the index of refraction? •3. If glass has an n value of 1.5, how long would it take the light to travel through a hypothetical 1 km, piece of glass? What happens…….. •When a laser is fired through a narrowing slit? Refraction • The change in direction of a wave as is crosses the boundary between two media in which the wave travels at different speeds. Snell’s Law n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 Index of Refraction Material Vacuum Air Ice Water Ethyl Alcohol Plexiglas Crown Glass Light Flint Glass Dense Flint Glass Zircon Diamond Rutile Gallium phosphide Index of Refraction 1.0000 1.0003 1.3100 1.3330 1.3600 1.5100 1.5200 1.5800 1.6600 1.9230 2.4170 2.9070 3.5000 Dispersion • The separation of light into colors arranged according to their frequency, by interaction with a prism or diffraction grating. Rainbows • White light separates into different colors (wavelengths) on entering the raindrop because red light is refracted by a lesser angle than blue light. On leaving the raindrop, the red rays have turned through a smaller angle than the blue rays, producing a rainbow. Sample Questions •1. What is the angle of refraction of light entering water from air at an angle of 45 degrees? n1 sin 1 n2 sin 2 Calculate the refracted angle for • 1. Light leaving water at 10 degrees into air. • 2. Light entering a diamond from air with an angle of 20 degrees. • 3. Light entering a diamond from water with an angle of 40 degrees. Total Internal Reflection • When traveling from more dense to less dense, there’s a critical angle whereby light doesn’t enter the second medium Sin (crit) = n refracted n incident •Determine the critical angle for diamond to water •Sin (crit) = 1.33 2.47 Inv Sin = 32.6 degrees Calculate the critical angle for •1. Diamond to Air •2. Water to Air •3. Zircon to plexi-glass