* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 国际贸易 International Trade
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
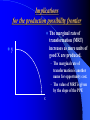
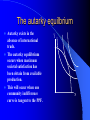
广东省省级精品课程 国 际 贸 易 第一章 广东外语外贸大学 导论 何元贵 教授 Chapter 1: §1. INTRODUCTION General Review 1、The History and Station of the Course International Trade Soviet Model in Early Times. International Economics in 90’s. One of Compulsory Course for Students Majored in Economics. 2、The Relation between International Trade and other Subjects 2.1 The Subject Origin of International Trade International Economics(International Trade and International Finance) Economics Philosophy 2.2 International Trade vs Philosophy & Science 2.3 The Relation between International Trade and other Courses in International Trade Subject Economics is the forward course , especially Microeconomics; It’s the forward course of WTO, Transnational Corperations , International Investment, and etc; It’s the parallel course with General Review of Chinese Foreign Trade. 3、Reference Material 1) Peter Lindert(彼得.林得特), International Economics,上海译文出版社,1985. 2) Dominick Salvatore, International Economics, Eighth Edition, John Wiley & Sons Inc., 2004. 3)Paul Krugman and Maurice Obstfeld, International Economics: Theory and Policy (Fifth Edition), Addison-Westley Publishing Company , 2000. 4) All kinds acdemic journals and newpapers, such as: International Trade, Journal of International Trade 、 World Economy、 International Business Daily、人大报刊复印资料。 5) Internet. Such as: 中华人民共和国商务部.htm 4、 Plan and Arrangement 1) 3 hours classes study every week; 2) 3 homeworks,one is course paper; 3) 1 seminar 4) 1 final test 5) 1 innovative teaching class 6) Course Evaluation The grading system for the course is based on the students’ academic performance. That includes : 30% homework & class performance +70% final exam. §2. The Emergence & Development of International Trade & the theory of International Trade 1、 The Emergence & Development of International Trade 1.1 Concept International trade is the exchange activity of goods and services across international borders or territories. Foreign trade is the exchange activity of goods and services between one country (district) with others. 1.2 The Prerequisite for Emergence of International Trade ( 1 ) There are surplus products for exchange; ( 2 ) Establishment of national states with their own sovereignty. 1.3 The History of International Trade 1) The early international trade occurred in ancient Roma and Greece. Definitely, it’s only “trade between districts”. 2) Only after industrial revolution, international trade and world market had definitely formed and got developed. 3) After the Second World War, international trade entered a new developing era, especially in the fields of service trade, Transnational Corperations , International Investment. Value of World Merchandise Trade Unit: US$ hundred million (亿美圆) Year 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 Export 554.00 1131.00 3145.81 19936.25 34250.43 61648.40 Import 580.00 1194.00 3289.21 20474.25 35565.09 63728.75 1.4 The History of Chinese Foeign Trade Early in Xihan,China started trade with Middle East and Europe through the famous “ Silk Road” 。 From the set of “ Silk Road ” to “the Opium War (1840-1842)” , the development of Chinese foreign trade were stganant。 Until mid 19’s , China had benn opened its foreign trade door by European and American artillery。 China casted off the control of western countries only after the New China founded in 1949. But then,for the reasons such as embargo from western countries which leaded by U.S., China had to carry on closed-door policy again. So,the export ratio of China in the world dropped from 1.9% in 1959 to 0.8% in 1969, then 0.74% in 1978! After 1978, Chinese foreign trade entered into a fast developing period.From 1978 to 2006,the value of Chinese merchandise trade increased from US$ 20640 million (206.4亿美圆) to US$ 1760690 million, the yearly average growth rate is over 15%,far more than that of other countries and the world average growth. China became the third country of trade in the world. Chinese service trade got developed in late 80’s. The value of service export increased from the only US$ 2700 million in 1982 to US$ 5748 million in 1990, then US$ 157081 million in 2005, and became the eighth service export country in the world. Questions(homework 1): (1) Balance of foreign trade of China in 2008 and 2009 ? (2) Balance of srevice trade of China in 2008 and 2009 ? (3) How about the Chinese in world trade? ratio and rank (4)Statistic trade datas of other main countries. 2、 The Produce & Development of the Theory of International Trade 国际贸易中充满的异国情调和浪漫 主义色彩,在历史上曾使许多国家的商 人、航海家、旅行家和小说家为之神往。 他们的口述笔扎在促进各族人民的经济 贸易交往中曾起过很大作用。错综复杂 的国际贸易问题也吸引了各个时代的经 济学家们的注意力。每一代的著名经济 学家都参加到国际贸易问题的讨论中。 经典作家和其他一些著名的经济学家曾 在这上面倾注过大量的心血。 (姚曾荫,国际贸易概论,第8页,人民出版社,1987) The Development Track of International Trade Theory Early 15’s—Mid 18’s, Mercantilism; Mid 18’s,Trade based on absolute advantage (Adam Smith);trade based on comparative advantage (David Ricardo ) ; After 20’s, H-O Model ; The Leontief Paradox by W. W. Leontief ; Specific factor model by Paul Samuelson ; Bhagwati Effect by Jagdish Bhagwati; Intra-industry Trade Model by Paul Krugman; Trade Model in Product Cycle by Raymond Vernon. 3、 Study Pattern International trade theory is divided to: Positive theory Normative theory Positive Analysis: Mainly shows the relations between economic variables, analyses the reasons and results of all kinds trade behavior and policys, but not give judgment and comment. Positive Analysis is a kind of technical analysis. Normative Analysis: is mainly the diagnosis and judgment or comment to the results of positive analysis .And the diagnosis and comment reflect different cognition and value view. Relation between Positive Analysis and Normative Analysis: Usually closely related, can not be cutted. Positive analysis supply the basis for normative analysis. A theory without positive analysis is always short of conviction 。On the other hands,if a theory only composed by positive analysis but no normative analysis, it ’ll lose its economic social significance. So, international trade theory should be the unite of positive analysis and normative analysis. Most statements are not easily categorized as purely positive or purely normative. 4、Usual Economic Analysis Tools (1) The autarky equilibrium analysis --- production possibility frontier (PPF), opportunity cost, indifference curve; (2) Part equilibrium analysis --- supply curve, demand curve. Implications for the production possibility frontier y The marginal rate of transformation (MRT) increases as more units of good X are produced. – The marginal rate of transformation is another name for opportunity cost. – The value of MRT is given by the slope of the PPF. X Community indifference curves A community indifference curve displays the combinations of two products that offer the community the same level of satisfaction. Characteristics of community indifference curves: – Negative slope – Convex to the origin – Different curves do not cross Community indifference curve Y III II I X The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) falls as more of good X is consumed. The MRS is the amount of one commodity that must be given up as one gains additional units The autarky equilbrium Autarky exists in the absence of international trade. The autarky equilibrium occurs when maximum societal satisfaction has been obtain from available production. This will occur when one community indifference curve is tangent to the PPF. Y X Review : C1. INTRODUCTION §1. General Review 概述 1、国际贸易课程的历史及其地位 2、国际贸易与其他学科之间的关系 3、国际贸易课程学习参考资料 4、本学期学习安排 §2. 国际贸易及其理论的产生和发展概述 1、国际贸易的产生和发展(世界和中国) 2、国际贸易理论的发展 3、国际贸易的研究方法 4、国际贸易研究常用的经济分析工具