* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 32 Intro to Animal Evolution
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Animal communication wikipedia , lookup
Animal cognition wikipedia , lookup
History of zoology since 1859 wikipedia , lookup
Body Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Animal coloration wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
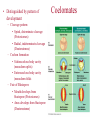
Introduction to Animal Evolution Ch. 32 AP Biology Ms. Haut What is an Animal? • Multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes • Animal cells lack cell walls • 2 tissues unique to animals: nervous and muscular • Most reproduce sexually, with diploid stage dominating life cycle Animal Development • Zygote undergoes cleavage to form blastula • During gastrulation embryonic tissues that develop into adult body parts form Phylogenetic Tree of Animals Parazoans • Includes Phylum Porifera (sponges) • Classified as parazoa because they lack true tissues Eumetazoans • Include nearly all other animal phyla • Organisms that contain true tissues • Radiata and bilateria are the major branches Radiata • Radial Symmetry • Organisms that are sessile (attached to substratum) or plankton (drifting) • Equips them to meet the environment equally from all sides – Cniderians (jellyfishes, corals, anenomes) – Ctenophora (comb jellies) Bilateria • Bilateral Symmetry • Cephalization seen—concentration of sensory equipment (central nervous system) • Equips them for mobile lifestyle • 2 branches: – Organisms without body cavities (Acoelomates) – Organisms with body cavities (Pseudocoelomates and Coelomates) Acoelomates • Phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms) • Triploblastic (3 germ layers) animals with solid bodies (no cavity between digestive tract and outer body walls Pseudocoelomates • Phylum Rotifera (rotifers) • Phylum Nematoda (roundworms) • Triploblastic (3 germ layers) animals • body cavity between digestive tract and outer body walls incompletely lined with mesoderm Coelomates • Body cavity completely lined by mesoderm • 2 evolutionary lines – Protostomes – Deuterostomes Protostomes Mollusks Arthropods Annelids (segmented worms) Deuterostomes Echinoderms Chordata • Distinguished by pattern of development – Cleavage pattern: • Spiral, determinate cleavage (Protostomes) • Radial, indeterminate cleavage (Deuterstomes) – Coelom formation • Schizocoelous body cavity (mesoderm splits) • Enterocoelous body cavity (mesoderm folds – Fate of Blastopore • Mouth develops from blastopore (Protostomes) • Anus develops from blastopore (Deuterostome) Coelomates