* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Outbreak-of
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
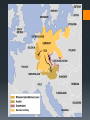
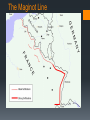
Outbreak of WWII The coming storm Hitler pulled out of the League of Nations, began rearming, and instituted a peace time draft (violation of the Treaty of Versailles) Alliances and Actions in 1936 Anti-Comintern Pact- Germany and Japan- precursor to military alliance Rome-Berlin Axis with Mussolini’s Italy Invasion of the Rhineland- German speaking region between Germany and France Unopposed by England and France, hoping Hitler would be satisfied 1938 The Anschluss- invasion and annexation of Austria- imprisoning its chancellor Again, Britain and France did not react, hoping that Hitler will be satisfied Hitler demanded the Sudetenland- German speaking region of Czechoslovakia Munich Conference- leaders of France and England met with Hitler Mussolini and accepted their promise not to expand further into Europe in exchange for the Sudetenland (which effectively gave him all of Czechoslovakia) English Prime Minister Neville Chamberlin declared he had achieved ‘peace in our time ‘ 1938 Hitler and Stalin Joseph Stalin rose to power after the Bolshevik revolution in 1917 and ruled the USSR from 1929-1953 Succeeded Lenin as head of the Socialist party, despite Lenin’s misgivings Naturally paranoid and suspicious, began a series of purgesattempting to eliminate political enemies who opposed the Communist Party Focus specifically on the military which weakened the Red Army severely Did modernize the USSR by taking direct control of industryalthough caused famine that killed millions 1939- Hitler and Stalin sign the German-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact USSR agreed not to enter the war in exchange for influence over the Balkans and eastern Poland This allowed Germany to invade Poland without resistance The War Begins Sept 1, 1939 Germany invaded Poland Blitzkrieg (lightning war)- speed, force, and surprise- coordination of ground and air attacks. France and Britain declared war on the 3rd, but did little while Poland fell. France moved its troops to the Maginot line- supposedly invincible line of defense along the German border April of 1940- Hitler surprises Denmark and gains control of the capital in 2 hours- Norway by June. Britain elects a new PM, Winston Churchill who had been warning of the threat Hitler posed since 1932 The Maginot Line The War Begins cont. May of 1940- Hitler began his assault on Western Europe Went through Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands before pushing into France Luxembourg surrendered in 1 day, the Netherlands in 5. Escape at Dunkirk British attempted to intervene but they were forced back and cornered on the beach at Dunkirk The British Royal Air Force (RAF) held the Germans off long enough for 338,000 troops to escape across the channel, leaving their tanks and weapons behind. In 6 weeks, Germany had conquered most of Europe, only Britain remained The Battle of Britain Hitler wanted to negotiate but Churchill refused- “we shall fight them on the beaches...we shall never surrender” Germany begins a bombing campaign intended to cripple Britain and force its surrender RAF was incredibly outnumbered (704 planes vs. 2682 for the Luftwaffe) At first, targets were mainly military, but as the siege dragged on, Hitler expanded into civilian targets Known as the London Blitz Ended in May 1941- Germany gave up its attempt to take the British Isles New Enemies and Crucial Mistakes Abandoning his plan to take Britain, Hitler broke his nonaggression pact with the USSR and invaded in June 1941 Attempting to seize labor and resources Moved quickly through Ukraine, and by fall German troops were approaching Moscow Instead of pressing for the capital, he took Leningrad; during that time, the winter moved in Temperatures plunged to -40, causing equipment malfunction and frostbite On December 6, Soviets repulsed a German attack on Moscow AprilJune 1940 Battle of Britain June 1940May 1941 June 1941 Sept 1939 May 1940 Now, please use the colors on your table to shade Germany and its conquered territories, the USSR, and Britain America’s Response to the War in Europe FDR issued a proclamation of neutrality, although he recognized the threat Hitler posed and wanted to support Britain and France Cash and Carry- law that FDR pushed through Congress allowed warring nations to purchase arms as long as they paid cash and transported their own goods Sept. 1940- FDR instituted the first peacetime draft in US history Election of 1940- FDR promised to keep the US out of foreign wars Lend Lease Act- when Britain ran out of cash, this allowed the president to sell, exchange, lend or lease war material to any country Eventually was extended to the USSR US navy aided in British detection of German U boats Collision course in the Pacific 1940- Japan occupied Indochina (modern day Vietnam)- goal of capturing French oil in the Dutch East Indies. US responded with an embargo (official ban on trade with a certain country) on scrap metal, oil and aviation fuel. FDR also froze Japanese bank accounts in the US Devastating blow to Japan who was almost completely dependent on US oil imports Without US oil, Japan would run out of oil in months Japan attempted to negotiate with FDR to allow its further expansion into China; FDR refuses Military coup in 1941 places military General Tojo in command of Japan Japan was expected to attack the Dutch East Indies for oil next Attack on Pearl Harbor 7:55 am- December 7, 1941 the first Japanese bombs fall on Pearl Harbor Subs torpedoed the docks while planes struck the US airfields, where over 400 airplanes were parked. Within 30 minutes, the US fleet of 70 warships was virtually destroyed USS Arizona sustained the most damage and sunk with thousands of crewmen still on board Totals- 2,403 killed, 1,178 injured Despite the damage, Japan did not achieve all its goals- failed to destroy the aircraft carriers which were still at sea. The next day, FDR declares December 7th “a day that will live in infamy’ and the US declares war on Japan Works Cited Mintz, S., & McNeil, S. (2016). World War II. Digital History. Retrieved March 21, 2016, from http://www.digitalhistory.uh.edu/era.cfm?eraID=11&smtID=2