* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4.2 - Elmwood Park Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
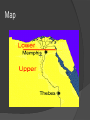
THE OLD KINGDOM YouTube: The Old Kingdom http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tSKB OilYBiY&sns=em The Old Kingdom Egypt was first made of two kingdoms Upper and Lower Upper-Southern Nile River Valley Lower-Northern Delta Menes was king of Upper Egypt He led his army from the Southern Valley into Lower Egypt Conquered the Lower Kingdom and married a princess The Old Kingdom His marriage united the kingdoms He wore two crowns, the Upper and Lower crowns High White one from the south (Upper) Low red one from the north (Lower) Menes declared a new capital of Egypt in Memphis Border city The Double Crown Map Old Kingdom 2600 BCE, the Old Kingdom arose (500 years) Cities were centers of religion and government City centers housed Kings, priests, government officials, and artisans Many Egyptians did not live in the city, but large estates on the Nile banks. Rich owners had gardens and pools Home of the Rich The homes had many paintings depicting daily life Family, servants and artisans lived there Artisan were hired to build boats, weave linen, and make tools/pottery Egyptian Farmers Most Egyptians did not live in the center of the city or on the banks of the Nile. Most lived on the rich estates as farmers Homes made of reed and mud, and later sun-baked brick. Had one room, palm leave roof and built on high ground to avoid flood waters Worked fields, built monuments, dug ditches, and repaired roads The Pharaoh Pharaoh is a king Meaning “great house” Pharaoh was ruler, priest, and a god Center of life and ruled on earth as god’s ruled in heaven Owned all land, often gave as a gift to the rich Maintained the land, kept up with it to make sure it could produce The Pharaoh Made sure canals were made and repaired Developed granaries to house the grain so people would not starve if a bad harvest Elected all officials Taxed and issued building permits, trade went through Pharaoh first Word of Pharaoh was law The Pharaoh People believed fate of Egypt depended on Pharaoh’s actions Carried out rituals to ensure good harvest Treated with respect, flutes were played when he appeared Bowed and smelled the earth, or brought head to ground YouTube Video: The Pyramids http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ycUbk jfW1Xc&sns=em The Pyramids Pyramids were built out of respect for the Pharaoh’s. Pyramids were great tombs built for Pharaoh’s as “Houses of Eternity” Built in west to avoid flood waters Built to protect Pharaoh and his belongings EVERYTHING was placed in tomb The Pyramids Making the Pyramids Farmers worked on them for the 3 summer months (flooded fields) Used copper tools to cut granite and limestone blocks that were shipped down the Nile from the quarries After unloaded workers brought them to building site and dragged the blocks up ramps to create the layers YouTube Video: Making the Pyramids http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6Cpj MxXG52s Making the Pyramids Religious Beliefs Believed in many god’s River God Hapi and Sun God Re were most important River brought water and fertile soil and sun grows crops Osiris is god of harvest and eternal life The God: Re (Sun God) The God: Hapi (River God) The God’s: Osiris (God of Harvest) Mummification Egyptians used the technique of embalmment to preserve the bodies of the dead. First only used with Pharaoh to preserve the body so the soul could live on and watch over Egypt Body placed in wood box and covered with natron Natron dried up water in body and shrunk it Mummification Body was wrapped in linen Poor people were buried in sand, while rich in tombs