* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mid-coronal
Radiation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Industrial radiography wikipedia , lookup
Backscatter X-ray wikipedia , lookup
Center for Radiological Research wikipedia , lookup
Positron emission tomography wikipedia , lookup
Radiation burn wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear medicine wikipedia , lookup
Radiosurgery wikipedia , lookup
Medical imaging wikipedia , lookup
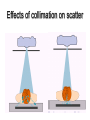
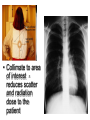
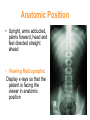
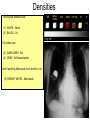
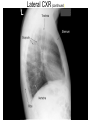
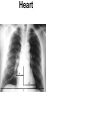
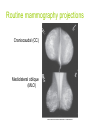
Mid Term Revision Imaging Procedure 1 Dr Mohamed El Safwany, MD. Creating the Image • Scatter –Creates fog –Lowers contrast (more grays) • Increases as –kV increases –Field size increases –Thickness of part increases Effects of collimation on scatter • Collimate to area of interest reduces scatter and radiation dose to the patient Grids • A device with lead strips that is placed between the patient and the cassette • Used on larger body parts to reduce the number of scattering photons from reaching the image Grid is placed between patient (behind table or upright bucky) & cassette If placed BACWARDS CAN CAUSE GRID ERRORS Factors that affect the detail of an image SID Source to Image Distance • The greater the distance between the source of the x-ray (tube) and the image receptor (cassette), the greater the image sharpness. • Standard distance = 40 in. most exams • Exception = Chest radiography 72 in. *See page 74 in your book Shape Distortion • Misrepresentation of the shape of an object • Controlled by alignment of the beam, part (object), & image receptor • Influences: Central ray angulation & body part rotation Bone Classification • • • • Long Flat Short Irregular Centers of Endochondral Ossification • Primary center- midbody or diaphysis • Secondary center- ends or extremities of the long bones or epiphysis – Epiphyseal plates: found between the diaphysis and the epiphysis until skeletal growth is complete Anatomic Position • Upright, arms adducted, palms forward, head and feet directed straight ahead • Viewing Radiographs: Display x-rays so that the patient is facing the viewer in anatomic position R Body Planes, Sections and Lines • Sagittal- any longitudinal plane dividing the body into right and left parts • Mid-sagittal or median plane- divides the body into equal right and left halves • Coronal- longitudinal plane dividing the body into anterior and posterior parts • Mid-coronal- divides the body into equal anterior and posterior parts • Horizontal or axial plane- transverse plane passing through the body at right angles to the longitudinal plane; divides into superior and inferior portions • Oblique plane- longitudinal or transverse that is on an angle or slant to the sagittal, coronal or horizontal planes. Understanding CT and MRI Images • Longitudinal sections can be taken in sagittal, coronal or oblique planes • Transverse (axial) or cross sections Gastrointestional Fluoroscopy • • • • • • • Esophogram/Barium Swallow Modified Barium Swallow/Dysphgiagram Upper GI Small Bowel Series Enteroclysis Contrast Enema Defecography Single Contrast vs Double Contrast • Single Contrast – Generally uses just thin Barium – Distends lumen with high density material – Easier for patient/less mucosal detail • Double Contrast/Air Contrast – Thick barium coats lumen – Effervescent tablets ingested to distend lumen with air – Produces ‘see-through’ images with greater mucosal detail – Greater sensitivity for small lesions, polyps, ulcers Contrast Enemas • • • • Barium or Gastrograffin Double contrast or single contrast Generally less sensitive than endoscopy Requires bowel prep to assess for mucosal lesions • Requires some element of patient cooperation Hysterosalpingogram • Used to evaluate endometrial canal and fallopian tubes • Infertility and uterine anomalies • Dye injected into cervical os under fluoro • Injection continued with goal to opacify the fallopian tubes and spill contrast into peritoneum Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) • Multi-planar scanning • Without ionizing radiation • Images generated using powerful magnets and pulsed radio waves passing through the body • Data from Pt’s body used to generate image • Field strength of magnets 0.3-3.0 Tesla MR Contrast Agents • Intravenous contrast---Gadolinium chelatebased contrast agents • Gadolinium is a paramagnetic lanthanide that is toxic as a free metal • Contrast to evaluate BBB, intracranial edema and hemorrhage • Novel agents being developed as tagged Monoclonal antibodies for Molecular Imaging MR Applications • Neuro-imaging -Excellent tool due to high soft tissue contrast resolution -Abundant water content of CNS allows for imaging soft intracranial tissue • Head and Neck imaging -Multi-planar capability allows for monitoring extent of disease -Differentiating subtle soft tissue boundaries of head and neck Aims: Basics• Best exam results• Appreciate the role radiology plays• Densities The big two densities are: (1) WHITE - Bone (2) BLACK - Air The others are: (3) DARK GREY- Fat (4) GREY- Soft tissue/water And if anything Man-made is on the film, it is: (5) BRIGHT WHITE - Man-made Inspiration/Expiration Anatomy Heart (continued) Lateral CXR (continued) Heart Size of heart• Size of individual • chambers of heart Size of pulmonary • vessels Evidence of stents, clips, • wires and valves Outline of aorta and IVC • and SVC Typical Mammography Unit Equipment is C-arm SID is fixed at 24 – 26” Compression Device Made of firm plastic Amount of compression: between 25 and 40 pounds pressure Compression may be uncomfortable! Digital Mammography State of the art! • No film or chemical processing • Images easily sent over internet • Much better definition Routine mammography projections Craniocaudal (CC) Mediolateral oblique (MLO) CT Terminology • Attenuation is measured in Hounsfield units – Scale -1000 to 1000 • -1000 is air • 0 is water • 1000 is cortical bone • Attenuation – Hyperattenuating (hyperdense) – Hypoattenuating (hypodense) – Isoattenuating (isodense) CT Terminology • What we can see – The brain is grey • • • • White matter is usually dark grey (40) Grey matter is usually light grey (45) CSF is black (0) Things that are brite on CT – – – – – Bone or calcification (>300) Contrast Hemorrhage (Acute ~ 70) Hypercellular masses Metallic foreign bodies CT Terminology • Window Width – Number of Hounsfield units from black to white • Level or Center – Hounsfield unit approximating mid-gray CT Terminology • DICOM – Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine – DICOM provides standardized formats for images, a common information model, application service definitions, and protocols for communication. Radiation Safety • Terminology – Gy = Gray is the absorbed dose (SI unit) • The equivalent of 1 joule/kg of tissue • Rad = radiation absorbed dose – Sv = Sievert is the dose equivalent (SI unit) • Absorbed dose multiplied by a quality factor • Rem = radiation equivalent man Radiation Safety • Effects of X rays. – – Absorption of photons by biological material leads to breakage of chemical bonds. The principal biological effect results from damage to DNA caused by either the direct or indirect action of radiation. Good Luck