* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
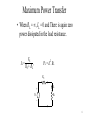
ECE 3301 General Electrical Engineering Section 19 Maximum Power Transfer Theorem 1 Maximum Power Transfer • It is often desired to transfer maximum power out of a network into a load resistance. • Since a Thevenin Equivalent Circuit may be found for any network we may consider a voltage source in series with a resistance. RS VS IL RL 2 Maximum Power Transfer • The current through the load resistance is: VS IL = RS + RL RS VS IL RL 3 Maximum Power Transfer • The power dissipated in the load resistance is : VS2RL PL = (RS + RL)2 RS VS IL RL 4 Maximum Power Transfer • When RL = 0, there is zero power dissipated in the load. All of the power available is dissipated in the source resistance. VS2RL PL = (RS + RL)2 RS VS IL RL 5 Maximum Power Transfer • When RL = , IL = 0 and There is again zero power dissipated in the load resistance. VS IL = , RS + RL PL = IL2 RL RS VS IL RL 6 Power Dissipated in Load Resistance Maximum Power Transfer Load Resistance • For what value of RL is maximum power delivered to RL? 7 Maximum Power Transfer • The power dissipated in the load resistance is: VS2RL 2 –2 PL = 2 = VS RL(RS + RL) (RS + RL) 8 Maximum Power Transfer • To find the maximum power transferred, the derivative of this quantity with respect to RL is placed equal to zero. dPL = VS2 [RL(– 2)(RS + RL) – 3 + (RS + RL) – 2] = 0 dRL 9 Maximum Power Transfer • The quantity in brackets is set equal to zero: 2RL(RS + RL) –3 = (RS + RL) –2 • Solving for RL reveals 2RL = RS + RL RL = RS 10 Maximum Power Transfer • Maximum Power is transferred when the Load Resistances matches the Source Resistance. RS VS IL RL = RS 11 Power Dissipated in Load Resistance Maximum Power Transfer Load Resistance RS = RL 12