* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stateless Addr. Autoconfiguration
Survey
Document related concepts
SIP extensions for the IP Multimedia Subsystem wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
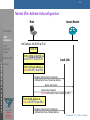
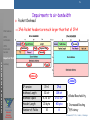
s IPv6 Impacts on UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY CT IC2 – Vivek Kulkarni [email protected] CT IC2 – Jochen Grimminger [email protected] Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Date: 30.07.2002 © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Contents: Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • IPv6 features • UMTS Architecture • UMTS End-to-End Services • Impacts of IPv6 • Summary © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Motivation for a new IP: Why a new IP? IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services One Compelling reason: Larger address space requirement !! • For billions of new devices, e.g., 3G and beyond cell phones, PDAs, appliances, cars, etc. • For billions of new users, e.g., in Asia (India, China, … etc.) • For “always on“ access technologies, e.g., xDSL, cable, Ethernet-to-the-home, etc. CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Other reasons are covered in Features of IPv6........ Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 Features IPv6 Features Base Functionality • Larger Address Space • Header Format Simplification • Improved Support for Extensions and Options Addressing and Routing • Expanded and Efficient Addressing Capabilities • Efficient Routing Protocols • ICMPv6 Plug and Play • Neighbor Discovery • Address Autoconfiguration Support for QoS • Flow Labeling Capability Security • Built-in Security through IPsec Mobility support • Mobile IPv6 Others • Path MTU Discovery • DNS for IPv6 UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Contents: Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • IPv6 features • UMTS Architecture • UMTS End-to-End Services • Impacts of IPv6 • Summary © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s UMTS Architecture IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 in 3GPP IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services Gp Iub RBS UE UTRAN RNC TECHNOLOGY CORPORATE Host GGSN Gn IP Network UMTS/GPRS Backbone (IPv4) SGSN Impacts of IPv6 Summary External PLMN Appl Appl TCP/UDP TCP/UDP IP IP Relay GTP-U GTP-U Relay PDCP GTP-U PDCP RLC UDP UDP UDP UDP MAC MAC IP IP IP IP L1 L1 L2/L1 L2/L1 L2/L1 L2/L1 Uu UTRAN Iu-PS SGSN IP L2 L2 L1 L1 GTP-U RLC UE IP Gn/Gp GGSN Gi Host User level IP Transport level IP Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 in 3GPP IPv6 Features Requirement for 3GPP network: UMTS Architecture • Both IPv4 / IPv6 are options for IP Connectivity UMTS End-to-End Services • The IM CN subsystem shall exclusively support IPv6 CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Requirement for UE: • The UE shall exclusively support IPv6 for the connection to services provided by the IM CN subsystem. • The UE can access IPv4 and IPv6 based services. Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Reference: 3GPP TS 23.221, Architectural requirements (Release 5) © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Normal IPv6 Address Autoconfiguration: Host Access Router IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary MAC Address : 00-60-97-aa-55-af Power On Forms Interface Identifier as 02-60-97-ff-fe-aa-55-af Local Link Forms Link-local address as fe80::260:97ff:feaa:55af Neighbor Solicitation For Duplicate Address Detection of Link-local address Router Solicitation Router Advertisement (Prefix Information, Source Link layer addr.) Forms Global address as Prefix::260:97ff:feaa:55af Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Neighbor Solicitation For Duplicate Address Detection of Global address © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 Autoconfiguration in 3GPP: Stateless Address Autoconfiguration In 3GPP UMTS IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary UE BSS/UTRAN SGSN GGSN “PDP Context Activate Request“ “PDP Context Activate Accept“. Also sends “ Link Local Address“ PDP context is activated Router Solicitation Gets/Builds full IPv6 Address Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Router Advertisement (Either full IPv6 address or Unique Prefix) © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Stateful Address Autoconfiguration (DHCPv6) In 3GPP UMTS IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Contents: Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • IPv6 features • UMTS Architecture • UMTS End-to-End Services • Impacts of IPv6 • Summary © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s UMTS Services Voice Non-Voice (Information and Content) IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture Content Connectivity (Internet) UMTS End-to-End Services Personal TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 CORPORATE Mobility People Connectivity Location Summary Direct link to a person Rich Voice (including Video Phones) Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Mobile Internet Access Mobile Intranet/ Extranet Access Customised Infotainment Always-on, IP based MMS Knowledge of location Location Based Services Source: UMTS Forum © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s VoIP Scenario ..... IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services 192.168.52.x CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary VOIP Application NAT-Router 202.123.41.10 192.168.52.3 VOIP Application IPv6 solves the problem of NAT by providing each device a unique IP-address. i.e. Global reachability Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Contents: Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • IPv6 features • UMTS Architecture • UMTS End-to-End Services • Impacts of IPv6 • Summary © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Impacts due to End-to-End IPv6 IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary • Impairments to air bandwidth efficiency due to o Packet Overhead o Addressing : Unicast, Multicast & Anycast o Neighbor Discovery and Autoconfiguration o Mobile IPv6 o Path MTU Discovery • Interoperability between IPv4 and IPv6 networks • IPv6 Impacts on 3GPP Terminals Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Impairments to air-bandwidth o Packet Ovehead IPv6 Features IPv6 Packet headers are much larger than that of IPv4 UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Removed Added IP version Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication IPv4 IPv6 Address Length 32-bit 128-bit Address Space 4.3 x 109 3.4 x 1038 Header Length 20 byte 40 byte 14 8 Number of Fields Global Reachability Increased Routing Efficiency © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s o Addressing In IPv6, there are more routable addresses than IPv4 IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Unicast: An address for a single interface. Multicast: An address for a set of interfaces (in a given scope) that typically belong to different nodes. IPv6 multicast addresses are used instead of broadcast addresses in IPv4. Anycast: An address for a nearest interface from the set of interfaces that typically belong to different nodes. What we will achieve with Expanded and Efficient Addressing Capabilities? • Use of Anycast address include services where redundancy is desirable, for e.g. - routers, name servers, software mirroring. Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • Simplified routing tables with prefix aggregation and improved table lookup. © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 Addresses: In IPv6, there are more routable addresses than IPv4 Impact of UE Addresses on Air-Interface IPv6 Features CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY UMTS Architecture Following are the addresses that Mobile Terminal MUST have in order to communicate in various scenarios. • Unspecified Address (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0) used during autoconfiguration UMTS End-to-End Services • Loopback Address (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1) Impacts of IPv6 • Link-Local address for each interface Summary Impact on Air-interface : yes Impact on Air-interface : no (Its internal to the node, so it will not affect air-interface) Impact on Air-interface : yes (as it is link-specific) but it will not be routed through GGSN. • Assigned Unicast Addresses (Multiple IP addresses/bearer or One IP address for multiple bearers separated by flow templates) Impact on Air-interface : yes • All-Nodes Multicast Addresses Impact on Air-interface : yes • Solicited-Node Multicast Address for each of its assigned unicast and anycast addresses Impact on Air-interface : yes • Multicast Addresses of all other groups to which the host belongs Impact on Air-interface : yes Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • IPv4-compatible IPv6 addresses (Used to communicate with IPv4-only nodes, NGTrans) Impact on Air-interface : yes © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s o Neighbor Discovery and Autoconfiguration IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Air-link bandwidth gets hampered because of frequent Neighbor Discovery/Autoconfiguration messages. Neighbor Discovery: Basic Use • to determine the link-layer addresses for neighbors • to find access routers • to keep track of reachable neighbors Address Autoconfiguration: Basic Use • to configure the Care of Address Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s o Mobile IPv6 Getting new Care off Address and sending Binding Updates will hamper air-link efficiency. IPv6 Features CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY UMTS Architecture General Idea: 1. MN gets new Care of Address (COA) in a foreign network UMTS End-to-End Services 2. MN registers the new COA with its Home Agent (HA) 3. CN sends to HA and HA tunnels towards MN Impacts of IPv6 4. MN sends Binding Update (BU) to CN and CN sends directly Summary Home Network Internet Home Address HA MN Foreign Network CN Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Home Address Care of Address MN © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s o Path MTU Discovery Path MTU Discovery will contribute to the air-link bandwidth. IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Path MTU Process: 1. Send a message to the destination with MTU of link. 2. If receive a ICMP “Packet Too Big” error message, then resend the message with the new MTU. 3. Do 1 and 2 until response from destination. 4. Last MTU is the Path MTU IPv6 domain MTU=1500 Bytes Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication IPv6 domain MTU=1500 Bytes Path MTU Discovery Path MTU Discovery Packet Too Big Msg. Packet Too Big Msg. IPv6 domain MTU=1280 Bytes MTU= 1280 Bytes © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 in 3GPP: IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture IPv6 Features Cause of Impairment Packet Header due to IPv6 packet Header Compression using IETF header (min. 40 bytes ROHC algorithms. But single packet basic header) messages like ICMP messages can UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Possible impairments to Air-Interface efficiency due to IPv6 Solution to the Impairment not be compressed. Addressing Summary Address there are more IPv6 This drawback will remain as it is a routable addresses part of IPv6 functionality. But its than IPv4. not a major one. frequent Router Either keep the router Autoconfiguration Advertisements advertisement interval much larger Or send Router advertisements through radio broadcast channels. Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 in 3GPP: IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture IPv6 Features Cause of Impairment Mobile IPv6 Getting new COAs, Some Regionalized registration / Sending Binding Hierarchical MIP solutions will help Updates to HA & CN to reduce signaling outside the local UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Possible impairments to Air-Interface efficiency due to IPv6 Solution to the Impairment administrative domain. Path MTU Repetitive Path MTU Either to use suitable Minimum MTU Discovery messages flowing or use fragment header over air-interface Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Interoperability between IPv4 and IPv6 networks IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture Transition Mechanism Purpose Scope Requirements Dual Stack To access both IPv4 and IPv6 services without additional translators / tunnels IPv4 IPv4 IPv6 IPv6 UE + UTRAN + SGSN + GGSN Dual Stack Infrastructure Tunneling To connect disjoint IPv6/IPv4 islands, separated by IPv4/IPv6 network IPv4 IPv4 IPv6 IPv6 Border Routers of UMTS Network Dual Stack Border Routers Translation To connect IPv6-only host to IPv4-only host and vice versa IPv6 IPv4 Border Routers of UMTS Network IPv6 IPv4 packet translator UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Dual IPv4/IPv6 Stack Each mobile terminal has to have both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses !!! IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture IPv6 Device UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary IPv6 Network IPv6 UE RNC IPv4 SGSN GGSN IPv4 Network IPv4 IPv4 Device IPv6 Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Reference: 3GPP TS 23.221 V5.5.0 (2002-06) © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Tunneling Communication possible between devices having same IP version !!! IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services UE RNC IPv6 SGSN GGSN TrGW CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary IPv4 Network IPv4 IPv6 TrGW IPv6 Device IPv6 Network e.g. 6to4,...etc Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Reference: 3GPP TS 23.221 V5.5.0 (2002-06) © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Tunneling : Automatic Tunneling IPv6 IPv4 communication problem is not solved !!! Uses IPv4-compatible IPv6 addresses, for e.g. ::IPv4-address IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services The border router extracts the IPv4 addresses embedded in IPv6 packet and tunnels it in IPv4 packet The receiving system recovers the original IPv6 message IPv6 domain IPv4 domain TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 CORPORATE IPv6 domain B A Summary (::w.x.y.z) (::a.b.c.d) SRC ::a.b.c.d DST ::w.x.y.z Payload Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication IPv6 header SRC a.b.c.d DST w.x.y.z SRC: ::a.b.c.d DST: ::w.x.y.z IPv4 header IPv6 header SRC ::a.b.c.d DST ::w.x.y.z Payload Payload © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Tunneling : Configured Tunneling (6Bone Experimental Test-bed) IPv6 IPv4 communication problem is not solved !!! Also requires manual configuration for tunneling. IPv6 Features Requires explicit configuration at every point to the IPv4 network UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary IPv6 domain A SRC: IPv6 DST: IPv6 Payload IPv6 domain IPv4 domain Tunneling Router R2 Tunneling Router R1 IPv6 header SRC IPv4 addr of R1 DST IPv4 addr of R2 SRC: IPv6 DST: IPv6 B IPv4 header SRC: IPv6 IPv6 header Payload DST: IPv6 Payload Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Translation Mechanisms : Computation load on the translation mechanism !!! IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services UE RNC SGSN GGSN TrGW IPv4 Network IPv6 IPv4 Device Impacts of IPv6 CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY IPv4 Summary IPv6 Used when communicating nodes do not share the same IP version. No modifications to the hosts. IPv6 packet IPv4 packet translation. e.g. NAT-PT, SIIT, TRT, Socks64,...etc. Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication Reference: 3GPP TS 23.221 V5.5.0 (2002-06) © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Translation Mechanisms : IP Header Translation IPsec (AH, ESP-tunnel mode) will get broken due to IP header translation!!! IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary 20 byte Header Variable length 14 different fields 4 byte (32 bit) addresses Checksum Field Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication 40 byte Header Fixed Length of 40 bytes 8 different fields 16 byte (128 bit) addresses No Checksum field Extension headers Flow label © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Mapping of NAT-PT [RFC2766] on UMTS scenario Stateful mechanism...!!! DNSv6/v4 IPv4 Domain IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services IPv4 Domain A NAT-PT IPv6 3G Network GGSN (IPv6-only) Operators Network Prefix::Interface Id CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary DNS Query: B? Gets B‘s address as NAT-PT-Prefix::131.1.2.1 Src Prefix::Interface Id Dst NAT-PT-Prefix::131.1.2.1 Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication DNSv4 Src NAT-PT-Prefix::131.1.2.1 Dst Prefix::Interface Id IPv4 Domain Pool of IPv4 (120.130.26/24) Addresses Assigns free IPv4 address from the pool to IPv6-only host B (IPv4-only) No entry in DNSv6/v4 cache. Translates DNSv6 to DNSv4 Query 131.1.2.1 DNSv4 Response B: IPv4 addr. Translates DNS Response and adds NAT-PT-Prefix Assumption: to IPv4 addr. Routing inside the operators network know how to route the packets towards Translator by static routes NAT-PT assigns free 120.130.26.10 address, translates the packet and maintains the state Src 120.130.26.10 Dst 131.1.2.1 Src 131.1.2.1 Dst 120.130.26.10 © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Mapping of TRT [RFC3142] on UMTS scenario Stateful mechanism and IPsec breaks completely...!!! IPv4 Domain TRT IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services IPv4 Domain A IPv6 3G Network GGSN (IPv6-only) Operators Network Prefix::Interface Id CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary IPv4 Domain B DNSv6/v4 (IPv4-only) DNS Query: B? DNSv6 adds TRT-Prefix to B‘s address as TRT-Prefix::131.1.2.1 Src Prefix::Interface Id Dst TRT-Prefix::131.1.2.1 Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication DNSv4 Src TRT-Prefix::131.1.2.1 Dst Prefix::Interface Id No entry in DNSv6/v4 cache. Translates DNSv6 to DNSv4 Query 131.1.2.1 DNSv4 Response B: IPv4 addr. Relays DNS Response after appending TRT-prefix Assumption: Routing inside the operators network know how to route the packets towards Translator by static routes Src TRT‘s IPv4 address Dst 131.1.2.1 Src 131.1.2.1 Dst TRT‘s IPv4 address © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s IPv6 Impacts on 3GPP Terminals IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture Three functionality groups: [draft-ietf-ipv6-cellular-host-03.txt] Path MTU Discovery [RFC 1981], TECHNOLOGY UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE Basic IPv6 Functionality: Basic parts of IPv6 Addressing Architecture [RFC 2373], IPv6 Specification [RFC 2460], Impacts of IPv6 Neighbor Unreachability Detection [RFC 2461], Summary Stateless Address Autoconfiguration [RFC 2462], ICMP for IPv6 [RFC 2463], IPv6 over PPP [RFC 2472],...etc IP Security: IP Security (IPsec) details for cellular hosts Many RFCs... IP Mobility: IP Mobility details for cellular hosts Mobile IPv6 is not yet a RFC.... Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Open Issues for IPv6 in 3GPP Recommendations for IPv6 in 3GPP Standards (April 2002) IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture [draft-ietf-ipv6-3gpp-recommend-02.txt] 1. UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Multiple prefixes may be assigned to each primary PDP context 2. Summary A given prefix must not be assigned to more than one primary PDP context 3. GGSN view each primary PDP context as a single IPv6 subnet Allow 3GPP nodes to use multiple identifiers within those prefixes, including randomly generated identifiers. Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication SGSN will be informed of each prefix that is currently assigned to a PDP context UE can generate and use privacy addresses © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Open Issues for IPv6 in general IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 IPv6 Transition Solutions for 3GPP Networks draft-wiljakka-3gpp-ipv6-transition-00.txt Latest update from 54th IETF, Yokohama • Nokia is favouring NAT64/46 as it has less security problems • IMS is the most challenging as I-CSCF and S-CSCF will need transition solutions to connect to external IPv4-only networks. • Dual Stack is recommended for the UEs. • IPv6/v4 interworking should be done in the network and not in the UE. • Don‘t recommend tunneling over air like (DSTM or 6over4) but if needed ROHC will help Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Open Issues for IPv6 in general ISP‘s view: Latest update from 54th IETF, Yokohama IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY UMTS End-to-End Services • MIPv6 not yet standardized. • Transition mechanisms have to be simple ones 6over4 tunneling, NAT-PT/TRT is the best and perhaps enough. Impacts of IPv6 • Multicast DNS (LLMNR) necessary for IPv6 deployment Summary • Key Applications for ISPs are not yet IPv6 ready.... • BIND (DNS) – v8 : No IPv6 support - v9 : not ready for heavy duty production use. • Qmail (Mail Transfer Agent) – with unofficial patches for IPv6. • Squid (Web Proxy Server) – IPv6 is only experimental basis. Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Contents: Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • IPv6 features • UMTS Architecture • UMTS End-to-End Services • Impacts of IPv6 • Summary © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Summary IPv6 benefits to Mobile Network Operators: IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 • Auto configuration • Embedded encryption support and authentication • Embedded mobility • Internet provider selection • Efficient packet processing in routers Summary IPv6 benefits to Mobile End Users: Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • Easy management & auto configuration • Efficient address allocation • Renumbering possible © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Summary: IPv6 Features TECHNOLOGY Status : Solved? Packet Overhead P UMTS End-to-End Services Addressing O Impacts of IPv6 Address Resolution and Autoconfiguration P Mobile IPv6 P Path MTU Discovery P UMTS Architecture CORPORATE Impairments due to IPv6 Summary Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Summary: IPv6 in 3GPP: IPv6 Features UMTS Architecture UMTS End-to-End Services CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Impacts of IPv6 Summary • • • IPv6 is mandatory in UTRAN. Backbone UMTS network will be IPv4 initially, but ultimately IPv6 shall be used. 3GPP R5 IMS uses IPv6 exclusively. IPv6 in IETF: • • • IPv6 Core Specifications achieved Draft Standard status. IPv6 Specs at Proposed Standard level are stable for more than 2 years now. Large-scale deployment is underway…. Open Issues: Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication • • • MIPv6 not yet RFC DNS for IPv6 Killer applications are yet to be developed for IPv6.... © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Thank you !!! Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY s Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Backup CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Backup Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger s Address Autoconfiguration: 48bit MAC Address to EUI-64 Interface Identifier Motivation IPv6 Features (one of the method to form Interface Identifier!!!) 00 : 60 : 97 : aa : 55 : af MAC Address (48-bit) Transition 00 60 97 aa 55 af IPv6 in 3GPP Status in IETF 00 60 97 CORPORATE TECHNOLOGY Implementations & Applications aa 55 af ff fe Summary & Conclusion 0 0 0 0 0 0 01 0 “Universal/Local“ (U/L) bit 1 = globally unique Interface Identifier (64-bit) Information & Communications Networks & Multimedia Communication 02 : 60 : 97 : ff : fe : aa : 55 : af Back © Siemens AG,CT IC 2, V. Kulkarni, J. Grimminger