* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Body systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
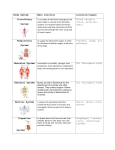
System- Provides shape and structure to the body. Allows for movement. Protects vital organs. Produces blood cells. Organs- bones, ligaments, cartilage Relationship with other organs- Gives the skeletal muscles something to pull against to provide bodily movement Medical Conditions Arthritis Leukemia (could also be immune) Osteoporosis Rickets System- Allows movement of the body to provide heat Organs- Smooth muscle, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, tendons Relationship with other organs Urination is caused by the contraction of muscle surrounding the bladder Contractions of the cardiac muscle in heart is responsible for the movement of blood throughout the circulatory system Many muscles are attached to bones of the skeletal system to provide bodily movement Medical Conditions Muscular dystrophy Fibromyalgia Myopathy cramps and spasms Tendonitis System- Receives and interprets information for the bodies internal and external environments. Sends messages to the body about how to react to changes in the environment. Organs- spinal cord, brain, nerves Relationship with other organs Receives information in the form of electrical signals from all organs in the body Has control over the functions of all organs in the body Linked to every organ in the body through a network of nerves Medical Conditions Alzheimer's disease Epilepsy Stroke Parkinson's disease Spina bifida System- controls body functions using chemicals messengers called hormones Organs- adrenal gland, thymus, thyroid gland, pituitary gland, pancreas Relationship with other organs Produces hormones that controls the growth of bones in the skeletal system The hormones it produces are transported throughout the body by the circulatory system Hormone production is dictated by signals received from the nervous system Medical Conditions Cushing’s disease Diabetes mellitus Thyroid cancer Addison's disease System- protects the body from foreign invaders by providing a tough protective layer. Helps maintain the body’s internal temperature. Protects against the sun’s UV radiation. Produces vitamin D. Organs- nails, hypodermis, hair, dermis, epidermis Relationship with other organs- Works with the immune system to provide the body with the first layer of defense against disease causing pathogens. Provides protection for the the organs of the digestive, respiratory, circulatory, urinary, and nervous systems (can also be skeletal or immune) Works with the nervous system to control body temperature (sweating, goose bumps) Medical Conditions Warts Basal cell carcinoma Eczema Acne psoriasis System- helps fight off disease causing foreign invaders Organs- lymph nodes, lymph vessels, white blood cells Relationship with other organs Runs parallel to the circulatory system to transport disease fighting white blood cells Medical Conditions Lymphomas Splenomegaly Multiple sclerosis (can also be considered nervous) Tonsillitis System- brings oxygen into the body, gets rid of excess carbon dioxide Organs- lungs, bronchi, nose, alveoli, trachea, diaphragm (also muscular), bronchioles Relationship with other organs Smooth muscle in the diaphragm help control breathing (also muscular system) Works with the circulatory system to provide oxygen to all the cells in the body and remove excess carbon dioxide Medical Conditions Asthma Bronchitis COPD Emphysema Cystic fibrosis Pneumonia System- Transports oxygen, waste, nutrients, hormones, hear, etc. around the body Organs- veins, arteries, heart, capillaries, red blood cells Relationship with other organs Works with the endocrine system to transport hormones throughout the body Works with the lymphatic/immune system to transport white bloods cells to site of infection Heartbeat is involuntary controlled by the nervous system Works with the digestive system to absorb and deliver nutrients to the cells Works with the excretory system to filter waste out of blood for removal Works with the respiratory system to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide Medical Conditions Heart disease Deep vein thrombosis Atherosclerosis Aneurism Myocardial infarction System- filters blood and rids the body of waste material. Maintains water and electrolyte balance in the body. Organs- kidneys, urethra, ureter, bladder Relationship with other organs Urination is caused by the contraction of muscle surrounding the bladder Filters blood from the circulatory system of waste products so they can be removed from the body Medical Conditions Acute renal failure Nephritis Cystitis Urinary incontinence Kidney stones System- breaks down food into smaller molecules and absorbs these nutrients into the body Organs- large intestine, small intestine, stomach, gall balder, esophagus, salivary glands, pancreas (also part of the endocrine), mouth, liver Relationship with other organs Works with the nervous system to trigger appetite Works with the muscular system to control the contractions of organs responsible for breaking down food Works with the circularity system to deliver digested nutrients to cells throughout the body Smooth muscle found in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine are responsible for the mechanical breakdown of food Works with the circulatory system to provide essential nutrients for all organs in the body Medical Conditions GERD Irritable bowel syndrome Crohn’s disease Celiac disease System- produces sex cells; sperm (male) and eggs (females). Provides suitable environment for the development of unborn baby (females) Organs- uterus, testes, ovaries Relationship with other organs Works with the endocrine system to control the production of sperm (males) and eggs (females) Requires the help of the muscular system during childbirth. Muscles surrounding the uterus contract to give birth. Medical Conditions infertility