* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Buddism and Taosim
Yiqiejing yinyi (Xuanying) wikipedia , lookup
Sanghyang Adi Buddha wikipedia , lookup
Buddha-nature wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and violence wikipedia , lookup
Early Buddhist schools wikipedia , lookup
Four Noble Truths wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist art wikipedia , lookup
Karma in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Dhyāna in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Persecution of Buddhists wikipedia , lookup
Dalit Buddhist movement wikipedia , lookup
Pratītyasamutpāda wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist philosophy wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhist ethics wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Myanmar wikipedia , lookup
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Noble Eightfold Path wikipedia , lookup
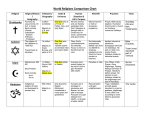
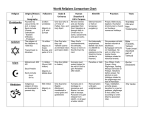
Taoism is one of the two great philosophical and religious traditions that originated in China. The other religion native to China is Confucianism. Both Taoism and Confucianism began at about the same time, around the sixth century B.C.E. China's third great religion, Buddhism, came to China from India around the second century of the common era. Together, these three faiths have shaped Chinese life and thought for nearly twenty-five hundred years (Hartz 3). One dominate concept in Taoism and Buddhism is the belief in some form of reincarnation. The idea that life does not end when one dies is an integral part of these religions and the culture of the Chinese people. Reincarnation, life after death, beliefs are not standardized. Each religion has a different way of applying this concept to its beliefs. This paper will describe the reincarnation concepts as they apply to Taoism and Buddhism, and then provide a comparison of the two. Taoism The goal in Taoism is to achieve tao, to find the way. Tao is the ultimate reality, a presence that existed before the universe was formed and which continues to guide the world and everything in it. Tao is sometimes identified as the Mother, or the source of all things. That source is not a god or a supreme being, as Taoism is not monotheistic. The focus is not to worship one god, but instead on coming into harmony with tao (Hartz, 8). Tao is the essence of everything that is right, and complications exist only because people choose to complicate their own lives. Desire, ambition, fame, and selfishness are seen as 1 hindrances to a harmonious life. It is only when a person rids himself of all desires can tao be achieved. By shunning every earthly distraction, the Taoist is able to concentrate on life itself. The longer the person's life, the more saintly the person is presumed to have become. Eventually the hope is to become immortal, to achieve tao, to have reached the deeper life. This is the after life for a Taoist, to be in harmony with the universe, to have achieved tao (Head1, 65). To understand the relationship between life, and the Taoism concept of life and death, the origin of the word tao must be understood. The Chinese character for tao is a combination of two characters that represent the words head and foot. The character for foot represents the idea of a person's direction or path. The character for head represents the idea of conscious choice. The character for head also suggests a beginning, and foot, an ending. Thus the character for tao also conveys the continuing course of the universe, the circle of heaven and earth. Finally, the character for tao represents the Taoist idea that the eternal Tao is both moving and unmoving. The head in the character means the beginning, the source of all things, or Tao itself, which never moves or changes; the foot is the movement on the path (Harts 9). Taoism upholds the belief in the survival of the spirit after death. "To have attained the human form must be always a source of joy. And then to undergo countless transitions, with only the infinite to look forward to, what comparable bliss is that! Therefore it is that the truly wise rejoice in, that which can never be lost, but endures always" (Leek 190). Taoist believe birth is not a beginning, death is not an end. There is an existence without limit. There is 2 continuity without a starting point. Applying reincarnation theory to Taoism is the belief that the soul never dies, a person's soul is eternal. "You see death in contrast to life; and both are unreal both are a changing and seeming. Your soul does not glide out of a familiar sea into an unfamiliar ocean. That which is real in you, your soul, can never pass away, and this fear is no part of her" (Head2 199). In the writings of The Tao Te King, tao is described as having existed before heaven and earth. Tao is formless, stands alone without change and reaches everywhere without harm. The Taoist is told to use the light that is inside to revert to the natural clearness of sight. By divesting oneself of all external distractions and desires, only then can one achieve tao. In ancient days a Taoist that had transcended birth and death, achieved tao, was said to have cut the Thread of Life (Kapleau 13). The soul, or spirit, is Taoism does not die at death. The soul is not reborn, it migrates to another life. This process, the Taoist version of reincarnation, is repeated until tao is achieved. The following translation from The Tao Te King best summarizes the the theory behind tao and how a Taoist can achieve Tao. The Great Way is very smooth, but the people love the by-paths. . . The wearing of gay embroidered robes, the carrying of sharp swords, fastidiousness in food and drink, superabundance of property and wealth: - this I call flaunting robbery; most assuredly it is not Tao. . . He who acts in accordance with Tao, becomes one with Tao. . . Being akin to Heaven, he possesses Tao. Possessed of Tao, he endures forever. . . Being great (Tao) passes on; passing on, it becomes remote; having become remote, it returns (Head3 109). 3 Buddhism The followers of the Buddha believe life goes on and on in many reincarnations or rebirths. The eternal hope for all followers of Buddha is that through reincarnation one comes back into successively better lives - until one achieves the goal of being free from pain and suffering and not having to come back again. This wheel of rebirth, known as samsara, goes on forever or until one achieves Nirvana. The Buddhist definition of Nirvana is "the highest state of spiritual bliss, as absolute immortality through absorption of the soul into itself, but preserving individuality" (Head1 57). Birth is not the beginning and death is not the end. This cycle of life has no beginning and can go on forever without an end. The ultimate goal for every Buddhist, Nirvana, represents total enlightenment and liberation. Only through achieving this goal is one liberated from the never ending round of birth, death, and rebirth (Head3 73). Transmigration, the Buddhist cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, involves not the reincarnation of a spirit but the rebirth of a consciousness containing the seeds of good and evil deeds. Buddhism's world of transmigration encompasses three stages. The first stage in concerned with desire, which goes against the teachings of Buddha, is the lowest form and involves a rebirth into any number of hells. The second stage is one in which animals dominate. But after many reincarnations in this stage the spirit becomes more and more human, until one attains a deep spiritual understanding. At this point in the second stage the Buddhist gradually begins to 4 abandon materialism and seek a contemplative life. The Buddhist in the third stage is ultimately able to put his ego to the side and become pure spirit, having no perception of the material world. This stage requires one to move from perception to non-perception. And so, through many stages of spiritual evolution and numerous reincarnations, the Buddhist reaches the state of Nirvana (Leek 171). The transition from one stage to another, or the progression within a stage is based on the actions of the Buddhist. All actions are simply the display of thought, the will of man. This will is caused by character, and character is manufactured from karma. Karma means action or doing. Any kind of intentional action whether mental, verbal or physical is regarded as karma. All good and bad actions constitute karma. As is the karma, so is the will of the man. A person's karma determines what he deserves and what goals can be achieved. The Buddhists past life actions determine present standing in life and current actions determine the next life, all is determined by the Buddhist's karma (Kapleau 20). Buddha developed a doctrine known as the Four Noble Truths based on his experience and inspiration about the nature of life. These truths are the basis for all schools of Buddhism. The fourth truth describes the way to overcome personal desire through the Eightfold Path. Buddha called his path the Middle Way, because it lies between a life of luxury and a life of poverty. Not everyone can reach the goal of Nirvana, but every Buddhist is at least on the path toward enlightenment. To achieve Nirvana the Buddhist must follow the steps of the Eightfold Path. 5 1. Right Knowledge is knowledge of what life is all about; knowledge of the Four Noble Truths is basic to any further growth as a Buddhist. 2. Right Aspiration means a clear devotion to being on the Path toward Enlightenment. 3. Right Speech involves both clarity of what is said and speaking kindly and without malice. 4. Right Behavior involves reflecting on one's behavior and the reasons for it. It also involves five basic laws of behavior for Buddhists: not to kill, steal, lie, drink intoxicants, or commit sexual offenses. 5. Right Livelihood involves choosing an occupation that keeps an individual on the Path; that is, a path that promotes life and well-being, rather than the accumulation of a lot of money. 6. Right Effort means training the will and curbing selfish passions and wants. It also means placing oneself along the Path toward Enlightenment. 7. Right Mindfulness implies continuing self-examination and awareness. 8. Right Concentration is the final goal to be absorbed into a state of Nirvana (Comptons). Compliance to the path does not guarantee reaching Nirvana, but it is the only path that leads to Nirvana. Only through following this path established by Buddha does a Buddhist have a chance to reach enlightenment, to free oneself from the continuous rounds of birth, death and rebirth, to have reached the ultimate goal - to be absorbed into a state of Nirvana. Comparison The goal in both Taoism and Buddhism is to reach the ultimate goal, to transcend life on earth as a physical being, to achieve harmony with nature and the universe. The ultimate goal for both religions is to achieve immortality. The Taoist called this ultimate goal Tao, while the Buddhist seek Nirvana. Whatever the name, the followers of these religions believe there is an existence beyond life which can be achieved provided the right path or behavior is followed. The path to Tao and Nirvana are similar, yet different. Both believe there is an inner light which guides a person in the right direction to the ultimate goal. Personal desires must be forsaken to enable the inner light to guide a person to achieve eternal bliss. "The teaching 6 regarding the inner light is just as prominent in the Taoist schools as it is among the practices of Buddhism" (Politella 36). The inner light concept is similar, but the actual path is the difference between Taoism and Buddhism. The path toward enlightenment for the Buddhist was defined by Buddha in his Eightfold Path. Only through following this path does the Buddhist reach Nirvana. The path to Tao is individual, it comes from within. No one can define a path for the Taoist, it must come from the inner light. "Tao means way, but in the original and succeeding manuscripts no direct path is explored or expounded. Desire, ambition, fame, and selfishness are seen as complications. That idea is consistent with Buddhist teachings; it is the personal life of each individual that gives Taoism its special form" (Leek 188). Taoism and Buddhism perceive life, death and rebirth as a continuous cycle. This cycle has no beginning and no end. The soul is eternal, yet the soul is not the object of reincarnation. Taoist believe the soul is not reborn, it "migrates to another life" (Head3 109). Buddhist also believe the soul is not reborn, but instead a "consciousness containing the seeds of good and evil deeds" is the object of rebirth (Leek 171). One major difference between Taoism and Buddhism is the concept of karma to the Buddhist. This idea that all actions are the display of thought, the will of man, is known as karma. Karma determines the Buddhist actions and position in life. A person's karma limits the goals which can be achieved. Karma determines where in the cycle of birth, death and rebirth the consciousness returns. This return can be in the form of an animal or human, and the 7 Buddhist must progress through a hierarchy to achieve Nirvana (Leek 171). The Taoist has no concept similar to karma, and no mention of the soul migrating to an animal form. The determining factor to one's life is contained in the individual behavior for the Taoist. By forsaking personal desires in life, by concentrating of the self, a longer life is prolonged. Eventually, by following the inner light, immortality can be achieved. The similarities between Taoism and Buddhism in the belief of life after death far outweigh the differences. Both religions believe the individual must focus on the self to achieve the ultimate goal. To focus on oneself, all desires and personal ambitions must be forsaken. One must focus on the self and the proper way of life to reach immortality. The cycle of life continues indefinitely until the Thread of Life is broken. Only through proper living, by following the correct path guided by the inner light, can one achieve the ultimate goal of Tao or Nirvana. By Rick Dempster 8