* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Neck [9-29
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
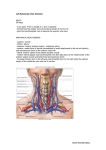
The Neck Bones, Ligaments, and Joints: Bones: - - Typical Cervical Vertebrae: small bodies, transverse foramen, bifid spinous process, groove for spinal nerve on transverse process Atlas, C1: anterior arch with tubercle and facet for dens, posterior arch with tubercle and sulcus for vertebral artery, lateral mass (with superior and inferior articular processes), transverse foramen Axis, C2: dens (odontoid process), transverse foramen Hyoid Bone: at the level of C3, does not articulate with any other bone. It attaches to the floor of the oral cavity (superiorly), the larynx (inferiorly), and the pharynx (posteriorly) Joints: - Atlanto-occipital Joints: between occipital bone and atlas, allows head to nod Atlanto-axial Joints: between atlas and axis, allows rotation of head Zygapophyseal joints: between superior and inferior articular processes, form posterior part of intervertebral foramen wall Ligaments: - Nuchal Ligament: prevents excessive flexion of head/neck, attaches to back of occipital bone and runs along spinous processes, eventually becoming the supraspinous ligament Alar Ligaments: prevent excessive rotation of head and atlas relative to the axis, attaches dens to medial surfaces of occipital condyles Transverse Ligament: holds dens in position, attaches posterior dens to medial surfaces of lateral masses of atlas Apical Ligament of Dens: attaches dens to foramen magnum Cruciform Ligament: connects foramen magnum, atlas, and axis Fascia of the Neck: Involved in spread of infection. Fascia Superficial Location From superficial fascia of thorax to the mandible Investing Surrounds all structures of the neck Prevertebral Surrounds vertebral column and deep muscles of back Contents Platysma Trapezius, SCM, all of neck Pierced by external and anterior jugular veins, and lesser occipital, great auricular, transverse cervical, and supraclavicular nerves Cervical vertebrae, scalene muscles, deep muscles of back. Extends to form axillary sheath. Pretracheal Carotid Sheaths Anterior neck, surrounds viscera Surround the 2 neurovascular bundles on either side of anterior neck Trachea, esophagus, thyroid Common carotid artery, internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and the vagus nerve Muscles of the Neck: Muscle Platysma Sternocleidomastoid Trapezius Attachments Superficial fascia of upper thorax and fascia of mandible Manubrium and medial clavicle to mastoid process and lateral superior Nuchal line Superior Nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, ligamentum nuchae, Innervation Action Facial nerve [VII] “scary face” Accessory nerve [XI] and C2-C3 (proprioception) Lateral flex to same side, rotate to opposite side, and flex head (bilat.) Rotate scapula, elevate, adduct, and depress scapula Accessory nerve [XI] and C3-C4 (proprioception) Splenius Capitis Levator Scapulae Anterior Scalenes Middle Scalenes Posterior Scalenes Omohyoid Sternothyroid Sternohyoid Thyrohyoid Stylohyoid Mylohyoid Geniohyoid spinous processes C7T12 to clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula Ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes C7T4 to mastoid process, skull below lateral superior nuchal line Transverse process of C1-C4 to upper part of medial border of scapula Transverse processes of C3-C6 to scalene tubercle and rib 1 Transverse processes of C2-C7 to rib 1 Transverse processes of C4-C6 to rib 2 Superior border of scapula medial to suprascapular notch to body of hyoid lateral to sternohyoid Posterior manubrium to oblique line on lamina of thyroid cartilage Posterior sternoclavicular joint and adjacent manubrium to body of hyoid medial to omohyoid attachment Oblique line on lamina of thyroid cartilage to greater horn and adjacent body of hyoid Styloid process to lateral hyoid body Posterior rami of middle cervical nerves Extend head, draw and rotate head to same side (unilaterally) C3, C4, and dorsal scapular nerve (C4, C5) Elevate scapula Anterior rami of C4-C7 Elevate rib 1 Anterior rami of C3 to C7 Anterior rami of C5 to C7 Elevate rib 1 Anterior rami of C1 to C3 through the ansa cervicalis Depresses and fixes hyoid bone Anterior rami of C1 to C3 through the ansa cervicalis Draws larynx (thyroid cartilage) downward Anterior rami of C1 to C3 through the ansa cervicalis Depresses hyoid after swallowing Anterior rami fibers of C1 (carried along [XII]) Facial Nerve [VII] Elevate rib 2 Depresses hyoid bone, raises larynx when hyoid is fixed Pulls hyoid upward posterosuperiorly Mylohyoid line on mandible to body of hyoid Anterior: mylohyoid nerve from inferior alveolar branch of mandibular nerve [V3] Support and elevate floor of mouth, elevate hyoid bone Inferior mental spine on inner mandible to Branch from anterior ramus of C1 (carried Fixed mandible elevates and pulls hyoid forward; Digastric Rectus Capitis Anterior Rectus Capitis Lateralis Longus Colli Longus Capitis anterior body of hyoid along [XII]) Anterior: digastric fossa on lower inside of mandible to shared tendon on hyoid body Posterior: medial mastoid process to shared tendon Atlas to basilar part of occipital bone Atlas to jugular process of occipital bone Transverse processes of C3-C5, bodies of C5-C7 and T1-T2 to atlas, transverse processes of C5 and C6, and bodies of C2-C4 Transverse processes of C3-C6 to basilar part of occipital bone Anterior: mylohyoid nerve from inferior alveolar branch of mandibular nerve [V3] Posterior: Facial Nerve [VII] Anterior rami of C1, C2 Anterior rami of C1, C2 Anterior rami of C2 to C6 Anterior rami of C1 to C3 fixed hyoid pulls mandible downward and inward Anterior: opens mouth by lowering mandible, raises hyoid Posterior: pulls hyoid upward and back Flex Atlanto-occipital joint Lateral flexion to same side Flex neck anteriorly and laterally, slight rotation to opposite side Flex head Triangles of the Neck: Triangle Anterior Triangle Submandibular Submental Muscular Borders Anterior border of SCM (laterally), inferior border of mandible (superiorly), and midline of the neck (medially) Inferior border of mandible, anterior and posterior digastric bellies Hyoid, anterior digastric belly, and midline Hyoid bone, superior omohyoid belly, anterior border of Vessels and Nerves Common carotid arteries and their branches: the external and internal carotids Internal jugular vein and its tributaries Cranial Nerves [VII], [IX], [X], [XI], and [XII], Transverse Cervical Nerve (from cervical plexus), and upper and lower roots of the ansa cervicalis [XII], mylohyoid nerve, facial artery and vein Tributaries to anterior jugular vein Other Contents Thyroid and parathyroid glands, cricoid cartilage, esophagus, trachea Suprahyoid muscles, submandibular gland, submandibular lymph nodes Suprahyoid muscles, submental lymph nodes Infrahyoid muscles, thyroid and parathyroid glands, SCM, and midline Carotid Posterior Triangle Subclavian Superior omohyoid belly , stylohyoid, posterior digastric belly, and anterior border of SCM SCM (anteriorly), trapezius (posteriorly), middle 1/3 clavicle (basally), occipital bone (apically) SCM, omohyoid, clavicle Major Arteries of the Neck: pharynx Tributaries to common facial vein, cervical branch of [VII], common carotid artery, external and internal carotid arteries, superior thyroid a., ascending pharyngeal a., facial and lingual aa., occipital a., internal jugular vein, [X], [XI], [XII], superior and inferior roots of ansa cervicalis, and transverse cervical nerve External jugular vein, posterior external jugular vein, subclavian artery and vein, transverse cervical artery, suprascapular artery, [XI], branches of cervical plexus, brachial plexus Subclavian branches, phrenic nerve Inferior belly of omohyoid Anterior scalene - Subclavian: 3 parts o 1st Part: ascends to medial border of anterior scalene, gives off vertebral artery (enters transverse foramen of C6), thyrocervical trunk (gives rise to inferior thyroid, transverse cervical, and suprascapular arteries), internal thoracic artery, left costocervical trunk o 2nd Part: passes between anterior and middle scalene muscles, gives off right costocervical trunk (gives rise to deep cervical and supreme intercostal arteries) o 3rd Part: emerges from lateral border of anterior scalene and crosses base of posterior triangle to rib 1, becoming the axillary artery, gives off dorsal scapular artery - Common Carotid: the right one originates from brachiocephalic trunk while the left originates from the aortic arch, both pass through carotid sheaths to give off 2 terminal branches: internal and external carotid arteries. The carotid sinus (dilation at bifurcation) contains blood pressure receptors ([IX]). The carotid body contains oxygen receptors ([IX] and [X]). - Internal Carotid: ascends toward base of skull giving no branches in neck, and enters the carotid canal in the petrous part of the temporal bone. It supplies the cerebral hemispheres, eyes and contents of the orbits, and the forehead. External Carotid: branches include (SomeAngryLadyFiguredOutPMS) o Superior Thyroid: thyrohyoid muscle, internal larynx, SCM and cricothyroid muscles, thyroid gland o Ascending Pharyngeal: pharyngeal constrictors and stylopharyngeus muscle, palate, tonsil, pharyngotympanic tube, meninges in posterior cranial fossa o Lingual: muscles of tongue, palatine tonsil, soft palate, epiglottis, floor of mouth, sublingual gland o Facial: all face strictures from inferior border of mandible to the masseter muscle to the medial corner of the eye, soft palate, palatine tonsil, pharyngotympanic tube, submandibular gland o Occipital: SCM muscle, meninges in posterior cranial fossa, mastoid cells, deep muscles of back, posterior scalp o Posterior Auricular: parotid gland and nearby muscles, external ear and scalp posterior to ear, middle and inner ear structures o Superficial Temporal: parotid gland and duct, masseter muscle, lateral face, anterior external ear, temporalis muscle, parietal and temporal fossae o Maxillary: external acoustic meatus, lateral and medial tympanic membrane, TMJ, dura mater of lateral wall of skull and inner table of cranial bones, trigeminal ganglion and dura in vicinity, mylohyoid muscle, mandibular teeth, skin on chin, temporalis muscle, outer table of skull bones in temporal fossa, infratemporal fossa structures, maxillary sinus, upper teeth and gingival, infra-orbital skin, palate, roof of pharynx, nasal cavity - Major Veins of the Neck: Superficial and Deep Drainage: all returns to the jugular system to enter subclavian veins - - External Jugular Vein: passes within superficial fascia and is superficial to SCM, formed by: o Posterior external jugular vein o Transverse cervical vein o Suprascapular vein o Posterior auricular vein o Retromandibular vein (posterior division) : formed in parotid gland by superficial temporal vein maxillary vein Anterior Jugular: connect to form jugular venous arch before entering subclavian veins Internal Jugular Vein: Begins as a dilated continuation of the sigmoid sinus (dural venous sinus) and receives blood from the inferior petrosal sinus. It leaves the jugular foramen of the skull and descends in the carotid sheath, joining with the subclavian veins to form the brachiocephalic veins. Its tributaries include: o Inferior Petrosal Sinus o Facial o o o o o Lingual Pharyngeal Occipital Superior Thyroid Middle Thyroid Nerves in the Anterior Triangle of the Neck: - [VII] Facial: from stylomastoid foramen, innervates posterior belly of digastric, stylohyoid, and platysma [IX] Glossopharyngeal: from jugular foramen, innervates stylopharyngeus, carotid sinus, and sensory for pharynx [X] Vagus: from jugular foramen, enters carotid sheath, innervates pharynx (motor), carotid body, superior laryngeal nerve [XI] Accessory: from jugular foramen, no branches in anterior triangle [XII] Hypoglossal: from hypoglossal canal, supplies tongue, no branches in anterior triangle Transverse Cervical nerve: branch of cervical plexus from C2 and C3 anterior rami, loops around SCM and supplies cutaneous area of anterior triangle Ansa Cervicalis: loop of fibers from C1-C3 that innervate the “strap muscles” (infrahyoids). It begins as branches from C1 join [XII]. C1 makes up superior root while C2 and C3 make up the inferior root. Nerves in the Posterior Triangle of the Neck: - - [XI] Accessory: from jugular foramen, innervates the trapezium and the SCM. Cervical Plexus: Anterior rami of C2-C4 with muscular and cutaneous branches. The muscular branches include the phrenic nerve, the ansa cervicalis, and innervations to prevertebral and lateral vertebral muscles. Cutaneous branches include: o Transverse cervical nerve: lateral and anterior neck o Lesser occipital nerve: neck and scalp posterior to the ear o Great auricular nerve: skin of parotid area, ear, and mastoid process o Supraclavicular nerves: skin of clavicle and shoulder down to rib 2 Brachial Plexus: C5-T1 Sympathetic Trunk: - Cervical part of sympathetic trunk lies anterior to longus colli and capitis muscles and posterior to common carotid artery and is connected to each cervical nerve by a gray ramus communicans. Three ganglia are associated with the cervical aspect of the sympathetic trunk: o Superior Cervical Ganglion: located between C1 and C2 vertebrae, its branches go to internal and external carotid arteries, C1-C4, pharynx, and to the heart as superior cardiac nerves o Middle Cervical Ganglion: located at vertebra C6, its branches go to C5-C6 and to the heart as middle cardiac nerves o Inferior Cervical Ganglion (Stellate Ganglion): located at vertebra C7, its branches go to C7-T1, vertebral artery, and to the heart as inferior cardiac nerves Lymphatics of the Neck: - - Thoracic Duct: empties into the junction of the left internal jugular and left subclavian veins. It is joined by the left jugular trunk, left subclavian trunk, and the left bronchomediastinal trunk On the right the right jugular trunk, right subclavian trunk, and the right bronchomediastinal trunk empty into the junction of the right internal jugular and right subclavian veins Superficial Lymph Nodes: drain face and scalp, follow patterns of arterial system in this area o Occipital Nodes: associated with occipital artery, drain posterior scalp and neck o Mastoid Nodes: associated with posterior auricular artery, drain posterolateral scalp o Pre-auricular and Parotid Nodes: associated with superficial temporal and transverse facial arteries, drain anterior auricle, Anterolateral scalp, upper half of face, the eyelids, and the cheeks o Submandibular Nodes: associated with facial artery, drain forehead, gingivae, teeth, and tongue o Submental Nodes: drain center part of lower lip, chin, floor of mouth, tip of tongue, and lower incisor teeth Superficial Cervical Lymph Nodes: located along external jugular vein on the surface of the SCM, drain occipital and mastoid nodes Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes: located along internal jugular vein, divided into upper and lower groups based on the intermediate tendon of the omohyoid muscle, receive all lymph drainage from the head and nearby lymph vessels form the jugular trunks o Jugulodigastric Node: drains tonsils o Jugulo-omohyoid Node: drains tongue Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands: - - Thyroid: anterior in the neck and lateral to thyroid cartilage, made up of 2 lateral lobes, 2 pyramidal lobes that touch the hyoid, and a central isthmus (2nd and 3rd tracheal cartilages), surrounded by pretracheal fascia. o Supplied by the superior thyroid artery (external carotid) which divides into anterior and posterior glandular branches and the inferior thyroid artery (thyrocervical trunk) which divides into inferior and ascending branches. o Drained by the superior thyroid vein (internal jugular), middle thyroid vein (internal jugular), and inferior thyroid vein (brachiocephalic) o Lymph drains to paratracheal and deep cervical nodes o The recurrent laryngeal nerves run closely along the posterolateral aspects of the thyroid gland Parathyroid: 4 small, ovoid glands located on the posterior surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland, designated as superior and inferior. o Supplied by inferior thyroid arteries and the venous and lymphatic drainage follows that of the thyroid gland