* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 221 exam 3
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Taura syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
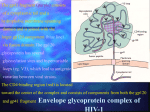
BioSc221/325 Exam 3 Name ______________________________ Multiple choice. (1 point each) Choose the one best answer to each of the following questions. ____ Viral protein that assembles in the host cytoplasmic membrane and functions in attachment to a new host cell. A. matrix protein B. hemagglutinin C. pilin D.replicase ____ The symptoms of viral infection are primarily due to A. the body's response to the invasion B. toxins released by the virus C. insertion of the viral genome into the host cell D. all of the above ____ Amantidine, an antiviral drug, inhibits A. endocytosis B. lysozomal fusion C. matrix protein changes D. neuraminidase ____ Which of the following areas of the body has a resident microbiota? A. lung alveoli B. liver C. bladder D. ear ____ Which statement(s) is/are false? A. Gram positive organisms dominate the microbiota of the skin. B. The presence of Propionibacterium acnes is a clear indication of disease. C. Staphylococcus epidermidis is a commensal organism that occasionally causes disease. D. All of the above ____ Which of the following phenomena is/are associated with the metabolic and biochemical activities of the colonic microbiota? A. Vitamin synthesis B. Production of amines C. Production of organic acids D. All of the above ____ Influenza virus inhibits host cell translation and promotes translation of viral transcript by a process known as A. CAP stealing B. reverse transcription C. blocking the shine-dalgarno sequence of host transcripts D. latency ____ The microbiota of the skin tend to be A. salt tolerant B. pH sensitive C. always aerobes D. all of the above ____ Anaerobic microbes that dominate the colonic microbiota belong to the genus A. Lactobacillus sp. B. Bacteroides sp. C. Clostridium sp. D. Escherishia sp. ____ Illness that can result from a dramatic decrease in the resident colonic microbiota after aggressive antibiotic therapy A. pseudomembranous colitis B. tetanus C. infant botulism D. dysentery ____ Morpholines are antifungal compounds that inhibit A. Protein synthesis B. Ergosterol synthesis C. Mitochondrial respiration D. Chitin synthesis ____ Group of primarily photosynthetic protists that are the cause of "red tides". A. Algae B. Diatoms C. Dinoflagellates D. Euglenoids ____ Group of archaezoan protists that include the disease causing microbie Giardia intestinalis. A. parabasalians B. amoeboflagellates C. apicomplexa D. diplomonads ____ The archaezoan Trychonympha benefits the termite Reticulotermes by production of A. methane B. hydrogen C. acetate D. vitamins ____ Group of microbes that undergo a complex lifestyle including a slug and fruiting body stage and serves as a model system for development. A. diplomonads B. slime molds C. lichens D. fungi ____ Viral proteins that interact with the membrane-embedded portion of envelope proteins and with capsid proteins to help link the envelope to the capsid. A. matrix protein B. nucleoprotein C. envelope glycoprotein D. capsomere ____ Envelope glycoprotein that cleaves sialic acid residues from carbohydrate residues on the cell surface. A. hemaglutinin B. neuraminidase C. glycoprotein D. nucleoprotein ____ RNA-dependent RNA polymerase found in influenza virus which produces a + strand from the - strand influenza virus genome. A. reverse transcriptase B. helicase C. neuraminidase D. replicase Short answer. (1 point each) Lichens are organisms resulting from the symbiotic relationship between which two types of organisms? What is neutropenia? What is opsonization? What are the three possible roles of the resident microbiota of the human body? List two possible outcomes of a viral infection? Name two viral characteristics used to classify mammalian viruses Describe one reason why a virus might produce completely different outcomes in two different people. Name one piece of evidence that suggests the archaezoa represent the earliest eukaryotes? If you were designing an antiviral drug what aspect of viral replication might be a good target? The Baltimore system of viral classification is based upon the relationship between the viral genome and what molecule? The microbiota of the small intestine and the colon are quite different. Name two reasons for this difference. How does lactoferrin inhibit the growth of microorganisms? Specialized lymphoid tissue underlies the skin or mucosal epithelium. Name one of these tissues (acronym is OK). Name one of the antibacterial substances found in mucin. Describe two mechanisms by which microbes avoid killing by neutrophils. Which complement protein serves as a signal to direct neutrophils to the sight of a bacterial infection? What is the hallmark of septic shock? What are cytokines? Short Essay Questions. Please answer three of the following four short essay questions (6 points each - 6 bonus points possible for answering all 4 questions) Describe the stages in the life cycle of the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium sp. Describe the process by which an enveloped virus escapes from it’s host cell by budding. Select an area of the human body that has a resident microbiota and describe the conditions in that location and the types of microbes found there. Describe the ingestion and killing of microbes by a neutrophil and explain why neutrophils are described as “sloppy” eaters.