* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AlgI B Notes 8.8 5-19-14
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
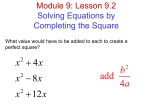
Algebra I Honors Notes Section 8.8– Completing the Square Objective: Solve quadratic equations by completing the square Date: _____________ (CC.9-12.A.REI.4a) We can make any trinomial a perfect square trinomial by completing the square. This makes it easy to solve the equation by taking the square root of each side. In a perfect square trinomial, there is a relationship between the coefficient of the ___________ term and the _________________ term. x 2 6x 9 x 2 8 x 16 _______ 9 _______ 16 EXAMPLE 1: Completing the Square. Complete the square to form a perfect-square trinomial. 2 A) x 10 x _____ Step1: Identify b. 2 Step2: Find b . 2 2 Check: Add b to the expression. 2 B) x 2 9 x _____ Step1: Identify b. 2 Step2: Find b . 2 2 Check: Add b to the expression. 2 Check it out! Complete the square to form a perfect-square trinomial. 1a) x 2 12 x _____ 1b) x 2 5 x _____ 1c) 8 x x 2 _____ To solve a quadratic equation in the form x 2 bx c , first complete the square of x 2 bx . Then you can solve using square roots. EXAMPLE 2: Solving x 2 bx c by Completing the Square. Solve by completing the square. Check your answer. A) x 2 14 x 15 Step1: Write the equation in the form x 2 bx c 2 Step2: Find b . 2 Step3: Complete the square. Step4: Factor and simplify. Step5: Take the square root of both sides. Step6: Write and solve two equations. B) x 2 2 x 2 0 Step1: Write the equation in the form x 2 bx c 2 Step2: Find b . 2 Step3: Complete the square. Step4: Factor and simplify. Step5: Take the square root of both sides. Step6: Write and solve two equations. Check it out! Solve by completing the square. Check your answer. 2a) x 2 10 x 9 2b) t 2 8t 5 0 EXAMPLE 3: Solving ax 2 bx c by Completing the Square. Solve by completing the square. A) 2 x 2 12 x 20 0 Step1: Write in the form x 2 bx c 2 Step2: Find b . 2 Step3: Complete the square. Step4: Rewrite using like denominators. Step5: Factor and simplify. Step6: Take the square root of both sides. Step76: Write and solve two equations. B) 3x 2 10 x 3 Step1: Write in the form x 2 bx c 2 Step2: Find b . 2 Step3: Complete the square. Step4: Rewrite using like denominators. Step5: Factor and simplify. Step6: Take the square root of both sides. Step76: Write and solve two equations. Step6: Write and solve two equations. Check it out! Solve by completing the square. Check your answer. 3a) 3x 2 5 x 2 0 3b) 4t 2 4t 9 0 EXAMPLE 4: Problem Solving Application A landscaper is designing a rectangular brick patio. She has enough bricks to cover 144 square feet. She wants the length of the patio to be 10 feet greater than the width. What dimensions should she use for the patio? Check it out! 4) An architect designs a rectangular room with an area of 400 ft². The length is to be 8 ft longer than the width. Find the dimensions of the room. Round your answers to the nearest tenth of a foot.