* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
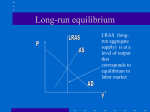
Inflationary and Recessionary Gaps With the Classical / Monetarist / Neo-Classical Model long run equilibrium is as follows: LRAS Price Level Pf AD Yf RGDP Short run equilibrium may differ from Long Run macroeconomic SR: period of time when prices of final g&s change, but factor prices do not – so final prices are in equilibrium, but factor prices are not macroeconomic LR: period of time when factor prices do adjust to final prices, AS=AD at full employment of fop in the LR SR equilibrium may be to the R of LRAS Inflationary gap SR equilibrium may be to the L of LRAS Deflationary gap Real GDP LR real GDP 2 3 4 5 Time Year 2: recessionary gap actual output is less than real GDP unemployment of resources LRAS price level SRAS AD Y2 Yf RGDP Y2 to Yf is the recessionary gap the economy is operating at less than full employment in the SR also called unemployment equilibrium as Y2 to Yf represents unemployed fop Year 3 : full employment Price level LRAS SRAS AD Yf RGDP Year 4: inflationary gap LRAS SRAS AD Yf Y4 RGDP Yf to Y4 is an inflationary gap the economy is operating at greater than full employment in the SR o fop are over-employed – workers are working overtime, capital is employed in double shifts