* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Analytical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
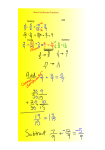
Date, October 5th, 2010 AIM: How do we solve one- and two- step equations? Objectives: SWBAT -solve equations of the type x + a = b, where a and b are rational numbers, by isolating the variable using inverses, by guess and check, by manipulating algebra tiles - check the solutions and write the solution set - solve equations of the type ax = b, where a and b are rational signed numbers, by isolating the variable using reciprocals, guess and check. - investigate the connections between solving equations of the form ax=b and x+a=b - select and apply the appropriate isolation method for solving equations of the form ax=b as compared to solving equations of the form x+a=b - isolate the variable using properties of inverses and identities - solve equations of the type ax + b = c where a, b, and c are rational signed numbers Standards: A.A.21 Determine whether a given value is a solution to a given linear equation in one variable A.A.22 Solve all types of linear equations in one variable (including 1-step, 2-step ) A.A.26 Solve algebraic proportions in one variable which result in linear or quadratic equations (only linear for now) Quiz: Choose 2. 1. 5x 35 2. 35= 3 + 5x Key Points Common Mistakes 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4d 2 6 To solve equations, use inverse operations in the reverse order of operations 5-x=10 is actually a two-step equation. –x is the same as -1*x. Students will solve an equation “4-b=10” by adding 4. Students are afraid when they do not get integers as answers 3. Students forget what to do when they see Do Now Minilesson d 6. 4 Substitution into equations, inverse operations. One way to find the solution of an equation is to get the variable _alone_on one side of the equal sign. We can do this using ___Inverse operations_, which are operations that undo one another. Since we use the inverse (opposite) operation to undo, we perform these operations in the opposite order from the _order of operation. First undo ___addition and subtraction. Then, undo multiplication and division. One way to find the solution of an equation is to get the variable _________on one side of the equal sign. We can do this using ______________________________, which are operations that undo one another. Since we use the inverse (opposite) operation to undo, we perform these operations in the opposite order from the _____________________________________. The inverse of addition is ____________________________; subtraction is ___________________________; Multiplication is ________________________; division is _____________________________. Note: -x is the same as _____________________. To Solve Two-Step Equations: First undo _______________________________. Then, undo ___________________________________. Guided Practice Think, Pair, Share ( group work) Independent Practice Processing Questions Summary Demonstrate solving one and two steps equations See attached. 9 problems dealing with one and two steps equations and proportions. 1) 3x-2 = 4 2) 10= m +2 4 In example 1 and 2 what operation do we undo first, why and how do we do it? How is solving a two step equation like working the order of operations backwards? MATH MASTER: ____________________________________________________ ALGEBRA DATE:_____________________________________________________________ PAGE: _______ AIM:_____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ DO NOW( 5 MINUTES) 1. Substitute the given value into the equation and see if it makes the sentence true or false. a) 3x 5 3 ( x 0) b) 2x 4 2 ( x 1) 2. What is the difference between #1 and #2? 3. Can you find a solution for each equation? If so, how do you know? a) g+7 = 11 b) 4c = -96 4.What is the sum of 75 and 48 ? [A.N.3] (1) 123 (3) 9 6 (2) 9 3 (4) 41 3 MINI-LESSON( 3 minutes) Frayer Model 1) 3x-2 = 4 2) 10= m +2 4 Procedure: GUIDED PRACTICE( 5 MINUTES) Check: Procedure: Check: MEDIAL SUMMARY ( 3 MINUTES) In examples 1 and 2 what operations do we undo first? Why? How did we do this? THINK( 5 MINUTES ) , PAIR AND SHARE( 3 MINUTES) Solve each equation. Show all your steps. Choose two equations to check. 1) 3x 21 3) 4 2x 10 x 2) 2 4 4) x 5 1 3 5) 7 x 8 Check 6) x2 5 9 Check INDEPENDENT PRACTICE( 15 MINUTES) 1) x -15 = 20 4) 7- 3k = -14 7) -8-c = 11 2) x 12 4 5) -8-c = 11 8) 4 m 6 9 3) 3x-15 =33 6) a 15 30 5 9) 2x 3 10 ( Summary Reflection 4 minutes) Quiz ( 7 minutes) REFLECTION: WHAT DID YOU LEARN TODAY? On a SUMMARY: How is solving a two step equation like working the order of operations backwards? scale of 1 to 10, how well do you think you met ___________________________________________ today’s objective? What questions do you still have? ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ TOTAL POINTS