* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download index
IEEE 802.1aq wikipedia , lookup
Multiprotocol Label Switching wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Piggybacking (Internet access) wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Internet protocol suite wikipedia , lookup
UniPro protocol stack wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Routing in delay-tolerant networking wikipedia , lookup
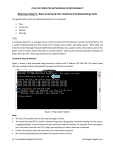
Aim 1: To study the NETWORK COMMANDS 1. PING Ping is a computer network administration utility used to test whether a particular host is reachable across an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the round-trip time for packets sent from the local host to a destination computer, including the local host's own interfaces. Ping operates by sending Internet Control Message. Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets to the target host and waits for an ICMP response, sometimes casually called a pong. Ping Program was written By “Michael John Muuss” in December 1983. Ping local host .Pings the local host, this will allow you to see if the computer is able to send information out and receive the information back. Note that this does not send information over a network but may allow you to see if the card is being seen. ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx Allows you to ping another computer where the x's are located are where you would place the IP address of the computer you are attempting to ping. If this is not able to complete, this should relay back an unsuccessful message, which could be an indication of cable issues, network card issues, hub issue, etc. ping computerhope.com 1. PING computerhope.com (204.228.150.3) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from www.computerhope.com (204.228.150.3): icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=0.267ms 2. c:\>ping Usage: ping [-t] [-a] [-n count] [-l size] [-f] [-i TTL] [-v TOS] [-r count] [-s count] [[-j host-list] | [-k host-list]] [-w timeout] target_name To see statistics and continue - type Control-Break; To stop - type Control-C. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 1 Options: -t - Ping the specified host until stopped. -a - Resolve addresses to hostnames. -n count - Number of echo requests to send. -l size - Send buffer size. -f - Set Don't Fragment flag in packet. -i TTL - Time To Live. -v TOS - Type Of Service. -r count - Record route for count hops. -s count - Timestamp for count hops. -j host-list - Loose source route along host-list. -k host-list - Strict source route along host-list. -w timeout - Timeout in milliseconds to wait for each reply. C:\>ping –t 127.0.0.1 Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 2 C:\>ping –a 127.0.0.1 C:\>ping –n 5 127.0.0.1 Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 3 C:\>ping –l 5 127.0.0.1 C:\>ping –f 127.0.0.1 Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 4 C:\>ping –i 8 127.0.0.1 C:\>ping –v 3 127.0.0.1 Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 5 C:\>ping –r 5 127.0.0.1 C:\>ping –s 4 127.0.0.1 Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 6 C:\>ping –w 2 127.0.0.1 Example PING -n 1 -w 7500 Server_06 PING -w 7500 MyHost && ECHO MyHost found PING -w 7500 MyHost || ECHO MyHost not found PING -n 5 www.microsoft.com PING -n 5 -w 7500 microsoft.com Troubleshooting with ping Ping the IP address of your local loopback, using the command ping 127.0.0.1. Ping the assigned IP address of your local network interface card (NIC). Ping the IP address of another known good system on your local network. Verify connectivity to a remote network by sending a ping to the IP address of the default gateway. Verify remote connectivity by sending a ping to the IP address of a system on a remote network. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 7 2. IPCONFIG The ipconfig command is a technician's best friend when it comes to viewing the TCP/IP configuration of a Windows system. ipconfig (internet protocol configuration) in Microsoft Windows is a console application that displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP and Domain Name System DNS settings. The standard path is %WINDIR%\System32\ipconfig.exe which usually resolves to C:\WINDOWS\System32\ipconfig.exe the ipconfig command shows basic information such as the name of the network interface, the IP address, the subnet mask, and the default gateway. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 8 C:\Documents and Settings\patni>ipconfig/all Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 9 ipconfig Switches Switch Description ? Displays the ipconfig help screen /all Displays additional IP configuration information /release Releases the IP address of the specified adapter /renew Renews the IP address of a specified adapter Symptom Field to Check in ipconfig Output User is unable to connect to any other system. Make sure the TCP/IP address and subnet mask are correct. If the network uses DHCP, make sure DHCP is enabled. User is able to connect to another system on the same subnet but is not able to connect to a remote system. Make sure the default gateway is correctly configured. User is unable to browse the Internet. Make sure the DNS server parameters are configured correctly. User is unable to browse across remote subnets. Make sure the WINS or DNS server parameters are configured correctly. On a Windows 98 Second Edition and Windows Me systems, the winipcfg command is used in addition to the ipconfig command. The difference between the two utilities is that winipcfg is a graphical utility. IPconfig performs the same function as ipconfig, but on a Linux, UNIX, or Macintosh system. Because Linux relies more heavily on command-line utilities than Windows, the Linux and UNIX version of ifconfig provides much more functionality than ipconfig. A console application is a computer program designed to be used via a textonly computer interface ,such as a text terminal, the command line interface of some operating systems. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 10 The loopback is a special function within the protocol stack that is supplied for troubleshooting purposes. The Class A IP address 127.X.X.X is reserved for the loopback; although convention dictates that you use127.0.0.1, you can use any address in the 127.X.X.Xrange, except for the network number itself (127.0.0.0) and the broadcast address (127.255.255.255). You can also ping by using the default hostname for the local system, which is called local host. (for example, ping localhost). C:\>ipconfig 127.0.0.1 >ipconfig Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) ……it shows the information 11 C:\>ipconfig /? >ipconfig /? Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) …..it is used to display this help message 12 bit offset 0–3 4–7 8–15 16–18 0 Version Header length (-v) Differentiated Services Total Length 32 Identification 64 Time to Live ( -i ) 96 Source Address 128 Destination Address 160 Options ( if Header Length > 5 ) 160 or 192+ Flags (-f ) Protocol 19–31 Fragment Offset Header Checksum Data Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 13 3. TRACE ROUTE The trace route utility does exactly what its name implies it traces the route between two hosts. It does this by using Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets to report information back at every step in the journey. Each of the common network operating systems provides a trace route utility, but the name of the command and the output vary slightly on each. Trace route provides a lot of useful information, including the IP address of every router connection it passes through and, in many cases, the name of the router (although this depends on the router's configuration). Trace route also reports the length, in milliseconds, of the round-trip the packet made from the source location to the router and back. This information can help identify where network bottlenecks or breakdowns might be. Trace Route Utility Commands Operating System Trace Route Command Syntax Windows Server 2000/2003 tracert <IP address> Novell NetWare iptrace Linux/UNIX traceroute <IP address> Macintosh traceroute <IP address> C:\>tracert Usage: tracert [-d] [-h maximum_hops] [-j host-list] [-w timeout] target_name Options: -d do not resolve addresses to hostnames. -h maximum_hops Maximum number of hops to search for target. -j host-list loose source route along host-list. -w timeout Wait timeout milliseconds for each reply. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 14 Example C:\>tracert 24.7.70.37 The tracert display on a Windows-based system includes several columns of information. The first column represents the hop number. You may recall that 'hop' is the term used to describe a step in the path a packet takes as it crosses the network. The next three columns indicate the round-trip time, in milliseconds, that a packet takes in its attempts to reach the destination. The last column is the hostname and the IP address of the responding device. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 15 The following is the output from a tracert command on a Windows Server 2003 system that doesn't manage to get to the remote host: C:\>tracert comptia.org In this example, the trace route request only gets to the seventh hop, at which point it fails; this failure indicates that the problem lies on the far side of the device in step 7 or on the near side of the device in step 8. In other words, the device at step 7 is functioning but might not be able to make the next hop. The cause of the problem could be a range of things, such as an error in the routing table or a faulty connection. Alternatively, the seventh device might be Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 16 operating 100%, but device 8 might not be functioning at all. In any case, you can isolate the problem to just one or two devices. The trace route utility can also help you isolate a heavily congested network. In the following example, the trace route packets fail in the midst of the tracert from a Windows Server 2003 system, but subsequently are able to continue.Trace route utilities allow you to identify the location of a problem in the connectivity between two devices. After you have determined this location, you might need to use a utility such as ping to continue troubleshooting. In many cases, as in the example, the routers might be on a network such as the Internet and therefore not within your control. In that case, there is little you can do except inform your ISP of the problem. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 17 4. NET STAT The netstat command displays the protocol statistics and current TCP/IP connections on the local system. Used without any switches, the netstat command shows the active connections for all outbound TCP/IP connections. In addition, several switches are available that change the type of information netstat displays. Switch Description -a Displays the current connections and listening ports -e Displays Ethernet statistics -n Lists addresses and port numbers in numerical form -p Shows connections for the specified protocol -r Shows the routing table -s Lists per-protocol statistics interval Specifies the length of time to wait before redisplaying statistics The netstat utility is used to show the port activity for both TCP and UDP connections, showing the inbound and outbound connections. When used without switches, the netstat utility has four information headings. • Proto Lists the protocol being used, either UDP or TCP. • Local address Specifies the local address and port being used. • Foreign address Identifies the destination address and the port being used. • State Specifies whether the connection is established. The netstat command shows outbound connections that have been established by TCP. The following shows a sample output from a netstat command without using any switches: Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 18 C:\>netstat The netstat -e command shows the activity for the NIC and displays the number of packets that have been both sent and received. C:\>netstat –e Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 19 The netstat -e command shows more than just the packets that have been sent and received: • Bytes The number of bytes that have been sent or received by the NIC since the computer was turned on. • Unicast packets Packets sent and received directly to this interface. • Non-unicast packets Broadcast or multicast packets that were picked up by the NIC. • Discards The number of packets rejected by the NIC, perhaps because they were damaged. • Errors The errors that occurred during either the sending or receiving process. As you would expect, this column should be a low number. If it is not, it could indicate a problem with the NIC. • Unknown protocols The number of packets that were not recognizable by the system. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 20 The netstat -a command displays statistics for both TCP and User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Here is an example of the netstat -a command C:\WINDOWS>netstat –a The following list briefly explains the information provided by the netstat -a command • Proto The protocol used by the connection. • Local Address The IP address of the local computer system and the port number it is using. If the entry in the local address field is an asterisk (*), it indicates that the port has not yet been established. • Foreign Address The IP address of a remote computer system and the associated port. When a port has not been established, as with the UDP connections, *:* appears in the column. • State The current state of the TCP connection. Possible states include established, listening, closed, and waiting. The output includes four columns, which show the protocol, the local address, the foreign address, and the state of the port. The TCP connections show the local and foreign destination addresses and the current state of the connection. UDP, however, is a little different; it does not list a state status because UDP is a connectionless protocol and does not establish connections. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 21 Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 22 The netstat -r command is often used to view the routing table for a system. A system uses a routing table to determine routing information for TCP/IP traffic. The following is an example of the netstat -r command from a Windows Me system: C:\WINDOWS >netstat -r Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 23 The netstat -s command displays a number of statistics related to the TCP/IP protocol suite. Understanding the purpose of every field in the output is for your reference, sample output from the netstat -s command is shown here C:\>netstat -s Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 24 Aim 2: Write the case study of DOMAIN NAME SYSTEM(DNS) The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the participants. Most importantly, it translates domain names meaningful to humans into the numerical (binary) identifiers associated with networking equipment for the purpose of locating and addressing these devices worldwide. An often-used analogy to explain the Domain Name System is that it serves as the "phone book" for the Internet by translating human-friendly computer hostnames into IP addresses. For example, www.example.com translates to 192.0.32.10. The Domain Name System makes it possible to assign domain names to groups of Internet users in a meaningful way, independent of each user's physical location. Because of this, World Wide Web (WWW) hyperlinks and Internet contact information can remain consistent and constant even if the current Internet routing arrangements change or the participant uses a mobile device. The Domain Name System distributes the responsibility of assigning domain names and mapping those names to IP addresses by designating authoritative name servers for each domain. Authoritative name servers are assigned to be responsible for their particular domains, and in turn can assign other authoritative name servers for their sub-domains. This mechanism has made the DNS distributed and fault tolerant and has helped avoid the need for a single central register to be continually consulted and updated. In general, the Domain Name System also stores other types of information, such as the list of mail servers that accept email for a given Internet domain. By providing a worldwide, distributed keyword-based redirection service, the Domain Name System is an essential component of the functionality of the Internet. Other identifiers such as RFID tags, UPC codes, International characters in email addresses and host names, and a variety of other identifiers could all potentially utilize DNS.The Domain Name System also defines the technical underpinnings of the functionality of this database service. For this purpose it defines the DNS protocol, a detailed specification of the data structures and communication exchanges used in DNS, as part of the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP). Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 25 Applications Hostnames and IP addresses do not necessarily match on a one-to-one basis. Many hostnames may correspond to a single IP address: combined with virtual hosting, this allows a single machine to serve many web sites. Alternatively a single hostname may correspond to many IP addresses: this can facilitate fault tolerance and load distribution, and also allows a site to move physical location seamlessly. There are many uses of DNS besides translating names to IP addresses. For instance, Mail transfer agents use DNS to find out where to deliver email for a particular address. The domain to mail exchanger mapping provided by MX records accommodates another layer of fault tolerance and load distribution on top of the name to IP address mapping. E-mail Blacklists: The DNS system is used for efficient storage and distribution of IP addresses of blacklisted e-mail hosts. The usual method is putting the IP address of the subject host into the sub-domain of a higher level domain name, and resolve that name to different records to indicate a positive or a negative. A hypothetical example using blacklist.com 102.3.4.5 is blacklisted => Creates 5.4.3.102.blacklist.com and resolves to 127.0.0.1 102.3.4.6 is not => 6.4.3.102.blacklist.com is not found, or default to 127.0.0.2 E-mail servers can then query blacklist.com through the DNS mechanism to find out if a specific host connecting to them is in the blacklist. Today many of such blacklists, either free or subscription-based, are available mainly for use by email administrators and anti-spam software. Software Updates: many anti-virus and commercial software now use the DNS system to store version numbers of the latest software updates so client computers do not need to connect to the update servers every time. For these types of applications, the cache time of the DNS records are usually shorter. Sender Policy Framework and DomainKeys, instead of creating their own record types, were designed to take advantage of another DNS record type, the TXT record. To provide resilience in the event of computer failure, multiple DNS servers are usually provided for coverage of each domain, and at the top level, thirteen very powerful root servers exist, with additional "copies" of several of them distributed worldwide via Anycast. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 26 Dynamic DNS (also referred to as DDNS) provides clients the ability to update their IP address in the DNS after it changes due to mobility. Protocol details DNS primarily uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on port number 53 to serve requests. DNS queries consist of a single UDP request from the client followed by a single UDP reply from the server. The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is used when the response data size exceeds 512 bytes, or for tasks such as zone transfers. Some operating systems, such as HP-UX, are known to have resolver implementations that use TCP for all queries, even when UDP would suffice. DNS resource records A Resource Record (RR) is the basic data element in the domain name system. Each record has a type (A, MX, etc.), an expiration time limit, a class, and some type-specific data. Resource records of the same type define a resource record set. The order of resource records in a set, returned by a resolver to an application, is undefined, but often servers implement round-robin ordering to achieve load balancing. DNSSEC, however, works on complete resource record sets in a canonical order. RR (Resource record) fields Description Field NAME TYPE CLASS Name of the node to which this record pertains. Type of RR. For example, MX is type 15. Class code. TTL Unsigned time in seconds that RR stays valid, maximum is 2147483647. RDLENGTH Length of RDATA field. RDATA Additional RR-specific data. Length (octets) (variable) 2 2 4 4 (variable) NAME is the fully qualified domain name of the node in the tree. On the wire, the name may be shortened using label compression where ends of domain Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 27 names mentioned earlier in the packet can be substituted for the end of the current domain name. TYPE is the record type. It indicates the format of the data and it gives a hint of its intended use. For example, the A record is used to translate from a domain name to an IPv4 address, the NS record lists which name servers can answer lookups on a DNS zone, and the MX record specifies the mail server used to handle mail for a domain specified in an e-mail address (see also List of DNS record types). RDATA is data of type-specific relevance, such as the IP address for address records, or the priority and hostname for MX records. Well known record types may use label compression in the RDATA field, but "unknown" record types must not (RFC 3597). The CLASS of a record is set to IN (for Internet) for common DNS records involving Internet hostnames, servers, or IP addresses. In addition, the classes CH (Chaos) and HS (Hesiod) exist. Each class is a completely independent tree with potentially different delegations of DNS zones. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 28 Aim 3: Write the case study of SIMPLE NETWORK MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL (SNMP) Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a UDP-based network protocol. It is used mostly in network management systems to monitor networkattached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention. SNMP is a component of the Internet Protocol Suite as defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It consists of a set of standards for network management, including an application layer protocol, a database schema, and a set of data objects. SNMP exposes management data in the form of variables on the managed systems, which describe the system configuration. These variables can then be queried (and sometimes set) by managing applications. Basic components An SNMP-managed network consists of three key components: Managed device = Slave device Agent = software which runs on Slave device Network management system (NMS) = software which runs on Master A managed device is a network node that implements an SNMP interface that allows unidirectional (read-only) or bidirectional access to node-specific information. Managed devices exchange node-specific information with the NMSs. Sometimes called network elements, the managed devices can be any type of device, including, but not limited to, routers, access servers, switches, bridges, hubs, IP telephones, IP video cameras, computer hosts, and printers. An agent is a network-management software module that resides on a managed device. An agent has local knowledge of management information and translates that information to or from an SNMP specific form. A network management system (NMS) executes applications that monitor and control managed devices. NMSs provide the bulk of the processing and memory resources required for network management. One or more NMSs may exist on any managed network. Protocol Details Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 29 SNMPv1 and SMI-specific data types:The first version of the SMI (SMIv1) specifies the use of a number of SMIspecific data types, which are divided into two categories: Simple data types. Three simple data types are defined in the SNMPv1 SMI, all of which are unique values: The integer data type is a signed integer in the range of -231 to 231-1. Octet strings are ordered sequences of 0 to 65,535 octets. Object IDs come from the set of all object identifiers allocated according to the rules specified in ASN.1. Application-wide data types. The following application-wide data types exist in the SNMPv1 SMI:Network addresses represent addresses from a particular protocol family. SMIv1 supports only 32-bit (IPv4) addresses (SMIv2 uses Octet Strings to represent i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. addresses generically, and thus are usable in SMIv1 too. SMIv1 had an explicit IPv4 address datatype.) Counters are non-negative integers that increase until they reach a maximum value and then roll over to zero. SNMPv1 specifies a counter size of 32 bits. Gauges are non-negative integers that can increase or decrease between specified minimum and maximum values. Whenever the system property represented by the gauge is outside of that range, the value of the gauge itself will vary no further than the respective maximum or minimum, as specified in RFC 2578. Time ticks represent time since some event, measured in hundredths of a second. Opaques represent an arbitrary encoding that is used to pass arbitrary information strings that do not conform to the strict data typing used by the SMI. Integers represent signed integer-valued information. This data type redefines the integer data type, which has arbitrary precision in ASN.1 but bounded precision in the SMI. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 30 vii. Unsigned integers represent unsigned integer-valued information, which is useful when values are always non-negative. This data type redefines the integer data type, which has arbitrary precision in ASN.1 but bounded precision in the SMI. Security implications SNMP versions 1 and 2c are subject to packet sniffing of the clear text community string from the network traffic, because they do not implement encryption. All versions of SNMP are subject to brute force and dictionary attacks for guessing the community strings, authentication strings, authentication keys, encryption strings, or encryption keys, because they do not implement a challenge-response handshake. Entropy is an important consideration when selecting keys, passwords and/or algorithms. Although SNMP works over TCP and other protocols, it is most commonly used over UDP that is connectionless and vulnerable to IP spoofing attacks. Thus, all versions are subject to bypassing device access lists that might have been implemented to restrict SNMP access, though SNMPv3's other security mechanisms should prevent a successful attack. SNMP's powerful configuration (write) capabilities are not being fully utilized by many vendors, partly due to lack of security in SNMP versions before SNMPv3 and partly due to the fact that many devices simply are not capable of being configured via individual MIB object changes. SNMP tops the list of the SANS Institute's Common Default Configuration Issues with the issue of default SNMP community strings set to ‘public’ and ‘private’ and was number ten on the SANS Top 10 Most Critical Internet Security Threats for the year 2000. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 31 Aim 4: Study of IP Routing IP Routing is an umbrella term for the set of protocols that determine the path that data follows in order to travel across multiple networks from its source to its destination. Data is routed from its source to its destination through a series of routers, and across multiple networks. The IP Routing protocols enable routers to build up a forwarding table that correlates final destinations with next hop addresses. These protocols include: 1. BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) IS-IS (Intermediate System - Intermediate System) OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) RIP (Routing Information Protocol) When an IP packet is to be forwarded, a router uses its forwarding table to determine the next hop for the packet's destination (based on the destination IP address in the IP packet header), and forwards the packet appropriately. The next router then repeats this process using its own forwarding table, and so on until the packet reaches its destination. At each stage, the IP address in the packet header is sufficient information to determine the next hop; no additional protocol headers are required. The Internet, for the purpose of routing, is divided into Autonomous Systems (ASs). An AS is a group of routers that are under the control of a single administration and exchange routing information using a common routing protocol. For example, a corporate intranet or an ISP network can usually be regarded as an individual AS. The Internet can be visualized as a partial mesh of ASs. An AS can be classified as one of the following three types. A Stub AS has a single connection to one other AS. Any data sent to, or received from, a destination outside the AS must travel over that connection. A small campus network is an example of a stub AS. A Transit AS has multiple connections to one or more ASs, which permits data that is not destined for a node within that AS to travel through it. An ISP network is an example of a transit AS. A Multihomed AS also has multiple connections to one or more ASs, but it does not permit data received over one of these connections to be forwarded out of the AS again. In other words, it does not provide a Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 32 transit service to other ASs. A Multihomed AS is similar to a Stub AS, except that the ingress and egress points for data traveling to or from the AS can be chosen from one of a number of connections, depending on which connection offers the shortest route to the eventual destination. A large enterprise network would normally be a multihomed AS. An Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) calculates routes within a single AS. The IGP enables nodes on different networks within an AS to send data to one another. The IGP also enables data to be forwarded across an AS from ingress to egress, when the AS is providing transit services. Routes are distributed between ASs by an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP). The EGP enables routers within an AS to choose the best point of egress from the AS for the data they are trying to route. The EGP and the IGPs running within each AS cooperate to route data across the Internet. The EGP determines the ASs that data must cross in order to reach its destination, and the IGP determines the path within each AS that data must follow to get from the point of ingress (or the point of origin) to the point of egress (or the final destination). The diagram below illustrates the different types of AS in a network. OSPF, ISIS and RIP are IGPs used within the individual ASs; BGP is the EGP used between ASs. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 33 Aim 5: Study of Serial Line Internet Protocol(SLIP) and PointTo-Point Protocol(PPP) Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) Serial Line Interface Protocol (SLIP) is a TCP/IP protocol used for communication between two machines that are previously configured for communication with each other. For example, the Internet server provider may provide the user with a SLIP connection so that the provider's server can respond to requests, pass them on to the Internet and forwards requested Internet responses back to the user. The dial-up connection to the server is typically on a slower serial line rather than on the parallel or multiplex lines such as a line of the network the user is hooking up to. It is commonly used on dedicated serial links and dial-up connections that operate at speeds between 1200bps and 56Kbps. SLIP modifies a standard Internet datagram by appending a special SLIP END character to it, which allows datagrams to be distinguished as separate. SLIP requires a port configuration of 8 data bits, no parity, and EIA or hardware flow control. SLIP does not provide error detection, being reliant on other high-layer protocols for this. Over a particularly error-prone dial-up link therefore, SLIP on its own would not be satisfactory. A SLIP connection needs to have its IP address configuration set each time before it is established whereas Point-toPoint Protocol (PPP) can determine it automatically once it has started. The Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) is a mostly obsolete encapsulation of the Internet Protocol designed to work over serial ports and modem connections. It is documented in RFC 1055. SLIP has been largely replaced by the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), which is better engineered, has more features and does not require its IP address configuration to be set before it is established. A version of SLIP with header compression is called CSLIP (Compressed SLIP). SLIP is a STREAMS-based computer networking facility that provides for the transmission and reception of IP packets over serial lines. SLIP allows the use of TCP/IP networking applications such as rlogin and telnet over serial lines. SCO SLIP is an implementation of the Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) as defined in RFC 1055 and RFC 1144. SLIP can be used to connect one host to another via a single, physical serial line connection between serial ports or over longer distances using a modem at each end of a telephone line. A computer that is running SLIP over one or more serial lines and that is also connected to a computer network (such as an Ethernet) can serve as a communication gateway Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 34 between computers on a network and computers at the far end of each serial line. How SLIP framing works? An IP datagram is passed down to SLIP, which breaks it into bytes and sends them one at a time over the link. After the last byte of the datagram, a special byte value is sent that tells the receiving device that the datagram has ended. This is called the SLIP END character , and has a byte value of 192 decimal (C0 hexadecimal, 11000000 binary). And that's basically it: take the whole datagram, send it one byte at a time, and then send the byte 192 to delimit the end of the datagram. A minor enhancement to this basic operation is to precede the datagram by an END character as well. The benefit of this is that, it clearly separates the start of the datagram from anything that preceded it. To see why this might be needed, suppose at a particular time one has only one datagram to send, datagram #1. So, the user sends #1 and then sends the END character to delimit it. Now, suppose there is a pause before the next datagram shows up. During that time, there is no transmission, but if there is line noise, the other device might pick up spurious bytes here and there. If the user later receives datagram #2 and just starts sending it, the receiving device might think the noise bytes were part of datagram #2. Starting datagram #2 off with an END character tells the recipient that anything received between this END character and the previous one is a separate datagram. If that's just noise, then this “noise datagram” is just gibberish that will be rejected at the IP layer. Meanwhile, it doesn't corrupt the real datagram one wishes to send. If no noise occurred on the line between datagrams, then the recipient will just see the END at the start of datagram #2 right after the one at the end of #1 and will ignore the “null datagram” between the two. Point-To-Point Protocol (PPP) In networking, the Point-to-Point Protocol, or PPP, is a data link protocol commonly used to establish a direct connection between two networking nodes. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 35 It can provide connection authentication, transmission encryption privacy, and compression. PPP is used over many types of physical networks including serial cable, phone line, trunk line, cellular telephone, specialized radio links, and fiber optic links such as SONET. Most Internet service providers (ISPs) use PPP for customer dial-up access to the Internet. Two encapsulated forms of PPP, Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) and Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM (PPPoA), are used by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to connect Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Internet service. PPP is commonly used as a data link layer protocol for connection over synchronous and asynchronous circuits, where it has largely superseded the older, non-standard Serial Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) and telephone company mandated standards (such as Link Access Protocol, Balanced (LAPB) in the X.25 protocol suite). PPP was designed to work with numerous network layer protocols, including Internet Protocol (IP), Novell's Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX), NBF and AppleTalk. PPP is also used over broadband connections. RFC 2516 describes Point-toPoint Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE), a method for transmitting PPP over Ethernet that is sometimes used with DSL. RFC 2364 describes Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM (PPPoA), a method for transmitting PPP over ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5), which is also sometimes used with DSL. PPP Features The PPP follows an address notification system and using this IP address the dial up client works and the IP address established for the particular link is also requested by their networks. All this takes place automatically in the PPP. The PPP provides two methods of authentication; one is the Password Authentication Protocol that uses a password to authenticate or the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol which uses the handshake of the server with the dial up as an authentication. The PPP allows different types of protocols to function on its platform and on the same link. The PPP also additionally checks the link established by the protocol and includes something called the link level echo facility which checks if the link is operating properly. The main tasks of the Point to Point Protocol are to check if the condition of the line or the telephone line that it is operating on is OK. The Point to Point Protocol also checks the password and after going through all these initial checks it establishes the connection with the internet service provider servers and requests for an IP address. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 36 This IP address is used by the PPP on the internet to communicate with all other network protocols and servers as long as the connection lasts. The PPP also transports the packets of information from one server to the other and uses the same IP address to address the computer which has requested for the information. PPP Frames There are many protocols that are included in the PPP frame that work in tandem to send and receive data on a network. The packages of data that are being sent and received on the network is called frame. The Point to Point Protocol usually follows a general and a standard format for all the frames that it sends or receives. In order to understand the network and its functionalities and later trouble shoot a network administrator should be able to understand these frames to be able to diagnose issues related to the protocols. The Point to Point Protocol follows specified set of formats for different purposes on the network. The formats that are commonly used by the Point to Point Protocol are Link Control Protocol, and other authentication protocols like PAP and CHAP. The Point to Point Protocol also has a varied version called the PPP multilink protocol. All these protocols are used to transport the small bits of data over the link. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 37 Aim 6: Study of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a dynamic routing protocol for use in Internet Protocol (IP) networks. Specifically, it is a link-state routing protocol and falls into the group of interior gateway protocols, operating within a single autonomous system (AS). It is defined as OSPF Version 2 in RFC 2328 (1998) for IPv4.[1] The updates for IPv6 are specified as OSPF Version 3 in RFC 5340 (2008). OSPF is perhaps the most widely-used interior gateway protocol (IGP) in large enterprise networks; IS-IS, another link-state routing protocol, is more common in large service provider networks. The most widely-used exterior gateway protocol is the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), the principal routing protocol between autonomous systems on the Internet. OSPF has two primary characteristics. The first is that the protocol is open, which means that its specification is in the public domain. The OSPF specification is published as Request For Comments (RFC) 1247. The second principal characteristic is that OSPF is based on the SPF algorithm, which sometimes is referred to as the Dijkstra algorithm, named for the person credited with its creation. OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that calls for the sending of link-state advertisements (LSAs) to all other routers within the same hierarchical area. Information on attached interfaces, metrics used, and other variables is included in OSPF LSAs. As OSPF routers accumulate link-state information, they use the SPF algorithm to calculate the shortest path to each node. As a link-state routing protocol, OSPF contrasts with RIP and IGRP, which are distance-vector routing protocols. Routers running the distance-vector algorithm send all or a portion of their routing tables in routing-update messages to their neighbors. Packet Format Version Type Packet Router Area Checksum Authentication Authentication Data number length ID ID type Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 38 OSPF packets consist of nine fields. The following descriptions summarize the header fields illustrated above Version Number: - Identifies the OSPF version used. Type:- Identifies the OSPF packet type as one of the following: i. Hello: Establishes and maintains neighbor relationships. ii. Database Description: Describes the contents of the topological database. These messages are exchanged when an adjacency is initialized. iii. Link-state Request: Requests pieces of the topological database from neighbor routers. These messages are exchanged after a router discovers (by examining database-description packets) that parts of its topological database are out of date. iv. Link-state Update: Responds to a link-state request packet. These messages also are used for the regular dispersal of LSAs. Several LSAs can be included within a single link-state update packet. v. Link-state Acknowledgment: Acknowledges link-state update packets. Packet Length—Specifies the packet length, including the OSPF header, in bytes. Router ID—Identifies the source of the packet. Area ID—Identifies the area to which the packet belongs. All OSPF packets are associated with a single area. Checksum—Checks the entire packet contents for any damage suffered in transit. Authentication Type—Contains the authentication type. All OSPF protocol exchanges are authenticated. The Authentication Type is configurable on a per-area basis. Authentication—Contains authentication information. Data—Contains encapsulated upper-layer information. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 39 Aim 7: Study of Supernetting and Subnetting Supernetting A supernet is an Internet Protocol (IP) network that is formed from the combination of two or more networks (or subnets) with a common Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) routing prefix. The new routing prefix for the combined network aggregates the prefixes of the constituent networks. It must not contain other prefixes of networks that do not lie in the same routing path. The process of forming a supernet is often called supernetting, route aggregation, or route summarization. Supernetting within the Internet serves as a preventative strategy to avoid topological fragmentation of the IP address space by using a hierarchical allocation system that delegates control of segments of address space to regional network service providers.[1] This method facilitates regional route aggregation. The benefits of supernetting are conservation of address space and efficiencies gained in routers in terms of memory storage of route information and processing overhead when matching routes. In Internet networking terminology, a supernet is a block of contiguous subnetworks addressed as a single subnet. Supernets always have masks that are smaller than the masks of the component networks. Supernetting alleviates some of the issues, such as excessively large route tables which increase router latency, with the original classful addressing scheme for IP addresses by allowing multiple networks address ranges to be combined, either to create a single larger network, or just for route aggregation to keep the "Internet Routing Table" (or any routing table) from growing too large. Supernetting combines a group of routes into a single route advertisement. The number of subnets and network addresses contained in Internet routing tables is rapidly increasing due to the rapid expansion of the Internet. This growth has had a negative impact on CPU resources, bandwidth, and memory used to maintain routing tables. Therefore, route summarization was introduced to reduce the size of network routing tables. If configured properly, supernetting can reduce the latency associated with router hop, since the average speed for routing table lookup will be increased Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 40 due to the reduced number of entries. The overhead for routing protocols can also be reduced since fewer routing entries are being advertised. Subnetting A subnetwork, or subnet, is a logically visible, distinctly addressed part of a single Internet Protocol network.[1] The process of subnetting is the division of a computer network into groups of computers that have a common, designated IP address routing prefix. Subnetting breaks a network into smaller realms that may use existing address space more efficiently, and, when physically separated, may prevent excessive rates of Ethernet packet collision in a larger network. The subnets may be arranged logically in a hierarchical architecture, partitioning the organization's network address space (see also Autonomous System) into a tree-like routing structure. Routers are used to interchange traffic between subnetworks and constitute logical or physical borders between the subnets. They manage traffic between subnets based on the high-order bit sequence (routing prefix) of the addresses. A routing prefix is the sequence of leading (most-significant) bits of an IP address that precede the portion of the address used as host identifier and, if applicable, the set of bits that designate the subnet number. Routing prefixes are expressed in CIDR notation, which uses the first address of a network followed by the bit-length of the prefix, separated by a slash (/) character. For example, 192.168.1.0/24 is the prefix of the IPv4 network starting at the given address, having 24 bits allocated for the network number, and the rest (8 bits) reserved for host addressing. The IPv6 address specification 2001:db8::/32 is a large network for 296 hosts, having a 32-bit routing prefix. In IPv4 networks, the routing prefix is traditionally expressed as a subnet mask, which is the prefix bit mask expressed in quad-dotted decimal representation. For example, 255.255.255.0 is the subnet mask for the 192.168.1.0/24 prefix. All hosts within a subnet can be reached in one routing hop, implying that all hosts in a subnet are connected to the same link. A typical subnet is a physical network served by one router, for instance an Ethernet network, possibly consisting of one or several Ethernet segments or local area networks, interconnected by network switches and network bridges) or a Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN). However, subnetting allows the network to be logically divided regardless of the physical layout of a network, since it is possible to divide a physical network into several subnets by configuring different host computers to use different routers. Ayush Patni (0834cs061011) 41