* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to DSP
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
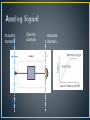
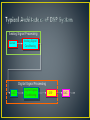
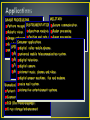
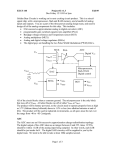
Engr. Hinesh Kumar Lecturer, I.B.T, LUMHS • • • • • • • • • Signal Signal Classification Signal Processing Concept of Systems DSP Elements of DSP Advantages of DSP Limitations Applications • A word ‘Signal’ comes from latin ‘Signum’ which means ‘Sign’. • “ A signal is a quantity or effect such as current or voltage that can be varied in such a way as to convey information.” OR • “ A signal is defined as a mathematical function that conveys information about the state or behavior of a physical system.” • Examples: electrical current, voltage, force, speed, speech, music, picture and video signals etc Analog Time Amplitude Continuous Continuous VS Digital Discrete Discrete • An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature. • An analog signal is a signal that exists at every instant of time • A continuous signal is often referred to as continuous time or analog. • The independent variable is a continuous variable • Continuous signal can assume any value over a continuous range of numbers • It is a special form of discrete discrete in time and amplitude. • A digital signal is acquired sampled analog value into a (quantization). • These signals are called digital are represented by digits. time signal which is by representing the finite set of values because the samples Representation, transformation and manipulation of signals and the information they contain. Signal operation include: (1) Transform, filter, inspection, spectrum analysis; (2) Modulation and coding; (3) Analog Signal Processing; (4) Digital Signal Processing. Computer, Semiconduct and Information Science 1960’s-1970’s System Device or technology of signal processing Analog System System with analog input and output. Digital System System with digital input and output. Acoustic domain Electric domain Acoustic domain Continuous-time system: the input and output signals are continuous time Acoustic domain Electric domain Acoustic domain Digital domain Discrete-time system has discrete-time input and output signals Acoustic domain Electrical domain Digital domain Electrical domain Acoustic domain Analog Computer a bit loud a bit loud Digital Computer DSP DAC ADC 1010 1001 OUTPUT • Converting a continuously changing waveform (analog) into a series of discrete levels (digital). • The analog waveform is sliced into equal segments and the waveform amplitude is measured in the middle of each segment • The collection of measurements make up the digital representation of the waveform • • • • • A basic DSP system is composed of: An ADC providing digital samples of an analog input A Digital Processing system A DAC converting processed samples to analog output Real-time signal processing: All processing operation must be complete between two consecutive samples Analog Signal Processing Sensor Analog Signal Conditioning Digital Signal Processing ADC Digital Signal Conditioning DSP DAC 1. An analog input 2. An analog filter, 3. An analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) unit, 4. A digital signal (DS) processor, 5. A digital-to-analog conversion (DAC) unit, 6. and a reconstruction (anti-image) filter. • The analog input signal, which is continuous in • time and amplitude. • It is the signal generated from some transducer or some communication system. • Examples of such analog signals include current, voltage, temperature, pressure. • It may be biomedical signal like ECG or EEG. • Generally it is analog in nature. It is denoted by x(t). • This is basically a low pass filter. • It is used for the following purposes. It removes the high frequency noise contained in input signal. As the name indicates, it avoids aliasing effect. That means it is used to band limit the signal. • The band-limited signal at the output of the analog filter is then sampled and converted into the digital signal, which is discrete both in time and in amplitude. • This is required because digital signal processor accepts the signal which is digital in nature. • It processes input signal digitally. • In a simple language processing of input signal means modifying the signal as per requirement. • It consists of lowpass, highpass, and bandpass digital filtering, or other algorithms for different applications. • DS processor is a special type of digital computer consists of , a microprocessor, or an advanced microcontroller; and can be implemented using software in general. • The DAC unit, converts the output of the digital signal processor into an analog output signal. • The signal is continuous in time and discrete in amplitude. • Output signal of DAC is an analog, that means it is a continuous signal. • It may contain high frequency components which are unwanted. • To remove these components, reconstruction filter is used. 1. Versatility Digital systems can be reprogrammed for multiple applications ( where programmable DSP chips are used). Moreover, digital systems can be ported to different hardware 2. Repeatability Digital systems can be easily duplicated. These systems do not depend upon component tolerances and temperature. 3. Simplicity: It is easy to built any digital system as compared to an analog one. 4. Accuracy: To design an analog system, analog components like resistors, capacitors and inductors are used. The tolerance of these components reduce accuracy of the system. While in case of DSP; much better accuracy is obtained. 5. Remote Processing Analog signals are difficult to store because of problems like noise and distortion. While digital signal can be easily stored on storage media like magnetic tapes, disks etc. Thus as compared to analog signals digital signals can be easily transposed. So remote processing of digital signal can be done easily. 6. Implementation of algorithms: The mathematical processing algorithms can be easily implemented in case of digital signal processing. But such algorithms are difficult to implement in case of analog signals. 7. Easy Up gradations: Because of the use of software, digital signal processing systems can be easily upgraded as compared to analog systems. 8. Compatibility: In case of digital systems, generally all applications needs standard hardware. Thus operation of DSP system is mainly dependent on software. Hence universal compatibility is possible as compared to analog systems. 9. Cheaper: In many applications, the digital systems are comparatively cheaper than analog systems. 1. System Complexity: DSP system needs use of converters like ADC and DAC. This increases the system complexity compared to analog systems. Similarly in many applications, the time required for this conversion is more. • Bandwidth Limitation: In case of DSP system, if input signal is having wide bandwidth then it demands for high speed ADC. This is because to avoid aliasing effect, the sampling rate should be at least twice the bandwidth. Thus such signals require fast digital signal processors. But always there is practical limitation in the speed of processors and ADC. 3. Power Consumption: A typical digital signal processing chip contains more than four lakh transistors. Thus power dissipation is more in DSP systems as compared to analog systems 4. For small applications digital signal processing systems are expensive as compared to analog systems MILITARY IMAGE PROCESSING INSTRUMENTATION &Secure CONTROL communication Pattern recognition Spectrum analysis Radar processing Robotic vision Sonar processing Image enhancementPosition and rate control applications Noise reduction Missile guidance Satellite Consumer weather map SPEECHdigital, & AUDIO cellar mobile phones Data compression animation Speech recognition universal mobile telecommunication system Speech synthesis digital television TELECOMMUNICATION Text digital to speech camera Echo cancellation digitalinternet audio music, phonesAdaptive and video equalization digital answer machines, faxconferencing and modems Video voice mail system Biomedical data communication interactive entertainment systems Patient monitoring Scanners ECG (Electrocardiograph) X-ray storage/enhancement