* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GUIDELINES FOR AUTHORS
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Jordan normal form wikipedia , lookup
Perron–Frobenius theorem wikipedia , lookup
Singular-value decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Gaussian elimination wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
Non-negative matrix factorization wikipedia , lookup
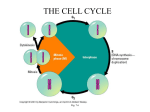
299 TRIPLE FEATURES OF ULTRASONIC IMAGE RECOGNITION1 N.G. Fedotov2, L.A. Shul’ga2, A.S. Kol’chugin2, O.A. Smol’kin2, S.V. Romanov2 2 Penza State University, 40th Krasnaya St., Penza, 440026 Russia, phone +7 8412 368056, [email protected] Ultrasonic images recognition problem aimed at thyroid cancer diagnostics sensibility increasing is considered. Measurement of objects geometrical characteristics on ultrasonic images, based on stochastic geometry methods - trace-transformation and it based triple features formed is described. Introduction The basic method for screening of thyroid gland diseases is ultrasonic examination. The purposes of this examination are a detection of tumours and definition of theirs characteristics. The expert carries out the given procedure and the results are defined by his or her qualification and experience. Heterogeneity and complex structure is characteristic for images of ultrasonic examination. Algorithms of preprocessing of images on the basis of a method morphological grayscale reconstruction have been applied to simplification of procedure of recognition. Application of this algorithm has allowed to allocate tumours in a thyroid gland for their subsequent analysis. Calculating of the triple feature The main geometrical characteristics tumors are: the size, the form and border. For definition of the given parameters it is offered to use methods of stochastic geometry - tracetransformation. The basis of this method is scanning the image the determined lattice. The scanning result is trace transform or trace matrix. With help of subsequent trace matrix processing the three functionals composition view triple features are form. _______________________________________________________________________ 1 Support of the grant INTAS, Ref. No. 04-77-7036. Let F x, y – function of representation on the plane x, y . We fix on this plane scanning line l , , t , which made using normal coordinates and : x cos y cos , parameter t assign the point on the straight line. Functionals , P and T are bounded with normal coordinates , and current coordinate t correspondently. We fix the function of these two arguments g , T F l , , t as the result of action of functional T , under the stipulation that, values of variable and are constant. As a result of functional T we have matrix, the elements of matrix are values t ij T F l j , i , t , the parameters of scanning line are and , determine the position of this value in the matrix. We’ll name this matrix as trace-matrix. The next computation of the feature is in consistent columns processing with the help of functional P , and then using functional . So the feature calculated like consistent composition of three functional П F T P F l , , t . The Measurement of the tumor sizes As the sizes of infected formations present the maximal extent of object in any measurement 300 (we shall name its length) and the maximal extent of object in perpendicular to length a direction (we shall name its width). If we take functional T as a long of the bigger cut off section of straight line l , , t in this object, and P and - are upper bounds of the value, so we can get the maximum diameter of object (length). We know the value of this parameter k for this feature, and we analyze only row with parameter k 90 in the matrix and use the same functional P we can get the width of the object. Fig. 3. Tumor has clear border Fig. 4. Tumor has unclear border The definition of the shape of tumor While carrying out of ultrasonic examination the shape of infected formations in a thyroid gland is characterized as regular (Fig. 1) or irregular (Fig. 2). In the general case we can name regular shape, which is look like an ellipse. We’ll take the long of the bigger cut off of line section l , , t as functional T . Functional P is a value of fluctuation of t ij , and is average value. Received feature will be describing the borders. Conclusion Fig. 1. Tumor has regular shape Thus, carried out research has shown the effectiveness of application of stochastic geometry methods for definition of tumor characteristics in a thyroid gland. The utilization of trace-features allows to raise reliability of our dimension, defining the set characteristic, using various functionals. References Fig. 2. Tumor has irregular shape The function of quantity of point of intersection in the line l , , t is functional T , P and they are average values. So, the feature we got will be numerical characteristic of the object. So if value closed to 2, an object has regular shape, if more than 2 – has irregular shape. Characteristic of the border of tumor The borders are considered as clear (Fig. 3) or unclear (Fig. 4). 1. N.G. Fedotov. Stochastic geometry methods in pattern recognition. Moscow.: Radio i svyaz’, 1990. (in Russian). 2. N.G. Fedotov, L.A. Shulga, A.V. Moiseev. Recognition features and image preprocessing theory based on stochastic geometry // Izmeritel’naya tekhnika. – 2005. – No.8. - P. 8-13. (in Russian).