* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 天 津 医 科 大 学 授 课 教 案
Survey
Document related concepts
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
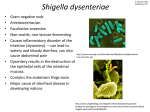
天 津 医 科 大 学 授 课 教 案 (共 课程名称: internal medicine 教师姓名:Dongxiaoying 2 页、第 1 页) 课程内容: BACILLUS DYSENTERY 职称:Associate chief physician 授课日期:25/4/2013 8 时— 10 时 授课对象: Foreign Students 授课方式: Lecture 教材版本:nternal medicine 学时数: 2 听课人数:80 本单元或章节的教学目的与要求: Master: pathogens name, definition, mode of transmission, clinical manifestations, means of prevention familiar with: pathogen classification, the main pathological changes, diagnosis, laboratory features, treatment Know: pathogenesis, epidemiology, differential diagnosis, complications treatment self – study: history, prognosis 授课主要内容及学时分配: Definition: 3 minutes Etiology: 7 minutes Incidence and outbreak Features: 2 minutes Epidemiology: 3 minutes Pathogenesis and pathology: 5 minutes Clinical manifestations: 10 minutes Diagnosis: 5 minutes Treatment: 10 minutes Prognosis and prevention: 5 minutes 重点、难点及对学生要求(包括掌握、熟悉、了解、自学) Dysentery pathogens name, the definition, mode of transmission, clinical manifestations, means of prevention, pathogen classification, the main pathological changes, diagnosis, laboratory features, the main treatment is lectures focus. Tenesmus clinical characteristics of bacillary dysentery to be key description Add the identify of tenesmus The identification and treatment of viral and bacterial diarrhea is easy to cause confusion. Appropriate to add some extra content to enhance students' understanding. 外语词汇: BACILLUS DYSENTERY 辅助教学情况: slides, pictures 复习思考题: What’s the pathogenic microorganism ? What’s the mode of spread? How to prevent the spread? What’s the clinical manifestations? 参考资料: Practice Guidelines for the Management of Infectious Diarrhea , IDSA guidelines. WHO/UNICEF joint statement clinical management of acute diarrhoea, The United Nations Children’s Fund/World Health Organization, 2004 Alfred S. Evans and Richard A. Kaslow ; Viral Infections of Humans –Epidemiology and Control, Fourth Edition Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s ; Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Fifth Edition 主任签字: 年 月 日 教务处制 天 津 医 科 大 学 授 课 教 案 (共 页、第 页) Definition: 3’ 1. Master the definition:Shigellosis is an acute bacterial infection caused by the genus Shigella resulting in colitis affecting predominantly the rectosigmoid colon. The disease is characterized by diarrhea, dysentery, fever, abdominal pain, and tenesmus. Shigellosis is usually limited to a few days. 2 emphasize.: Pathogen: the genus Shigella Position: rectosigmoid colon Symptoms: Dysentery syndrome Etiology: 7 minutes 1. Bacterial species and classification:Shigellae are no motile gram-negative bacilli belonging to the group Escherichia in the family Enterobacteriaceae. 2. familiar with four subtypes:Four species of shigellae are recognized on the basis of antigenic and biochemical properties, S. dysenteriae (group A), S. fiexneri (group B), S. boydii (group C), and S. Sonnei (group D). 2:through the the table below, compare subtype characteristics Table 1 Group Ornithine β decarboxylase -D-galactosidase A — — B — — C — — D + + serotype 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10 1a 、1d、 1c、 2a、 3a 、3c、 4a、 4b、 4c、 5a、 5b、 6、 x、 y 1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9、10、11、 12、13、14、15 3:through the the following picture, tell about the strain characteristics 4. add extra content, raise awareness of Shigella: 106-108 bacteria per gram in stool survive in soiled linen for up to seven weeks in fresh water for 5-11d in salt water for 12-30 hours in dust at room temperature for 6 weeks in sour milk for 4 weeks in kitchen refuse for 1-4 days Survival is prolonged at temperatures below 25ºC Freezing will not eliminate the organism, although it may reduce the number that survive. susceptibility Features: 2 minutes to understand outbreak history of dysentery: Epidemiology: 3 minutes key points: 1. source of infection: acute or chronic patients and bacteria-carriers。 2. Infection pathway: fecal-oral route. 3. Predisposition: widespread. Pathogenesis and pathology: 5 minutes 1.to understand pathogenesis and process: Since the microorganisms are relatively resistant to acid, shigellae pass the gastric barrier more readily than other enteric pathogens. The organism may be cultivated from stools for days or longer. The bacilli regularly initiate disease in 25% of healthy adults. This contrasts strikingly with the much larger numbers of typhoid or cholera bacilli required to produce disease in normal individuals. 2 . Master main pathological.: The primary pathological manifestation is the diffuse exudative fibrinous inflammation. The ulceration in Shigellosis is maplike and superficial. Clinical manifestations: 10 minutes 1. Require to master main content clinical manifestations: Prodrome: nonspecific Fever: Diarrhea and tenesmus Abdominal pain: in the left lower quadrant mainly Neurological manifestations: in severe patients only Complications: dehydration, Shigella septicemia , and hemolytic-uremic syndrome . Post dysenteric syndromes: arthritis and Reiter’s triad 2. stress tenesmus unique performance and increase extra content (differential diagnosis): Dictation Diagnosis: 5 minutes 1 .Master stool examination features in typical cases::microscopic examination of the stool often reveals numerous leukocytes and erythrocytes. 2. Familiar with other laboratory tests Blood examination: Sigmoidoscopic examination: Evidence in bacteriology: 3. to understand differential diagnosis Amebic dysentery: Ulcerative colitis: Treatment: 10 minutes familiar with main point contents of treatment: 1. General therapy: It includes relaxation, aspiration of oxygen, reducing the temperature, taking liquid diet, disinfections and insulation. 2. Fluid replacement: intravenous fluid replacement is required until initial fluid and electrolyte losses are corrected. With proper hydration, shigellosis is generally a self-limiting disease. 3. Antibiotic treatment: emphasis on children's antibiotics contraindications, memory following two points Do not give ciprofloxacin to children less than 17 years of age because there is a theoretical risk of cartilage damage.) Attention:Agents that decrease intestinal motility should not be used. Such preparations as diphenoxylate (a kind of antidiarrheal drug) and paregoric may exacerbate symptoms, presumably by retarding intestinal clearance of the microorganisms. There is no convincing evidence that pectin- or bismuth-containing preparations are helpful. Prognosis and prevention: 5 minutes 1. Require to master the following preventive approach Controlling the source of infection: Cutting the infection pathway: Preventing the predisposition: 2. Brief introduction to other preventive measures References Practice Guidelines for the Management of Infectious Diarrhea , IDSA guidelines. WHO/UNICEF joint statement clinical management of acute diarrhoea, The United Nations Children’s Fund/World Health Organization, 2004 Alfred S. Evans and Richard A. Kaslow ; Viral Infections of Humans –Epidemiology and Control, Fourth Edition Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett’s ; Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases, Fifth Edition 教务处制