* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5 - JScully
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of algebra wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic form wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
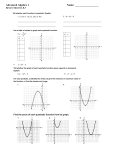
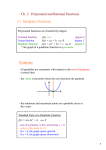
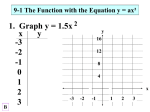
5.1 Use Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Example 1: y Example 2: x y x 1 Example 3: y x 2 Example 4: a. b. Transformation: ____________________ Transformation: ____________________ y y x x c. g(x) = ( x – 4)² + 3 d. Transformation: ____________________ Transformation: ____________________ y y x x f. g(x) = (x ─ 5)² + 4 e. g(x) = ( x + 2)² + 1 Transformation: ____________________ Transformation: ____________________ y y x x 3 Vertex of a parabola: ________________________________________________________ Vertex form: _______________________________________________________________ 4 Example 5: a. b. y y x c. x d. y y x x e. f. y y x x 5 Vertex Form: __________________________________ Example 6: Use the description to write the quadratic function g(x) in vertex form. a. The parent function f(x) = x² is shifted right 3 units, and up 4 units. c. The parent function f(x) = x² is shifted left 2 units, and down 5 units. d. The parent function f(x) = x² is shifted right 1 units, and up 3 units. e. The parent function f(x) = x² is reflected over the x The axis, shifted left 6 units, and down 2 units. f. The parent function f(x) = x² is reflected over the x axis, shifted right 1 unit, and down 7 units. Example 7: Describe the transformation from the parent function f(x) = x² a. g(x) = (x – 3)² + 1 _________________ b. g(x) = – (x + 2)² – 4 ______________ c. g(x) = (x + 1)² + 2 __________________ c. g(x) = (x – 5)² – 3 ______________ e. g(x) = – (x + 3)² – 5 _________________ f. g(x) = (x + 1)² – 7 ______________ g. g(x) = (x + 3)² + 8 __________________ h. g(x) = – (x – 5)² + 6 ______________ 6 The axis of symmetry is always the vertical line x = a number (the number is the ___________________ of the vertex) Example 1: a. Identify the axis of symmetry and vertex for the graph f(x) = 2(x + 2)² – 3, then draw the graph. y x Identify the axis of symmetry and vertex for the graphs, then draw the graphs. b. c. y y x x 7 Standard form of a quadratic equation: ___________________________________________________ Where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. If the equation is in standard form, the parabola has the following properties: The equation opens upward if a is ______________________. The equation opens downward if a is ____________________. The equation for the axis of symmetry is ________________. The y intercept is the ________ value. The vertex is the point ( , ) Example 3: a. b. y c. d. x e. 8 Example 4: a. b. c. y d. x e. Example 5: a. b. y y x x 9 When a parabola opens upward, the y-value of the vertex is the __________________ value. When a parabola opens downward, the y-value of the vertex is the __________________ value. Example 6: a. c. b. d. 10 5.3 Zeros of a function: _________________________________________________________________ Example 1: a. b. y y x x c. y x 11 Factor. 1. x² + 7x + 6 2. x² – x – 2 3. x² – 5x + 4 4. x² – 7x + 10 5. x² + x –12 6. x² –2x + 1 7. x² + 3x – 10 8. x² + 5x + 4 9. x² + 6x + 5 . 15. 5x² – 15x 16. 2x² – 16x + 30 17. – x² + x + 56 18. 3x² + 18x +27 12 When a polynomial has __________ terms, you can make two groups and factor out the __________ of each group. Factor by grouping. 1. 12x³ – 9x² + 20x – 15 3. 2x³ – 2x² – 3x + 3 2. 6x³ – 8x² – 15x + 20 4. 6x³ + 18x² + x + 3 To Factoring ax² + bx + c, when a ≠ 1 “AC Method” Step 1: Multiply a∙c Together: Step 2: What factors of a∙c combine to b? 6x² + 11x + 3 Step 3: Write as a 4 term polynomial Step 4: Factor by grouping 13 Factor completely. a. 4x² + 16x + 15 d. 9x² – 15x + 4 g. 5x² + 11x + 2 j. 2x² +13x + 15 b. 2x² + 11x + 12 e. 3x² + 13x + 12 h. 10x² – 9x – 1 k. 3x² + 10x + 8 c. 5x² – 14x + 8 f. 7x² – 3x – 10 i. 15X² + 4X – 3 l. 2x² – 7x –15 14 The solutions to a quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0 are called _____________. The roots of an equation are the values of the variable that make the equation ___________. You can find the roots of some quadratic equations by ________________ and applying the ______ product property. Example 2: a. b. f(x) = x² + 6x – 7 c. f(x) = x² – 3x – 28 d. g(x) = 4x² + 8x e. g(x) = 10x² – 25x f. g(x) = 6x² – 9x g. h. j. f(x) = 3x² + 8x + 4 k. f(x) = 2x² – 11x + 5 i. 15 Make a list of the first 15 square numbers: Difference of two squares: a² ─ b² = ( )( ) Example 4: a. b. 36x² = 49 c. 36x² = 100 d. e. 4x² = 25 f. 81x² = 144 16 Example 5: a. b. c. d. Write a quadratic function in standard form with zeros 6 and 2. e. Then Write a quadratic function in standard form with zeros -3 and -2. 17