* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Polythiophene wikipedia , lookup
Molecular scale electronics wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
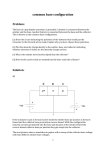
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS FOR CHAPTER 14 All questions have only one correct answer 1. [a] [b] [c] [d] In normal operation, the junctions of a p-n-p transistor are: both forward biased base-emitter forward biased and base-collector reverse biased both reverse biased base-collector forward biased and base- emitter reverse biased 2. [a] [b] [c] [d] In normal operation, the junctions of an n-p-n transistor are: both forward biased base-emitter forward biased and base collector reverse biased both reverse biased base-collector forward biased and base- emitter reverse biased 3. [a] [b] [c] [d] The current flow across the base-emitter junction of a p-n-p transistor: mainly electrons equal numbers of holes and electrons mainly holes the leakage current 4. [a] [b] [c] [d] The current flow across the base-emitter junction of an n-p-n transistor consists of mainly electrons equal numbers of holes and electrons mainly holes the leakage current 5. [a] [b] [c] [d] In normal operation an n-p-n transistor connected in common-base configuration has: the emitter at a lower potential than the base the collector at a lower potential than the base the base at a lower potential than the emitter the collector at a lower potential than the emitter 6. [a] [b] [c] [d] In normal operation, a p-n-p transistor connected in common-base configuration has: the emitter at a lower potential than the base the collector at a higher potential than the base the base at a higher potential than the emitter the collector at a lower potential than the emitter 7. [a] [b] [c] [d] If the per unit value of electrons which leave the emitter and pass to the collector is 0.9 in an n-p-n transistor and the emitter current is 4 mA, then: the base current is approximately 4.4 mA the collector current is approximately 3.6 mA the collector current is approximately 4.4 mA the base current is approximately 3.6 mA 8. [a] [b] The base region of a p-n-p transistor is: very thin and heavily doped with holes very thin and heavily doped with electrons [c] [d] very thin and lightly doped with holes very thin and lightly doped with electrons 9. The voltage drop across the base-emitter junction of a p-n-p silicon transistor in normal operation is about: 200 mV 600 mV zero 4.4V [a] [b] [c] [d] 10. [a] [b] [c] [d] For a p-n-p transistor: the number of majority carriers crossing the base emitter junction largely depends on the collector voltage in common-base configuration, the collector current is proportional to the collector-base voltage in common-emitter configuration, the base current is less than the base current in commonbase configuration the collector current flow is independent of the emitter current flow for a given value of collector-base voltage 11. If R L in Figure 1 is short-circuited, the ... [a] amplifier signal output would fall to zero [b] collector current would fall to zero [c] transistor would overload Figure 1 12. If R2 in Figure 1 is open-circuited the ... [a] amplifier signal output would fall to zero [b] operating point would be affected and the signal would distort [c] input signal would not be applied to the base Figure 1 13. A voltmeter connected across R E in Figure 1 reads zero. Most probably ... [a] the transistor base-emitter junction has short-circuited [b] R L has open-circuited [c] R2 has short-circuited 14. A voltmeter connected across R L in Figure 1 reads zero. Most probably ... [a] the V CC supply battery is flat [b] the base collector junction of the transistor has gone open circuit [c] R L has open-circuited 15. If R E in Figure 1 is short-circuited the ... [a] load line would be unaffected [b] load line would be affected 16. [a] [b] [c] [d] With reference to the output characteristics shown in Figure 2, the load line represents a load resistor of: 1 k 2 k 3 k 0.5 k Figure 2 17. [a] [b] [c] [d] With reference to the output characteristics shown in Figure 2, the no-signal collector dissipation for the operating point marked P is: 12 mW 15 mW 18 mW 21 mW Figure 2 18. [a] With reference to the output characteristics shown in Figure 2, the greatest permissible peak input current would be about 30 A [b] [c] [d] 35 A 60 A 80 A Figure 2 19. [a] [b] [c] [d] With reference to the output characteristics shown in Figure 2, the greatest possible peak output voltage would then be about 5.2 V 6.5 V 8.8 V 13 V Figure 2 20. [a] [b] [c] [d] With reference to the output characteristics shown in Figure 2, the power dissipated in the load resistor under no-signal conditions is: 16 mW 18 mW 20 mW 22 mW Figure 2