* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review Sheets 2016
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
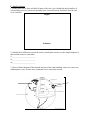
Grade 9 Geography Final Exam Review Sheets A – Natural Resource Industries of Canada 1.) On your own sheets of lined paper, identify any 1 major natural resource industry of Canada (we studied four) and describe its economic, cultural and historical importance. - Explain why it is so valuable to Canada. Then, describe the methods it uses to extract the natural resource (using key terms). - Identify any problems this industry is facing or causing. - Explain the solutions to these problems that could help the industry to be sustainable. 2.) Explain the difference between basic and non-basic jobs with an example for each. B – Immigration Complete the following chart to identify the various characteristics immigration to Canada: Types of Immigrants System Used to Process the Qualities needed in order for Application Applicant to be approved 1. 2. 3. 2.) Explain what the following terms mean and provide three (3) examples of each: Push Factor: ___________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Pull Factor: ____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Cultural Baggage: ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ C – Interpreting Political Cartoons Examine the political cartoon below carefully then, answer the questions about it that follow on the lines provided. 1. What is the overall general topic of the cartoon? _________________________________________________ 2. Is the artist saying that Canada is doing a good job with regard to this topic? ______ 3. How do you know this? Explain by referring to the cartoon.__________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ 4. What do you do (or have you done) to reduce your own greenhouse gas emissions? ___________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ D – Overall Key Terms, Definitions and Diagrams 1.) Match the following key terms with the correct industry. raw materials wheat farmer lab researcher (RIM) Tim Horton’s St. Benedict C.S.S. lawyer mining coal waitress doctor health clinic Primary Industry Secondary Industry Column A A. renewable resource B. non-renewable resource C. offshore limit D. industrial/structural E. pesticides F. esker G. ground fish H. pelagic fish I. crustaceans & molluscs J. purse-seining K. long-line L. otter trawler M. fuel minerals N. sustainable O. metallic minerals P. coniferous Q. fallow fields R. urbanization S. clear-cutting T. old growth forests U. herbicides V. no-till farming W. deciduous X. urban sprawl Y. competition Z. de-beaking chicken Word Choice List saw mill operator in shore fishing boat captain gravel quarry construction worker car manufacturer Tertiary Industry lumber jack firefighter tapping maple trees caviar canning plant limousine driver Quaternary Industry Column B ____ fish that feed off of the ocean floor ____ type of minerals that include gravel and sand ____ using a resource wisely so there is enough for future use ____ minerals such as coal, oil and natural gas ____ minerals such as gold, silver, iron, copper, etc. ____ a resource that reproduces itself naturally ____ a type of tree that has broad leaves and sheds in the fall ____ a forest that has never been logged before ____ a boundary offshore that a country has rights to for resources ____ when cities expand outwards in all directions ____ a resource that cannot reproduce itself in nature ____ leaving parts of crops in fields to prevent soil erosion ____ fish that feed near the surface of ocean water ____ the process of people moving from countryside into the city ____ lobsters, crabs, shrimp, mussels, clams, etc. ____ chemicals used to kill weeds to prevent them from choking out crops ____ cause of some family run farms going out of business ____ method of fishing using a net that drags along the ocean floor ____ a net that surrounds and circles around a school of fish ____ method of cutting trees where all are cut down in an Area ____ harmful practice used by some agribusiness (factory) farms ____ a type of tree that has cones and needles; evergreens ____ leaving farm fields bare which can lead to soil erosion ____ a narrow, winding ridge of gravel and sand left by meltwater ____ chemicals used to kill insects and bugs on crops _____ method of fishing using a long, baited line to attract fish E – Mapping Concepts 1.) Complete the following chart: Criteria Latitude Starting Line and Measure (in degrees) Measured in these directions from this major line Lines run across globes and maps in this direction Other major lines and measures Longitude This country was named ------------------------------------after the Equator as this line runs through it: 2.) In the space below, draw a complete compass rose with directions. Highlight the major cardinal directions and include their bearing degree measurements on your compass rose. 3.) What are the three main types of map scales? Identify them and include an example of what each would look like on a map. a) Name: ___________________________ Example: _________________________________ b) Name: ___________________________ Example: _________________________________ c) Name: ___________________________ Example: _________________________________ 4.) Convert the following scales: a) 1: 750 000 means that 1cm = _________________ cm b) 1cm equals 20 km written as a ratio scale = ________________________________ c) 1 cm equals 10 km as a line scale would look like: __________________________________ 5.) What does the following acronym stand for? S ___________ T ___________ A ___________ B ___________ L ___________ E ___________ D ___________ F - Earth’s Geology 1.) In the space below, draw and label all parts of the rock cycle. Include the major families of rock and the processes (with arrows pointing in the correct direction), that shows how the rock cycle circulates. Magma Sediments 2.) Identify three different ways that the earth’s crustal plates can move with a simple diagram of their motion relative to each other: i) __________________________ ii) __________________________ iii) _________________________ 3.) Draw a labeled diagram of the internal structure of the earth including: inner core, outer core, asthenosphere, crust, oceanic crust, continental crust, convection currents. G - Climate and Landforms 1.) Match the following: Column A A relief precipitation B convectional precipitation C cyclonic precipitation D Canadian Shield E Western Cordillera F Great Lakes/St. Lawrence Lowlands G Rocky Mountains H Innuitian Mountains I Appalachian Mountains Column B ____ made up mostly of Precambrian igneous rock ____ the youngest mountains in Canada ____ precipitations that falls on the windward side of mountains ____ the oldest mountains in Canada ____ precipitation that falls in the prairies provinces ____ made up of three main mountain ranges ____ precipitation that occurs in Cambridge ____ the landform region we live in ____ iciest mountain range in Canada H – Ecological Footprint 1.) In the space below, in paragraph format, explain what an ecological footprint is. How big is the Canadian ecological footprint compared to that of most other countries in the world? How many planet earths would we need in order to support everyone living on the planet with a Canadian lifestyle? Why is it important to “think globally and act locally” when connecting the ideas of ecological footprint and global village? Provide specific examples for how we can reduce our ecological footprint in terms of: water, energy consumption, waste production, and land use. How could these changes benefit the global village? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ I – Population Pyramids 1. Examine the population pyramids below and interpret them by answering the questions that follow. a) In which year does Canada have more births? How can you tell? What might explain the high birth rate in this year? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ b) Calculate the percentage of population that is the dependency load for each pyramid. The dependency load is the percentage of people who are not in a working age range, and therefore depend on others for support (financially, etc.). Show all work. In 1961 the dependency load was: In 2050 what is the projected dependency load expected to be? (number will be a % of the population) (number will be in the millions) /4 = _______% = ________ million people c) Based on the dependency load for 1961, what must the government have had to plan for? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ d) Based on the projected dependency load for 2050, what must the government of the near future have to plan for? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Part J – Location Factors On the lines provided below, identify the six location factors that businesses and industry make when trying to decide where to locate. Explain each factor beside as you identify them. 1. ________________________: _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________: _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________: _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 4. ________________________: _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 5. ________________________: _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 6. ________________________: _________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________