* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ostrya virginiana
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
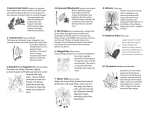
HOPHORNBEAM While walking through the woods, one might observe a small tree with shredding and peeling bark Although that tree may not be a Hickory (Genus Carya), it might be the Hophornbeam (Ostrya virginiana [P. Miller] K. Koch). Hophornbeams are not related to the Hickories. Hophornbeams are members of the Order Fagles and of the Family Betulaceae. Previous scientific synonyms for this tree were Carpinus triflora Moench, C. virginiana Miller, C. virginica Munchhausen, Ostrya americana F. Michaux, O. baileyi Rose, O. ostrya MacMillan, O. virginica (Munchhausen) Willdenow, and Zugilus virginica Rafinesque. The generic name, Ostrya, is from the ancient Greek words, ostrua or ostuoes, which are a name for a tree with hard wood. The specific epithet, virginiana, is Latin for “of Virginia”, where it was first identified. The common name, Hophornbeam, was named because its fruit clusters resemble hops. Other common names for this tree are American Hophornbeam, Beetlewood, Black Hazel, Deerwood, Eastern Hophornbeam, Hardhack, Hardtack, Hornbeam, Indian Cedar, Ironwood, Leverwood, and Rough-barked Ironwood. Hophornbeam is a slow-growing and a moderately long-lived tree. It tolerates snow and ice but not salt, flooding, or urban sites. DESCRIPTION OF THE HOPHORNBEAM Height: Its height is 20-60 feet. It is a small tree or a tall shrub. Diameter: Its trunk diameter is 6-36 inches. Crown: Its crown is rounded, irregular, and cone-shaped or vase-shaped. Its small branches are wide-spreading, long, slender, and drooping. Trunk: Its trunk is straight. The older trunks might be gnarled, knobby, twisted, or buttressed. This tree has only 1 trunk. Twigs: Its young twigs are pale green and finely hairy. Its older twigs become orange, red-brown, or dark brown. They are zigzag, flexible, have small lenticels, and are hard to break. Its leaf scars are alternate, slightly elevated, and crescent-shaped with 3 bundle scars. Its pith is white and continuous. White-tailed Deer (Odocoileus virginianus Zimmermann) and Eastern Cottontail Rabbits (Sylvilagus floridanus J.A. Allen) eat these twigs. Buds: Its terminal buds are non-existent. Its lateral buds are yellow greenish brown, slightly hairy, about 1/8-1/4 inches long, divergent, rounded, and pointed. Each bud has 6-8 bud scales that are finely and longitudinally grooved and are not aligned in rows. Ruffed Grouse (Bonasa umbellus L.), Songbirds (Suborder Passeri), and Squirrels (Family Sciuridae) eat these buds. Leaves: Its leaves are simple, alternate, and deciduous. They are arranged in 2 rows. Each leaf is about 1-6 inches long; about 1-2½ inches wide; and are elliptic, narrowly ovate, oblong, or lanceolate. Its tip is pointed, its base is rounded or cordated, and its margins are sharply and unevenly double-toothed. Its parallel lateral veins are forked near the margin. The larger teeth are located at the ends of the major lateral veins. It is dull dark yellow green above and paler and slightly hairy below. Its petioles are about ¼ inches long and hairy. These leaves turn dull yellow to brown in the fall and may persist upon the tree throughout the winter. Flowers: Its flowers are monoecious and have no petals. Its male (staminate) flowers are arranged in 1-3, 1-2½ inch long, stalkless dense, cylindrical catkin clusters located near the end of the branches. Each flower has 3-14 stamens and is green to red-brown. These catkins may be prominent in the winter. Its female (pistillate) flowers are arranged in ½3/4 inch long, slender, loose clustered catkins or spikes located at the tips of the branches. Each flower is ¼ inches long, red-green, and hairy. It has a short 2-lobed style. These flowers are wind-pollinated. Flowering season is April to May. Fruit: Its fruits are about 1¼-2¼ inches long. They are hanging cone-like clusters of thin, papery, inflated, sac-like, unlobed bracts. Each sac is about ½-¾ inches long and wide and has a ¼ inch, shiny brown, flattened, ovoid, ribbed nutlet. This tree bears fruit at 2025 years. Ruffed Grouse, Wild Turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo L.), Northern Bobwhite Quail (Colinus virginianus L.), and Squirrels eat these nutlets. Fruiting season is August to October. Bark: Its young bark is smooth, red-brown to purple, and has horizontal lenticels. Its mature bark is gray-brown, thin, rough, grooved, loose, and flaky. It has narrow, rectangular peeling strips that curl at both ends. This bark is rich in tannin. Wood: Its wood is hard, heavy, tough, strong, dense, durable, and split-resistant. It is fine-grained, close-grained, and diffuse-porous. It has light red-brown heartwood and thick white sapwood. Its growth rings are indistinct. Roots: Its roots are taproots. This tree is wind firm. Habitat: Its habitats consist of moist, well-drained upland woods. It is an understory tree and is shade tolerant. Range: Its range consists of the eastern U.S. and southeastern Canada as far west as the Great Plains, excluding Florida and the southeastern Atlantic coast. Uses of the Hophornbeam: Hophornbeam has limited commercial value. Its wood is used for tool handles, mallets, wedges, fence posts, sleigh runners, wagon wheel hubs, wagon tongues, pestels, mill cogs, rake teeth, oxen yokes, ladder rungs, bows, fishing poles, treenware, and fuel. Unfortunately, the wood dulls the sharp tools and does not take nails or wood screws easily. Hophornbeam has some medicinal, too. The bark and inner was used for treating sore muscles, malaria, fevers, indigestion, toothaches, consumption, and as tonic. A bark poultice was used for treating neck swellings. The wood chips were used for treating kidney troubles, coughs, and lung hemorrhage. The roots were used as tonic. REFERENCES MICHIGAN TREES By Burton V. Barnes and Warren H. Wagner, Jr. FALL COLOR AND WOODLAND HARVESTS By C. Ritchie Bell and Anne H. Lindsey AN ECLECTIC GUIDE TO TREES: EAST OF THE ROCKIES By Glen Blouin MEDICINAL ANS OTHER USES OF NORTH AMERICAN PLANTS By Charlotte Erichsen-Brown THE BOOK OF FOREST AND THICKET By John Eastman and Amelia Hansen TREES OF PENNSYLVANIA AND THE NORTHEAST By Charles Fergus and Amelia Hansen TREES OF EASTERN AND CENTRAL UNITED STATES AND CANADA By William M. Harlow FOREST TREES OF ILLINOIS By Jay C. Hayek, Editor 101 TREES OF INDIANA By Marion T. Jackson OUR NATIVE TREES By Harriet L. Keeler TREES OF ILLINOIS By Linda Kershaw NATIONAL WILDLIFE FEDERATION FIELD GUIDE TO TREES OF NORTH AMERICA By Bruce Kershner, Daniel Mathews, Gil Nelson, and Richard Spellenberg A FIELD GUIDE TO MEDICINAL PLANTS By Arnold and Connie Krochmal TREES OF MISSOURI By Don Kurz TREES OF THE CENTRAL HARDWOOD FORESTS OF NORTH AMERICA By Donald J. Leopold, William C. McComb, and Robert N. Muller THE AUDUBON SOCIETY FIELD GUIDE TO NORTH AMERICAN TREES (EASTERN REGION) By Elbert L. Little HOW TO KNOW THE TREES By Howard A. Miller and H. E. Jaques NATIVE AMERICAN MEDICINAL PLANTS By Daniel E. Moerman TREES OF EASTERN NORTH AMERICA By Gil Nelson, Christopher J. Earle, and Richard Spellenberg EASTERN TREES By George A. Petrides TREES AND SHRUBS By George A. Petrides. THE SIBLEY GUIDE TO TREES By David Allen Sibley OHIO TREES By T. Davis Sydnor and William F. Cowen NATIVE TREES OF THE MIDWEST By Sally S. Weeks, Harmon P. Weeks, Jr., and George R. Parker IDENTIFYING TREES By Michael D. Williams en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ostrya_virginiana