* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sedimentary Rocks Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
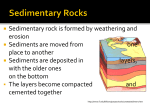
SEDIMENTARY ROCKS BEGIN WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY ROCK? A sedimentary rock is a rock that formed from the compaction and cementation of sediments. LAST NEXT BUT, WHAT IS A SEDIMENT? Sediments are fragments of rock that have been broken down as a result of weathering (wind, ice, running water, etc.) LAST NEXT SEDIMENTS ARE CLASSIFIED ACCORDING TO THEIR SIZE. CLAY SILT SAND PEBBLE COBBLE LAST BOULDER NEXT SEDIMENT NAMES AND SIZES CAN BE FOUND ON PAGE 7 OF THE ESRT LAST Scheme for Sedimentary Rock INORGANIC LAND-DERIVED SEDIM TEXTURE GRAIN SIZE Pebbles, cobbles, and/or boulders embedded in sand, silt, and/or clay Clastic (fragmental) Sand (0.006 to 0.2 cm) Silt (0.0004 to 0.006 cm) Clay (less than 0.0004 cm) COMPOSITION CO Rounded Mostly quartz, feldspar, and clay minerals; may contain fragments of other rocks and minerals Angular f Fine to co Very fine Compact easily CHEMICALLY AND/OR ORGANICALLY FORME TEXTURE Crystalline GRAIN SIZE Fine to coarse crystals COMPOSITION Halite Gypsum COM Crysta chemi precip and ev Dolomite Crystalline or bioclastic Bioclastic Microscopic to very coarse Calcite Precipitate origin or ce fragments Carbon Compacte plant rem Scheme for Metamorphic Rock NEXT Relationship of Transported Particle Size to Water Velocity 00.0 25.6 10.0 6.4 1.0 Boulders Cobbles Pebbles 0.2 0.1 Sand 0.01 0.006 Silt 001 0.0004 001 ...AND ON PAGE 6 OF THE ESRT. Clay 1000 500 100 50 10 5 1 0.5 0.1 0.05 0.01 STREAM VELOCITY (cm/s) LAST This generalized graph shows the water velocity NEXT Sediments are constantly being dropped off all over the Earth. This process is known as deposition. LAST NEXT Clastic sedimentary rocks are composed of sediments which have been compacted by the weight of water or other sediments, and cemented, or glued together. LAST NEXT Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification INORGANIC LAND-DERIVED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE GRAIN SIZE Pebbles, cobbles, and/or boulders embedded in sand, silt, and/or clay Clastic (fragmental) Sand (0.006 to 0.2 cm) Silt (0.0004 to 0.006 cm) Clay (less than 0.0004 cm) COMPOSITION COMMENTS Rounded fragments Mostly quartz, feldspar, and clay minerals; may contain fragments of other rocks and minerals Angular fragments Fine to coarse Very fine grain ROCK NAME MAP SYMBOL Conglomerate Breccia Sandstone Siltstone Compact; may split easily . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Shale CHEMICALLY AND/OR ORGANICALLY FORMED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE Crystalline GRAIN SIZE Fine to coarse crystals COMPOSITION Halite Gypsum COMMENTS Crystals from chemical precipitates and evaporites Bioclastic LAST Microscopic to very coarse MAP SYMBOL Rock salt Rock gypsum Dolostone Dolomite Crystalline or bioclastic ROCK NAME Calcite Precipitates of biologic origin or cemented shell fragments Carbon Compacted plant remains Limestone Bituminous coal Scheme for Metamorphic Rock Identification NEXT Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification INORGANIC LAND-DERIVED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE GRAIN SIZE Pebbles, cobbles, and/or boulders embedded in sand, silt, and/or clay Clastic (fragmental) Sand (0.006 to 0.2 cm) Silt (0.0004 to 0.006 cm) Clay (less than 0.0004 cm) COMPOSITION COMMENTS Rounded fragments Mostly quartz, feldspar, and clay minerals; may contain fragments of other rocks and minerals Angular fragments Fine to coarse Very fine grain ROCK NAME MAP SYMBOL Conglomerate Breccia Sandstone Siltstone Compact; may split easily . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Shale CHEMICALLY AND/OR ORGANICALLY FORMED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE GRAIN SIZE COMPOSITION COMMENTS ROCK NAME MAP SYMBOL Notice how they are classified according to the size of the sediments making them up. Crystalline Fine to coarse crystals Halite Gypsum Crystals from chemical precipitates and evaporites Bioclastic LAST Microscopic to very coarse Rock gypsum Dolostone Dolomite Crystalline or bioclastic Rock salt Calcite Precipitates of biologic origin or cemented shell fragments Carbon Compacted plant remains Limestone Bituminous coal Scheme for Metamorphic Rock Identification NEXT Conglomerate is composed of rounded sediments of all different sizes. LAST NEXT Breccia is composed of angular sediments of all different sizes. LAST NEXT Sandstone is composed of sand-sized sediments and may display layering. LAST NEXT Siltstone is composed of silt-sized sediments. LAST NEXT Shale is composed of clay-sized sediments and often contains fossils. LAST NEXT Sedimentary rocks may form in other ways, besides compaction and cementation of sediments. LAST NEXT Some are said to be crystalline, forming from evaporation or precipitation. LAST NEXT Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification INORGANIC LAND-DERIVED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE GRAIN SIZE Pebbles, cobbles, and/or boulders embedded in sand, silt, and/or clay Clastic (fragmental) Sand (0.006 to 0.2 cm) Silt (0.0004 to 0.006 cm) Clay (less than 0.0004 cm) COMPOSITION COMMENTS Rounded fragments Mostly quartz, feldspar, and clay minerals; may contain fragments of other rocks and minerals Angular fragments Fine to coarse Very fine grain ROCK NAME MAP SYMBOL Conglomerate Breccia Sandstone Siltstone Compact; may split easily . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Shale CHEMICALLY AND/OR ORGANICALLY FORMED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE Crystalline GRAIN SIZE Fine to coarse crystals COMPOSITION Halite Gypsum COMMENTS Crystals from chemical precipitates and evaporites Bioclastic LAST Microscopic to very coarse MAP SYMBOL Rock salt Rock gypsum Dolostone Dolomite Crystalline or bioclastic ROCK NAME Calcite Precipitates of biologic origin or cemented shell fragments Carbon Compacted plant remains Limestone Bituminous coal Scheme for Metamorphic Rock Identification NEXT An evaporite, like Rock Salt, forms when minerals dissolved in water are left behind as crystals when the water evaporates. LAST NEXT This area was once covered by a shallow, salty sea. Over time, the water evaporated, leaving the salt behind. This is how the sedimentary evaporite, Rock Salt forms. LAST NEXT The third, and final, type of sedimentary rocks are organic in nature. LAST NEXT These rocks form as a result of processes that involve living organisms. LAST NEXT Scheme for Sedimentary Rock Identification INORGANIC LAND-DERIVED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE GRAIN SIZE Pebbles, cobbles, and/or boulders embedded in sand, silt, and/or clay Clastic (fragmental) Sand (0.006 to 0.2 cm) Silt (0.0004 to 0.006 cm) Clay (less than 0.0004 cm) COMPOSITION COMMENTS Rounded fragments Mostly quartz, feldspar, and clay minerals; may contain fragments of other rocks and minerals Angular fragments Fine to coarse Very fine grain ROCK NAME MAP SYMBOL Conglomerate Breccia Sandstone Siltstone Compact; may split easily . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Shale CHEMICALLY AND/OR ORGANICALLY FORMED SEDIMENTARY ROCKS TEXTURE Crystalline GRAIN SIZE Fine to coarse crystals COMPOSITION Halite Gypsum COMMENTS Crystals from chemical precipitates and evaporites Bioclastic LAST Microscopic to very coarse MAP SYMBOL Rock salt Rock gypsum Dolostone Dolomite Crystalline or bioclastic ROCK NAME Calcite Precipitates of biologic origin or cemented shell fragments Carbon Compacted plant remains Limestone Bituminous coal Scheme for Metamorphic Rock Identification NEXT Bituminous Coal forms from the decomposition and compaction of plant remains over thousands of years. LAST NEXT Some forms of Limestone, like this coquina, form from the compaction and cementation of shells. LAST NEXT Sedimentary rocks are the only type of rocks that may contain fossils, or evidence of past life. LAST NEXT LAST NEXT LAST NEXT