* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SIDS Initiatives - School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
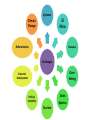
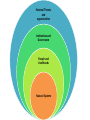
Cyclones El Nino Climate Change Deforestation Tsunamis Challenges Over Economic Development fishing Alien Political Instability Species Tourism How are they trying to manage these issues? ‘Evaluate’ - - - - Convention on Biological Diversity and Biodiversity Action Plans Linked to Rio Summit 1992 Countries which agreed with the Convention started to write their Biodiversity Action Plans (BAPs) which aim to restore and protect biological systems To complete a BAP they have to assess conservation status of species, create targets, establish budgets 2009 = 191 ratified the CBD but only a fraction have completed BAPs Several of the Pacific SIDS have complete BAPs e.g. Tuvalu, Micronesia, Samoa, Marshall Islands, Tonga, Cook Islands, Kiribatti All of these countries also signed up for the 2010 Biodiversity Target (to achieve significant reduction of current rate of biodiversity loss) – incorporated into the MDGs Islands First - NGO - Works for the small islands Helps to get their message heard in the UN Assembles scientific support Ensure that the SIDS are properly represented on the UN and in attendance at meetings Mobilises public support Attended Copenhagen 2009 MPAs - - Protected Marine Environments Established in the Pacific the Phoenix Islands Protected Area and is the size of California Also nominated for a World Heritage Site Organised by the government of Kiribati and 2 NGOs Conservation International and New England Aquarium Allows scientific research CRISP – coral reef initiatives for the Pacific - - - Sponsored by France and the French Development Agency Aims to create a vision for the future of coral reefs and the communities they support Also aims to help integration between developed countries (Australia, New Zealand and France) and developing countries (SIDS) One area they have developed is reef restoration but they also look at coastal integrated management and the socio – economic value of the reefs. WWF – World Wildlife Fund - Have a regional operation in the South Pacific Aims for: Effective fisheries managment Increasing populations of priority species Networks of MPAs Helping develop and secure national and regional conservation policies Projects based on ‘Bottom Up’ development and working with communities To what extent do these management options help solve the challenges facing the Pacific SIDs? Cyclones CBD & BAPS Islands First MPAS CRISP WWF El Nino Tsunamis Tourism Alien Species Political Instability Economic Develop ment Deforest Climate ation Change External Threats and opportunities Institutions and Governance People and Livelihoods Natural Systems Players • Players focuses on the organisations, groups and individuals who have a role to play within an issue • Players might be thought of as ‘decision makers’ or ‘stakeholders’ • Players may hold very different views on an issue, because they have different opinions and values • It is important students understand these different positions and perspectives CONSERVATIONISTS – an area of biodiversity to be protected from human activity INDIVIDUALS– an area to be enjoyed and explored; expectation that facilities and amenities will be available TOURISM INDUSTRY – an area for making profits, but also requiring conservation to maintain visitor numbers LOGGERS – an area of timber resources that could be exploited WATER INDUSTRY – an important source of freshwater to supply homes and industry Actions • Actions focuses on both the scale and standpoint of actions • There is a hierarchy of actions at different scales • There is often debate over which scale of management is best for a particular issue • Often an issue is managed at several scales • Chosen actions are influenced by players’ standpoints, especially political and economic beliefs Global agreements and international action National policy and management Local governance and individual actions Neo-liberal Socialist Grassroots Focus on commercial solutions and less government influence Focus on national planning and targets, often top-down Focus on bottomup and sustainable, small scale initiatives International, market-led National, government led Local, community led Futures • Futures focuses on the direction the contested planet should take • Three future scenarios are recognised: Business as usual Sustainable Radical • The first implies humans continue to behave in similar ways to the past i.e. high consumption and pollution • Sustainable futures suggests stabilising consumption and human environmental impacts • Radical implies concerted action to reverse environmental degradation • Each of the three futures have very different consequences and are supported by different players • Each approach has very different costs and benefits

















![[draft 3 – August 26] - Permanent Mission to the United Nations](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002283207_1-9fe48da960ce73311bff9a7b672b902e-150x150.png)



