* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6 Guided Questions
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
N-body problem wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
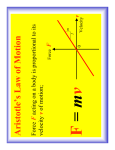
Guided Questions for Chapter 6: Forces and Motion 1. Why do objects fall to the ground at the same rate? 2. What is velocity of a falling object on the Earth? 3. After 3 seconds, how far as an object fallen? 4. What is the formula for the Velocity of a Falling Object? 5. In the formula, what is G equal to? 6. What force opposes the motion of objects through air? 7. What does air resistance depend upon? 8. What is Terminal Velocity? Explain how terminal velocity is reached. 9. What is free fall? 10. Where is free fall possible? 11. What 2 motions combine to cause orbiting? 12. What is centripetal force? 13. What provides the centripetal force that keeps objects in orbit? 14. What is projectile motion? 15. What two types of motion make up projectile motion? 16. What does Newton’s First Law state? Give an example of this law. 17. How does friction factor into Newton’s First Law of Motion? 18. How does inertia factor into Newton’s First Law of Motion? 19. What does Newton’s Second Law state? Give an example. 20. What are the 2 parts of Newton’s Second Law of Motion? 21. How can Newton’s Second Law be expressed in a formula? 22. What does Newton’s Third Law state? Give an example. 23. Why is Newton’s Third Law difficult to see? 24. Define momentum. 25. What is the formula for calculating momentum? 26. What does the Law of Conservation of Momentum state? 27. How does the Law of Conservation of Momentum apply to Newton’s Third Law of Motion?