* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
HW- pgs. 416-417 (6.29-6.36)
6.1 & 6.2 Quiz Tuesday 12-4-12
Ch. 6 Test Tuesday 12-11-12
www.westex.org HS, Teacher Website
11-28-12
Warm up—AP Stats
Are there a finite or infinite amount of numbers
between 0 and 1? Discrete goes with __________
and continuous goes with ____________.
Do evaluation…
Name _________________________
AP Stats
6 Probability and Simulation: The Study of Randomness
6.2 Probability Models
Date _______
Objectives
Explain what is meant by a probability model.
Construct a tree diagram.
Use the multiplication principle to determine the number of outcomes in a sample
space.
Explain what is meant by sampling with and without replacement.
Probability Models
We need a mathematical description, or model for randomness. The vocabulary for all
_______________ __________ is as follows:
The __________ _________ ___ of a random phenomenon is the set of all possible
outcomes. (whether discrete or continuous)
An ________ is any outcome or set of outcomes of a random phenomenon. Therefore an
event is a _________ of the sample space.
A probability model is a mathematical description of a __________ phenomenon consisting of
two parts: a sample space and a way of assigning probabilities to events.
To specify S, we must state what constitutes an ______________ outcome and then state
which outcomes can __________. Each member of S is a possible _________, which explains
the term sample _________.
Being able to number the outcomes in a sample space is obviously critical in determining
_____________.
Three techniques to make sure no outcomes are overlooked:
1. Tree diagrams
2. Multiplication Principle
3. Organized list of possible outcomes
TREE DIAGRAM
Construct a tree diagram for tossing a coin and then rolling a die.
MULTIPLICATION PRINCIPLE
If you can do one task in n1 number of ways and a second task in n2 number of ways, then both
tasks can be done in ____________ number of ways.
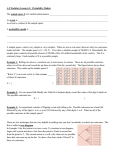
How many possible outcomes are in
the sample space of spinning this
spinner and rolling this die?
ORGANIZED LIST
How can we make an organized list of the sample space for flipping a coin 4 times in
succession?
0 Heads
1 Head
2 Heads
3 Heads
4 Heads
In mathematics, essential features of quite different phenomena can be described by the
same mathematical __________. Ex. The possible outcomes of an SRS of 1500 people in a
yes/no opinion poll are the same in principle as the possible outcomes of tossing a coin 1500
times.
Unfortunately some sample spaces are too large to list.
We have seen how our calculators can generate a random number for a discrete set of
numbers. Our calculators can also generate a number from a continuous sample space such as
between 0 and 1.
S = {all numbers between 0 and 1}
Sampling with replacement-if you want the second “draw” to have the same probability of any
particular event occurring then you use replacement.
Sampling without replacement-if you don’t replace whatever was selected the first time then
the probability of future events have changed due to whatever was picked the first time.
Example- How many license plates can be made using 3 letters, 2 numbers, and then 1 letter if
all letters and numbers can be repeated? (with replacement) How does your answer change if
letters and numbers CANNOT be repeated (without replacement) Use the context of the
problem to tell if it is WITH or WITHOUT replacement.
HW- pgs. 416-417 (6.29-6.36)
6.1 & 6.2 Quiz Tuesday 12-4-12
Ch. 6 Test Tuesday 12-11-12
www.westex.org
HS, Teacher Website