* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Powerpoint File
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Osteochondritis dissecans wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
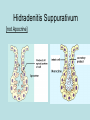
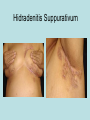
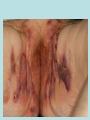
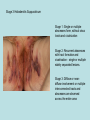
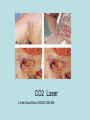
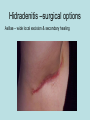
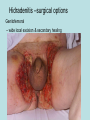
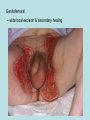
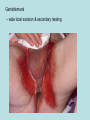
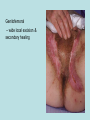
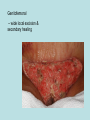
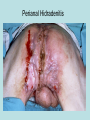
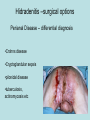
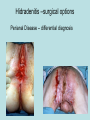
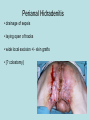
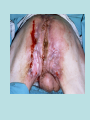
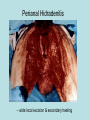
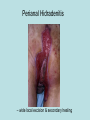
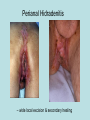
Hidradenitis Suppurativum Nigel A. Scott MD FRCS Royal Preston Hospital Hidradenitis Suppurativum Greek- hidros=sweat & aden=glands “Painful, inflamed lesions in the axillae, groin, and other parts of the body that contain apocrine glands” “…..painful eruptions and malodorous discharge” Quality of Life and Hidradenitis J.M. Von Der Werth, G.B.E. Jemec (2001) Morbidity in patients with hidradenitis suppurativa British Journal of Dermatology 144 (4), 809–813. Hidradenitis Suppurativum “Apocrine” Sweat Glands • develop during mid puberty • sweat contains fatty materials that are broken down by bacteria – main cause of sweat odour • emotional stress increases production of sweat Hidradenitis Suppurativum Apocrine Hidradenitis Suppurativum [not Apocrine] Hidradenitis Suppurativum • occlusion of the hair follicle (rather than the apocrine gland) due to a defect in terminal follicular epithelium Hidradenitis Suppurativum 1. occlusion of the hair follicle (rather than the apocrine gland) due to a defect in terminal follicular epithelium 2. bacteria invade the apocrine system via the hair follicles, become trapped beneath the keratinous plugs, and multiply rapidly in the apocrine sweat Hidradenitis Suppurativum 3. glands rupture and spread the infection extending the tissue destruction and skin damage Hidradenitis Suppurativum 3. glands rupture and spread the infection extending the tissue destruction and skin damage 4. bacterial superinfection with streptococci, staphylococci, and coliforms - BUT cultures from lesions are frequently sterile and antibiotics are not curative Hidradenitis Suppurativum • chronic acneiform infection of the cutaneous apocrine glands • involves adjacent subcutaneous tissue and fascia • hallmark - is sinus tracts (which can become draining fistulas) in the apocrine gland body areas. Hidradenitis Suppurativum Apocrine Gland distribution • axillae • periareolar, intermammary • pubic area, • infraumbilical midline, • gluteal folds, • genitofemoral areas • perianal region. Hidradenitis Suppurativum Stage 3 Hidradenitis Suppurativum Stage 1: Single or multiple abscesses form, without sinus tracts and cicatrization Stage 2: Recurrent abscesses with tract formation and cicatrisation - single or multiple widely separated lesions. Stage 3: Diffuse or neardiffuse involvement or multiple interconnected tracts and abscesses are observed across the entire area Hidradenitis 2-4% population 4F:1M Gender and disease location Area(s) of involvement Male (n = 15) Female (n = 42) P value Axilla 2 (13%) 37 (88%) <.0001 Unilateral 1 (50) 19 (51) NS Bilateral 1 (50) 18 (49) Inguinoperineal 13 (87%) Unilateral 1 (8) Bilateral 12 (92) Axilla and inguinoperineal 1 (7) 5 (12) <.0001 4 (80) .0131 1 (20) 3 (8) NS Kagan et al. Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: A 10-year experience Surgery 2005:138(4);734-741 Hidradenitis – medical options • topical clindamycin • hormonal cyproterone acetate; ethinyloestradiol • retinoids • infliximab CO2 Laser J Amer Acad Derm 2002:47:280-285 Hidradenitis –surgical options • drainage of sepsis – 100% recurrence • laying open of tracks • wide local excision +/- skin grafts “The surgical option of choice for late stage HS is wide local excision with healing by secondary intention” Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa Br J Surg 1992; 79: 863-6. Hidradenitis –surgical options Axillae – wide local excision & secondary healing Hidradenitis –surgical options Genitofemoral – wide local excision & secondary healing Genitofemoral – wide local excision & secondary healing Genitofemoral – wide local excision & secondary healing Genitofemoral – wide local excision & secondary healing Genitofemoral – wide local excision & secondary healing Perianal Hidradenitis Hidradenitis –surgical options Perianal Disease – differential diagnosis •Crohns disease •Cryptoglandular sepsis •pilonidal disease •tuberculosis, actinomycosis etc Anal Canal & Hidradenitis • the distal two thirds of the skin of the anatomic anal canal contains hair follicles with sebaeceous and apocrine glands •hidradenitis supprativum rarely involves the anal canal •if it does it tracks subcutaneously and not across the sphincter •it never tracks above the dentate line Anal Canal & Hidradenitis Crohns Cryptoglandular Hidradenitis Hidradenitis –surgical options Perianal Disease – differential diagnosis Perianal Hidradenitis • drainage of sepsis • laying open of tracks • wide local excision +/- skin grafts • [? colostomy] Perianal Hidradenitis – wide local excision & secondary healing Perianal Hidradenitis – wide local excision & secondary healing Perianal Hidradenitis – wide local excision & secondary healing Kagan et al. Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: A 10-year experience Surgery 2005:138(4);734-741 Axilla Perineum Inguinal Kagan et al. Surgical treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: A 10-year experience Surgery 2005:138(4);734-741 Hidradenitis – surgical outcomes Ritz et al Extent of surgery and recurrence rate of hidradenitis suppurativa Int J Colorectal Dis 1998;13:164-168. • 31 patients 6F:23M • mean age 31yrs • surgery • 6 abscess drained •14 limited excision, 2 suture •11 wide local excision Ritz et al Extent of surgery and recurrence rate of hidradenitis suppurativa Int J Colorectal Dis 1998;13:164-168. Drainage Local Excision & Suture WLE Hidradenitis Suppurativum Summary • common cause of serious morbidity 1-4%; 4F:1M • occlusion of the hair follicle (rather than the apocrine gland) due to a defect in terminal follicular epithelium • axilla/ inguinogenital, perianal • Stage 3: Diffuse or near- diffuse involvement or multiple interconnected tracts and abscesses are observed across the entire area • medical - topical clindamycin, oral contraceptive • perianal – differential diagnosis • wide local excision best results with or without mesh skin graft The DoH said: "The department has accepted the need for change and the revised approach will now be tested with junior doctors, selectors, deanery recruitment teams and employers."