* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical circuit symbols of components
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
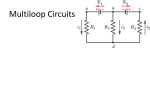
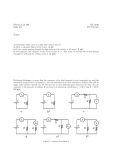
M.E.S.INDIAN SCHOOL Doha, Qatar INDEX S. No. FA-01 1 FA-01 2 FA-01 3 Activity Reading electrical meters (diagram based worksheet) Ohm’s Law (practical) 4 FA-01 Resistors in Series (practical) FA-01 Numerical Problems FA-02 Effective resistance 1 (diagram based numerical FA-02 Resistors in parallel FA-02 Electromagnet 2 3 FA-02 4 FA-02 Sign (matching type worksheet) Units and Symbols (multiple choice worksheet) 6 Submitted on Electrical Circuit Symbols FA-01 5 Due Date (practical) (make it yourself project) Our Power Projects (seminar) Numerical Problem 5 Certified that ……………………………………………………..of class X-….. has completed all the activities and experiments listed above. Name and signature of the teacher:……………………………….. Electrical circuit symbols Identify the component and fill in the table using the list given below. (Open key, cell, variable resistor, wire joint, ammeter, closed key, resistor, battery, voltmeter, crossing wire without joint, lamp ) …….Symbol……. ……………Component…………… Reading electrical meters The voltmeter and ammeter readings in an Ohm’s law experiment are shown on the left page. Record the voltmeter and Ammeter readings and calculate the resistance. Least count of voltmeter :…….……Range of voltmeter:…… Least count of ammeter:……………Range of ammeter:………… S.No Voltmeter reading Ammeter Reading Resistance V (volt) I (amp) R = V/ I (Ω) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mean R Plot a graph using the V – I values and calculate slope. x1 = x2 = y1 = y2 = V(volt) I (amp) y2 - y1 Resistance = ---------- = x2 - x1 Circuit Diagram Least count of voltmeter :………..…… Range of voltmeter:……………..…… Least count of ammeter:………..……… Range of ammeter:………….……… Voltmeter reading Ammeter Reading S.No V(volt) I (amp) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mean V – I Graph I (amp) Resistance R = V/I (ohm) V (volt) Ohm’s Law Date: Aim: To verify Ohm’s law and to find the resistance of a wire. Apparatus: A battery, switch, rheostat, resistor, ammeter, voltmeter, connecting wires. Theory: At constant temperature, current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the ends of the conductor. Procedure: Connect the circuit as shown in the diagram. Record the least count and range of the ammeter and voltmeter. Adjust the rheostat so that the current is very low. Record the ammeter and voltmeter readings. Adjust the rheostat to increase the current slightly. Record the new ammeter and voltmeter readings. Repeat the experiment to get five sets of voltmeter and corresponding ammeter readings. Plot a graph of voltage against current. Result: 1. Graph is a …………………………………line passing through the origin. Current through the resistor is ………………………. ……………………………........... to the potential difference. Ohm’s law is verified within the limits of experimental error. 2. Resistance of the given resistor = ……….…….Ω Precautions. 1. Ends of the connection wires should be cleaned to reduce contact resistance 2. Set the current to low value to avoid heating up of the circuit. 3. Close the key only while taking the readings to avoid heating. Units and Symbols Choose the correct answer 1. The SI unit of electric current is………. a) volt b) ampere c) watt d) joule 2. The symbol for a variable resistor is a) b) c) d) 3. Ω is the unit of …… a)current b)Potential difference c) power d) Resistance 4. If one joule of work is done to move one coulomb between two points, then the potential difference between those points is…… a) one watt b) one ampere c) one volt d) one ohm 5.Which of the following is connected in parallel in a circuit? a) b) c) d) 6. The unit of charge is …………. a) coulomb b) ampere c) volt d) watt 7. If a bulb dissipates one joule of energy per second then the power of the bulb is…. a) one volt b) one ampere c) one ohm d) one watt 8. Which is the symbol for the unit of current? a) V b) C 9. c) A d) W is the symbol of a device used to …….current a) measure b) stop c) control d) supply 10. The unit ohm is related to which of the following? a) b) c) d) Circuit Diagram Least count of voltmeter :……………… Range of voltmeter:……………… Least count of ammeter:…………… Range of ammeter:…………… R1 = …………… R2 =…………… Rs = R1 + R2 = ………………… S. No Voltmeter reading V (volt) Ammeter Reading I (amp) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mean R Resistance R = V/ I (Ω) Resistors in series Date: Aim: To find the effective resistance when resistors are connected in series. Apparatus: A battery, switch, rheostat, two known resistors, ammeter, voltmeter, connecting wires. Theory: When connected in series effective resistance increases. Combined resistance is equal to the sum of individual resistances. Procedure: Record the least count and range of the ammeter and voltmeter. Record the values of the given resistors. Connect the circuit as shown in the diagram. Adjust the rheostat so that the current is very low. Record the ammeter and voltmeter readings. Adjust the rheostat to increase the current slightly. Record the new ammeter and voltmeter readings. Repeat the experiment to get five sets of voltmeter and corresponding ammeter readings. t. Calculate the combined resistance of the given resistors. Result: 1. Combined resistance of the given resistors = ………….Ω 2. Effective resistance is ………………….. than that of individual resistors. Precautions. 4. Ends of the connection wires should be cleaned to reduce contact resistance 5. Set the current to low value to avoid heating up of the circuit. 6. Close the key only while taking the readings to avoid heating. Numerical problems 1. A current of 0.5 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb for 2 minutes. Find the amount of electric charge that flows through the circuit. 2. How much work is done in moving a charge of 5 C across two points having a potential difference 6 V? 3. An electric toaster draws a current of 5A when connected to a 220V power supply. Find the resistance of the heater. 4. Resistivity of Constantan at 20O C is 49 X 10-6 Ωm. Find the resistance of the heating element of length 50cm and area of cross section 7.0 X 10-6 m2 at the same temperature. Effective Resistance Find the effective resistance across PQ in the following circuits. P Q 2Ω 3Ω 5Ω 4Ω P Q 6Ω 6Ω 6Ω P Q 6Ω 6Ω 4Ω P Q 7Ω 3Ω 6Ω 6Ω P Q 3Ω P Q 3Ω P Q 5Ω Circuit Diagram Least count of voltmeter :………… Range of voltmeter :………… Least count of ammeter:…………… Range of ammeter:………………… R1 = …………… R2 =…………… Rp R1 X R2 = ---------- = ……………… R1 + R2 S. No Voltmeter reading V (volt) Ammeter Reading I (amp) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Mean R Resistance R = V/ I (Ω) Resistors in parallel Date: Aim: To find the effective resistance when resistors are connected in parallel. Apparatus: A battery, switch, rheostat, two known resistors, ammeter, voltmeter, connecting wires. Theory: When connected in parallel effective resistance decreases. Reciprocal of combined resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances. Procedure: Record the least count and range of the ammeter and voltmeter. Record the values of the given resistors. Connect the circuit as shown in the diagram. Adjust the rheostat so that the current is very low. Record the ammeter and voltmeter readings. Adjust the rheostat to increase the current slightly. Record the new ammeter and voltmeter readings. Repeat the experiment to get five sets of voltmeter and corresponding ammeter readings. Calculate the combined resistance of the given resistors. Result: 1. Combined resistance of the given resistors = ……..……. Ω 2. Effective resistance is ………………………………….. that of individual resistors. Precautions. 7. Ends of the connection wires should be cleaned to reduce contact resistance 8. Set the current to low value to avoid heating up of the circuit. 9. Close the key only while taking the readings to avoid heating. Electromagnet Make an electromagnet and test its strength. Materials required - iron nail – one, 2” long - insulated copper wire – one meter -1.5V dry cell – one How to construct- Wind the copper wire tightly on the iron nail. Tie the end of the wire on the nail with a thread. To test – remove the insulation from the ends of the wire. Connect the ends to the terminals of the cell and hold the nail near a pile of paper clips. What did you observe:…………………………………………….. …………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………… Suggest two ways to increase the strength of the electromagnet. 1……………………………………………………………………….. 2……………………………………………………………………….. Our Power Projects The main power projects in India are Hydro-electric power projects, Thermal power projects and nuclear power projects. Make a group of five students. Choose one of the power projects in India and conduct a seminar on its advantages and disadvantages. ( Your teacher may suggest the power project for you to avoid repetition) Power project :………………………………………………………… (eg: Bhakranangal Power project) Location:………………………..……………….……………………… Type of project:…………….……………….……………………….. (Hydro/Thermal/Nuclear….) My group will talk about the …………………………………….. Of this project ( advantages/disadvantages) My points: ……………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………. ………………………………………………………………………. Numerical Problems 1. Three resistors of 2 Ω. 5 Ω and 3 Ω respectively are connected in series. Find the effective resistance. 2. Three resistors of 2 Ω. 6 Ω and 3 Ω respectively are connected in parallel. Find the effective resistance. 3. An electric bulb is connected to a 220 V generator. What is the power of the bulb if the current through the bulb is 0.50A? 4. A room heater can offer a maximum resistance of 100 Ω when 5 A current flows through it for one minute. What is the maximum amount of heat produced by the heater? 5. An electric kettle consumes 1 kW of electric power when operated at 220 V. A fuse wire of what rating must be used for it? 6. Two lamps, one rated 100 W at 220 V, and the other 60W at 220 V, are connected in parallel to electric mains supply. What current is drawn from the line if the supply voltage is 220V? 7. An electric room heater is rated 2kW. Calculate the cost of using it for 2 hours daily for the month of September, if each unit costs Rs. 4.00.